
Image formed by a convex _______ is always virtual and smaller in size.
A. mirror
B. lens
C. Plano mirrors
D. none
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: A virtual image is an image that forms when rays appear to diverge from a point (or extended object) behind the mirror. Image formed by a plane mirror is an example of virtual image but the size of the image and the object remain the same.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When light from an object Falls on a mirror or a lens, it gets reflected or refracted and creates an image of the object. When the light rays from the object after reflection or refraction actually converge at a point we get a real image. When the light rays after reflection or refraction appear to diverge from a point, we get a virtual image of the object at that point. Real image is usually inverted and can be obtained on a screen wild virtual image is erect and is formed behind the mirror or in front of the lens.
A convex lens forms a virtual image when the object is kept between the lens and its focus but the image formed is an enlarged one. A convex lens acts as a magnifying lens. Therefore we can rule out option (B).
Whereas in the case of convex mirrors, the light falling on the mirror always appears to diverge from its image behind the mirror. So it does not matter where we place the object in front of the convex mirror the image formed will always be virtual and erect. The magnification is the ratio of height of the image to height of the object. The image formed by a convex mirror is always diminished in size. Consider the following convex mirror and notice that the focus of the mirror is present behind the mirror.
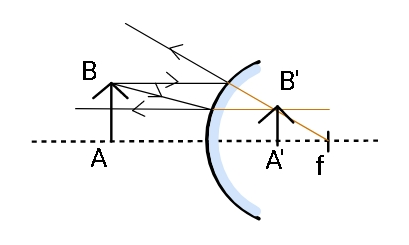
Therefore, the correct answer is option (A). Image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual and smaller in size.
Note: Convex mirrors our primary used as rear view mirrors while primary application of a convex lens is magnification. Convex lens is also called a magnifying lens. Therefore, this can sort out the answer easily for anyone. Also, on the rearview mirror, one would have noticed how small the vehicles look. This might give a hint about the nature of the image. If none of it works, one can always draw Ray diagrams to confirm the answer.
Complete step-by-step solution:
When light from an object Falls on a mirror or a lens, it gets reflected or refracted and creates an image of the object. When the light rays from the object after reflection or refraction actually converge at a point we get a real image. When the light rays after reflection or refraction appear to diverge from a point, we get a virtual image of the object at that point. Real image is usually inverted and can be obtained on a screen wild virtual image is erect and is formed behind the mirror or in front of the lens.
A convex lens forms a virtual image when the object is kept between the lens and its focus but the image formed is an enlarged one. A convex lens acts as a magnifying lens. Therefore we can rule out option (B).
Whereas in the case of convex mirrors, the light falling on the mirror always appears to diverge from its image behind the mirror. So it does not matter where we place the object in front of the convex mirror the image formed will always be virtual and erect. The magnification is the ratio of height of the image to height of the object. The image formed by a convex mirror is always diminished in size. Consider the following convex mirror and notice that the focus of the mirror is present behind the mirror.

Therefore, the correct answer is option (A). Image formed by a convex mirror is always virtual and smaller in size.
Note: Convex mirrors our primary used as rear view mirrors while primary application of a convex lens is magnification. Convex lens is also called a magnifying lens. Therefore, this can sort out the answer easily for anyone. Also, on the rearview mirror, one would have noticed how small the vehicles look. This might give a hint about the nature of the image. If none of it works, one can always draw Ray diagrams to confirm the answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




