
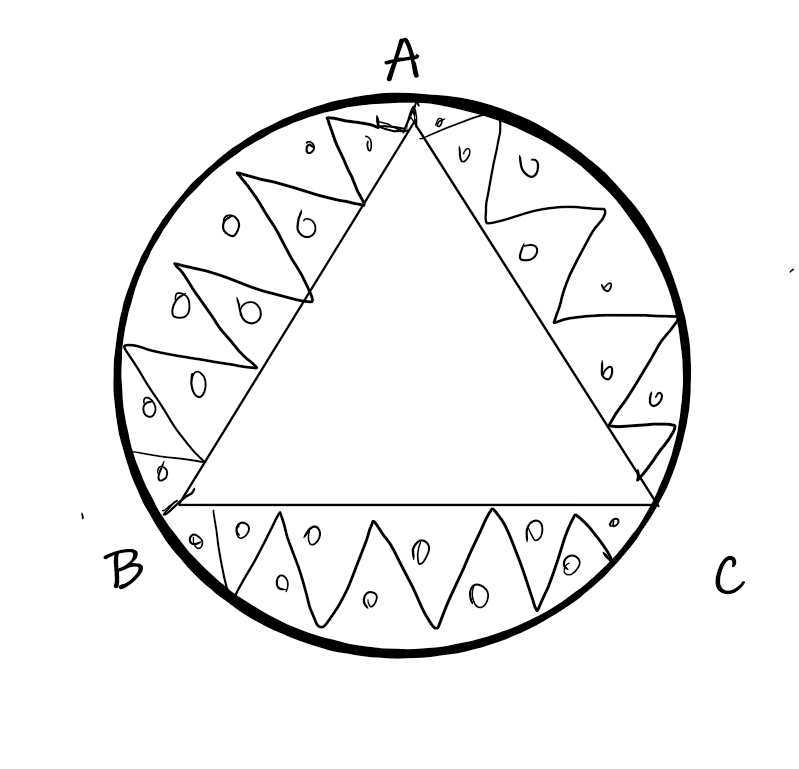
In a circular table cover of radius 32 cm, a design is formed leaving an equilateral triangle ABC in the middle as shown in figure below. Find the area of the design.

Answer
607.5k+ views
Hint: we will use the formula of the area of circle of radius r which is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\] and the formula of a triangle which is given by, \[\dfrac{1}{2}(base)(height)\]. After this we will use the Central Angle Theorem which is stated as “The central angle subtended by two points on a circle is twice the inscribed angle subtended by those points.”
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to find the area of the design.
Let ABC be the equilateral triangle and let O be the centre of the circle of radius r = 32cm.
We will first of all find the area of the circle.
The formula of the area of the circle of radius r is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Then A = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Substituting the value of the radius r = 32cm, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& A=\left( \dfrac{22}{7}(32)(32) \right)c{{m}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=\dfrac{22528}{7}c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we have to calculate the area of the equilateral triangle.
To calculate so we need to have the side of the triangle.
For that we will do some constructions given below.
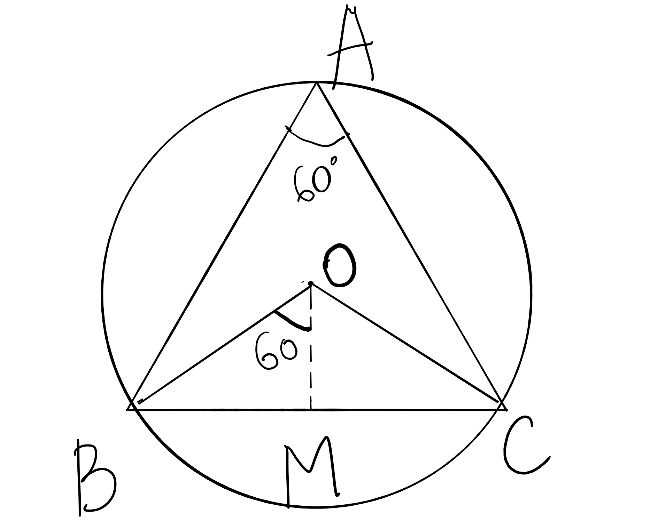
Draw OM perpendicular to BC.
