
In a cross between two tall pea plants some of the offspring produced were dwarf. Show with the help of Punnett square how this is possible.
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Any of the progeny may prove to be phenotypically dwarfed in a cross between two phenotypically tall plants. This means that it is heterozygous for both parents.
Complete answer:
A tabular description of combinations of paternal alleles with maternal alleles is the Punnett square. These tables can be used to analyse the probabilities of the genotypic result of the offspring of a single characteristic (allele), or where multiple parent traits are crossed. A brief description of Mendelian inheritance is the Punnett square.
Now, let’s explain the solution-
Some of the offspring produced were dwarf in a cross between two tall pea plants, meaning that parent pea plants were heterozygous for tallness (Tt), i.e. they possess a recessive gene (t) for dwarfness and the dwarf plant (tt) is the recessive gene alleles for dwarfness from both of the parent plants.
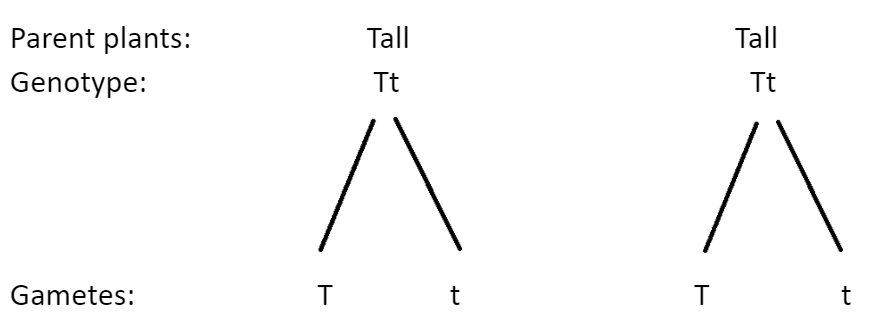
Punnett Square:
25% were dwarf plants. Progeny phenotypic ratio is 3:1 and progeny genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 (TT: Tt: tt).
Note: Punnett squares can precisely estimate the ratios of different measurable characteristics as well as their underlying genetic makeup in large-scale experiments, such as those performed by Mendel. There are two kinds of Punnett squares widely used. The first is important when studying a particular trait determined by one genetic locus. This is a cross called a monohybrid. The second method is used to forecast the outcome of breeding trials where two traits are being pursued and the Punnett square is wider with sixteen boxes.
Complete answer:
A tabular description of combinations of paternal alleles with maternal alleles is the Punnett square. These tables can be used to analyse the probabilities of the genotypic result of the offspring of a single characteristic (allele), or where multiple parent traits are crossed. A brief description of Mendelian inheritance is the Punnett square.
Now, let’s explain the solution-
Some of the offspring produced were dwarf in a cross between two tall pea plants, meaning that parent pea plants were heterozygous for tallness (Tt), i.e. they possess a recessive gene (t) for dwarfness and the dwarf plant (tt) is the recessive gene alleles for dwarfness from both of the parent plants.

Punnett Square:
| T | t | |
| T | TT | Tt |
| t | tT | tt |
25% were dwarf plants. Progeny phenotypic ratio is 3:1 and progeny genotypic ratio is 1:2:1 (TT: Tt: tt).
Note: Punnett squares can precisely estimate the ratios of different measurable characteristics as well as their underlying genetic makeup in large-scale experiments, such as those performed by Mendel. There are two kinds of Punnett squares widely used. The first is important when studying a particular trait determined by one genetic locus. This is a cross called a monohybrid. The second method is used to forecast the outcome of breeding trials where two traits are being pursued and the Punnett square is wider with sixteen boxes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




