
In a concave mirror when the object is located beyond $C$ the magnification is?
Answer
522.9k+ views
Hint:When a hollow sphere is split into sections and the outer surface of each cut part is painted, it transforms into a mirror, with the inner surface serving as the reflection surface. Concave mirrors are the name for this type of mirror.
Complete answer:
The ratio of image length to object length measured in planes perpendicular to the optical axis is called linear magnification (also called lateral or transverse magnification). Inverted images are represented by a negative linear magnification value.
The picture will still be centred somewhere between the centre of curvature and the focal point when the object is located outside the centre of curvature. The picture will be in the designated region regardless of the exact location of the object. The result would be an inverted image in this case. That is to say, if the object is upright, the picture would be upside down.
The image is shrunk in this case; that is, the image dimensions are smaller than the object dimensions. The picture is less than six feet tall if the object is a six-foot tall human. The magnification's absolute value is less than one in this situation. Real image is formed. We can see the image formation of the object placed beyond the centre of curvature in the figure depicted below:
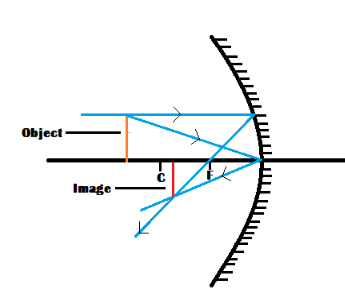
Note: At the picture spot, light rays actually converge. The actual copy of the object would appear projected onto a sheet of paper if a sheet of paper was put at the picture spot.Magnification is the proportion of the size of an image to the size of the object that produced it in optics.
Complete answer:
The ratio of image length to object length measured in planes perpendicular to the optical axis is called linear magnification (also called lateral or transverse magnification). Inverted images are represented by a negative linear magnification value.
The picture will still be centred somewhere between the centre of curvature and the focal point when the object is located outside the centre of curvature. The picture will be in the designated region regardless of the exact location of the object. The result would be an inverted image in this case. That is to say, if the object is upright, the picture would be upside down.
The image is shrunk in this case; that is, the image dimensions are smaller than the object dimensions. The picture is less than six feet tall if the object is a six-foot tall human. The magnification's absolute value is less than one in this situation. Real image is formed. We can see the image formation of the object placed beyond the centre of curvature in the figure depicted below:

Note: At the picture spot, light rays actually converge. The actual copy of the object would appear projected onto a sheet of paper if a sheet of paper was put at the picture spot.Magnification is the proportion of the size of an image to the size of the object that produced it in optics.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