Now we will use the Central Angle Theorem which is stated as “The central angle subtended by two points on a circle is twice the inscribed angle subtended by those points.”
Therefore as \[\angle BAC={{60}^{0}}\], Being an angle of the equilateral triangle.
Therefore, \[\angle BOC=2({{60}^{0}})={{120}^{0}}\], both the angles are made by the same arc BC of the given circle.
And now because OM is a perpendicular bisector therefore, it bisects the angle BOC.
Therefore, \[\angle BOM=\text{ }\dfrac{1}{2}(120{}^\circ )=60{}^\circ \].
Now consider\[\Delta BOM\],
Applying cos on the angle BOM, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& cos\text{ }60{}^\circ =\dfrac{OM}{OB} \\
& \Rightarrow cos\text{ }60{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{OM}{OB} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{OM}{OB}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now because OB is the radius of the circle and r = 32cm, gives OB = 32cm.
Substituting the value of OB, we get,
\[OM=\text{ }16\text{ }cm\].
\[\begin{align}
& Also,\text{ }\dfrac{BM}{OM}=\text{ tan}60{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{BM}{OM}=\text{ tan}60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting the value of OM as 16cm we get,
\[BM=\text{ }16\sqrt{3}\text{ }cm\].
Now the formula to calculate the area of the triangle is given by \[\dfrac{1}{2}(base)(height)\].
Here base of the \[\Delta BOC\] is BC = 2BM, which is,
\[BC\text{ }=\text{ }2\text{ }BM\text{ }=32\sqrt{3}\text{ }cm\] and the height is OM = 16cm.
Substituting the values, we get,
The area of \[\Delta BOC\] is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& A'=\dfrac{1}{2}(BC)(OM) \\
& \Rightarrow A'=\dfrac{1}{2}(32\sqrt{3})(16) \\
& \Rightarrow A'=8(32)\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now the area of \[\Delta ABC\] is equal to three times area of \[\Delta BOC\],
Therefore, the area of the \[\Delta ABC\] is,
Area of \[\Delta ABC=3(8(32)\sqrt{3})\]
\[\Rightarrow \] Area of \[\Delta ABC=768\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{3}}\].
Now the area of design = area of circle A - area of \[\Delta ABC\]
Substituting the values of both we get,
The area of the design \[=(\dfrac{22528}{7}-768\sqrt{3})c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] The area of the design = \[(3218.2857-1330.176)\]
\[\Rightarrow \] The area of the design \[=1888.1097c{{m}^{2}}\]
Therefore, we get the area of design as \[1888.1097c{{m}^{2}}\].
Note: The possibility of error in these types of question can be at the point where you have to calculate the area of the inscribed triangle. Always go for using the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2}(base)(height)\] and for doing so try to calculate the base and the height separately.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to find the area of the design.
Let ABC be the equilateral triangle and let O be the centre of the circle of radius r = 32cm.
We will first of all find the area of the circle.
The formula of the area of the circle of radius r is \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Then A = \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\].
Substituting the value of the radius r = 32cm, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& A=\left( \dfrac{22}{7}(32)(32) \right)c{{m}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=\dfrac{22528}{7}c{{m}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now we have to calculate the area of the equilateral triangle.
To calculate so we need to have the side of the triangle.
For that we will do some constructions given below.
