
How do impulses cross the synapse?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: Neurons (nerve cells) are specialized cells that have the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into an action potential. Impulses cross the synapse by means of chemical messenger called neurotransmitters.
Complete answer:
An action potential starts at a presynaptic neuron as the nerve impulse arrives at it. This action potential cannot jump from one neuron to the next neuron. So there is a mechanism of transmission called synaptic transmission which occurs at the synapse.
Synapse can be defined as a microscopic gap between the axon ends of presynaptic neuron and dendrite ends of postsynaptic neurons.
The presynaptic neuron possesses synaptic vesicles in its synaptic knob and these synaptic vesicles are filled with chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters which help in the transmission of the action potential.
When the action potential arrives at the axon-ending of presynaptic neuron, the synaptic vesicles fuse with synaptic membrane. As a result of the fusion neurotransmitters are released in the synaptic cleft (gap). The membranes (of dendrites) of postsynaptic neuron also have receptors.
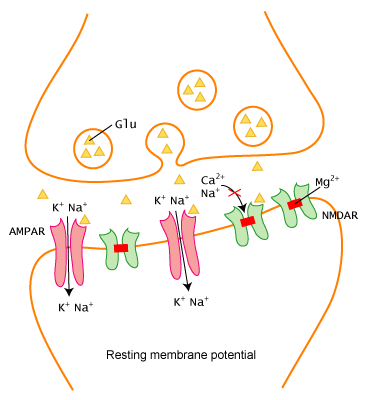
The neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron binds to the receptors of the postsynaptic neuron. These neurotransmitters change the permeability of postsynaptic neurons for certain ions i.e Na+ ions. Thus an action potential is started in the postsynaptic neuron.
Note: A nerve impulse is an electrical signal produced by the flow of ions across the plasma membrane of the neuron. It propagates (travels) along the surface of the membrane of a neuron at speeds ranging from 0.5 to 130 meters per second. Propagation of nerve impulses in nerve cells (axon) changes the permeability of the membrane. This change in permeability causes a change in the potential across the axon membrane.
Complete answer:
An action potential starts at a presynaptic neuron as the nerve impulse arrives at it. This action potential cannot jump from one neuron to the next neuron. So there is a mechanism of transmission called synaptic transmission which occurs at the synapse.
Synapse can be defined as a microscopic gap between the axon ends of presynaptic neuron and dendrite ends of postsynaptic neurons.
The presynaptic neuron possesses synaptic vesicles in its synaptic knob and these synaptic vesicles are filled with chemical messengers known as neurotransmitters which help in the transmission of the action potential.
When the action potential arrives at the axon-ending of presynaptic neuron, the synaptic vesicles fuse with synaptic membrane. As a result of the fusion neurotransmitters are released in the synaptic cleft (gap). The membranes (of dendrites) of postsynaptic neuron also have receptors.

The neurotransmitters released from the presynaptic neuron binds to the receptors of the postsynaptic neuron. These neurotransmitters change the permeability of postsynaptic neurons for certain ions i.e Na+ ions. Thus an action potential is started in the postsynaptic neuron.
Note: A nerve impulse is an electrical signal produced by the flow of ions across the plasma membrane of the neuron. It propagates (travels) along the surface of the membrane of a neuron at speeds ranging from 0.5 to 130 meters per second. Propagation of nerve impulses in nerve cells (axon) changes the permeability of the membrane. This change in permeability causes a change in the potential across the axon membrane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




