
What is the importance of DNA replication during reproduction?
Answer
616.5k+ views
Hint: During cell division, the genetic information is transferred from one generation to another.
Complete answer:
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid also termed as DNA is the genetic material for almost all the organisms. It makes its own copies in order to pass the genetic information from one cell to another or one generation to another.
The importance of DNA replication is listed below.
- DNA contains the information for the production of protein and enzyme synthesis required for the living of a cell.
- DNA replication results in the production of another copy of DNA which is transferred to a newly formed cell.
- If DNA is not replicated the daughter cell lacks the important proteins synthesis machinery which is required for survival this can lead to serious complications.
- Due to DNA replication diploid status of the autosomal cells is maintained.
- DNA is responsible for the transfer of genetic material from one generation to next. During the process of DNA replication, the formation of small changes takes place. These errors result in mutations. This forms the basis of Evolution and variety is formed.
- During DNA replication there is the formation of the similar copy of DNA with slight mutations. This maintenance of the uniqueness of that species and slight mutation provides a unique character to that individual organism.
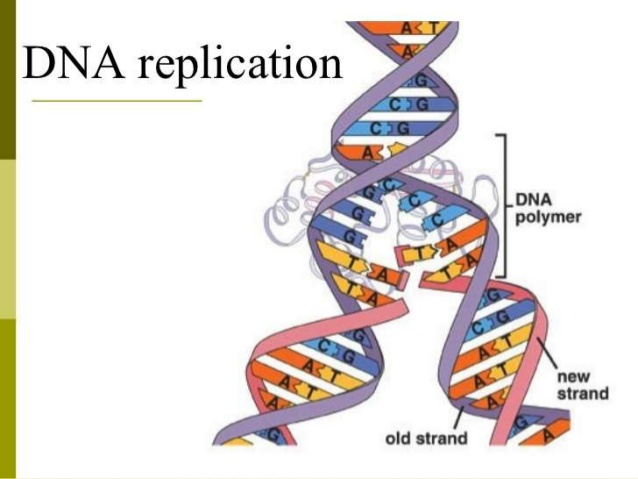
- DNA can replicate through three types of processes: dispersive, conservative and semi-conservative.
- The most accepted way is the semi-conservative replication of DNA
Note :
- Genes are the small fragments of DNA that contain information.
- Mutations are changes in DNA ( nucleotide ) sequence which can misinterpret the information stored by DNA.
- Semi-conservation of DNA means the DNA which contains one strand of parent DNA and another newly synthesized daughter DNA.
- Diploid is a condition in which an organism has a pair of homologous chromosomes.
Complete answer:
Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid also termed as DNA is the genetic material for almost all the organisms. It makes its own copies in order to pass the genetic information from one cell to another or one generation to another.
The importance of DNA replication is listed below.
- DNA contains the information for the production of protein and enzyme synthesis required for the living of a cell.
- DNA replication results in the production of another copy of DNA which is transferred to a newly formed cell.
- If DNA is not replicated the daughter cell lacks the important proteins synthesis machinery which is required for survival this can lead to serious complications.
- Due to DNA replication diploid status of the autosomal cells is maintained.
- DNA is responsible for the transfer of genetic material from one generation to next. During the process of DNA replication, the formation of small changes takes place. These errors result in mutations. This forms the basis of Evolution and variety is formed.
- During DNA replication there is the formation of the similar copy of DNA with slight mutations. This maintenance of the uniqueness of that species and slight mutation provides a unique character to that individual organism.
- DNA can replicate through three types of processes: dispersive, conservative and semi-conservative.
- The most accepted way is the semi-conservative replication of DNA

Note :
- Genes are the small fragments of DNA that contain information.
- Mutations are changes in DNA ( nucleotide ) sequence which can misinterpret the information stored by DNA.
- Semi-conservation of DNA means the DNA which contains one strand of parent DNA and another newly synthesized daughter DNA.
- Diploid is a condition in which an organism has a pair of homologous chromosomes.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers

Coming together federation is practiced in A India class 12 social science CBSE

Write the formula to find the shortest distance between class 12 maths CBSE