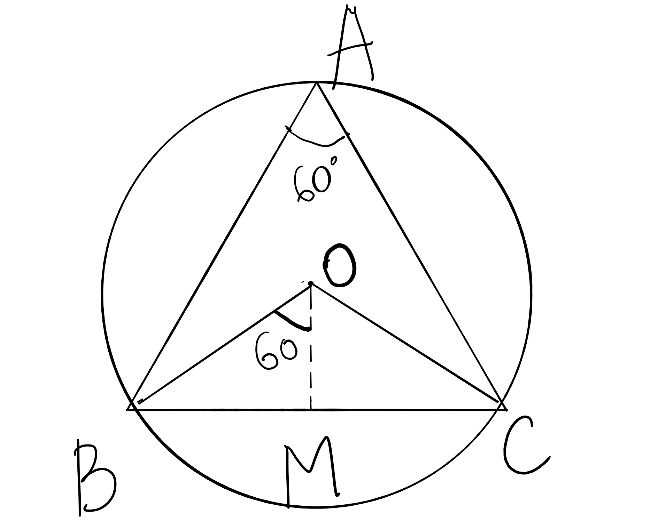
Draw OM perpendicular to BC.
Now we will use the Central Angle Theorem which is stated as “The central angle subtended by two points on a circle is twice the inscribed angle subtended by those points.”
Therefore as \[\angle BAC={{60}^{0}}\], Being an angle of the equilateral triangle.
Therefore, \[\angle BOC=2({{60}^{0}})={{120}^{0}}\], both the angles are made by the same arc BC of the given circle.
And now because OM is a perpendicular bisector therefore, it bisects the angle BOC.
Therefore, \[\angle BOM=\text{ }\dfrac{1}{2}(120{}^\circ )=60{}^\circ \].
Now consider\[\Delta BOM\],
Applying cos on the angle BOM, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& cos\text{ }60{}^\circ =\dfrac{OM}{OB} \\
& \Rightarrow cos\text{ }60{}^\circ =\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{OM}{OB} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{OM}{OB}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now because OB is the radius of the circle and r = 32cm, gives OB = 32cm.
Substituting the value of OB, we get,
\[OM=\text{ }16\text{ }cm\].
\[\begin{align}
& Also,\text{ }\dfrac{BM}{OM}=\text{ tan}60{}^\circ \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{BM}{OM}=\text{ tan}60{}^\circ =\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting the value of OM as 16cm we get,
\[BM=\text{ }16\sqrt{3}\text{ }cm\].
Now the formula to calculate the area of the triangle is given by \[\dfrac{1}{2}(base)(height)\].
Here base of the \[\Delta BOC\] is BC = 2BM, which is,
\[BC\text{ }=\text{ }2\text{ }BM\text{ }=32\sqrt{3}\text{ }cm\] and the height is OM = 16cm.
Substituting the values, we get,
The area of \[\Delta BOC\] is given by,
\[\begin{align}
& A'=\dfrac{1}{2}(BC)(OM) \\
& \Rightarrow A'=\dfrac{1}{2}(32\sqrt{3})(16) \\
& \Rightarrow A'=8(32)\sqrt{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Now the area of \[\Delta ABC\] is equal to three times area of \[\Delta BOC\],
Therefore, the area of the \[\Delta ABC\] is,
Area of \[\Delta ABC=3(8(32)\sqrt{3})\]
\[\Rightarrow \] Area of \[\Delta ABC=768\sqrt{3}c{{m}^{3}}\].
Now the area of design = area of circle A - area of \[\Delta ABC\]
Substituting the values of both we get,
The area of the design \[=(\dfrac{22528}{7}-768\sqrt{3})c{{m}^{2}}\]
\[\Rightarrow \] The area of the design = \[(3218.2857-1330.176)\]
\[\Rightarrow \] The area of the design \[=1888.1097c{{m}^{2}}\]
Therefore, we get the area of design as \[1888.1097c{{m}^{2}}\].
Note: The possibility of error in these types of question can be at the point where you have to calculate the area of the inscribed triangle. Always go for using the formula \[\dfrac{1}{2}(base)(height)\] and for doing so try to calculate the base and the height separately.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




