
If you study the effect of substrate concentration on an enzymatic reaction, what kind of curve would you obtain?
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: When the substrate concentration is high, then the rate of reaction will be high initially. But if the enzyme gets saturated with the substrate, then the reaction rate becomes constant.
Complete answer:
The rate of chemical reaction increases as the concentration of the substrates increases. Enzymes become saturated when the concentration of substrates is high. If we plot a substrate concentration graph on the X-axis, and the velocity in the Y-axis it is found that, as the substrate concentration increases, a corresponding increase in the reaction occurs. It thus forms an arc-shaped curve.
Enzymes are protein molecules that serve as biological catalysts that increase the reaction rate without altering the overall reaction. They are long-chain amino acids connected by peptide bonds. Enzymes are seen in all living cells, and they control the metabolic processes in which nutrients are converted into energy and new cells. The substrates are the reactants of the enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The enzyme is highly specific and operates on a specific substrate to produce a specific product. The enzyme-catalyzed reaction mechanism can be studied by determining the reaction rate and its changes in response to changes in substrate concentration, the concentration of enzymes, pH, temperature, etc. This is known as enzyme kinetics. The substrate binds to an enzyme at a specific site called the active site.
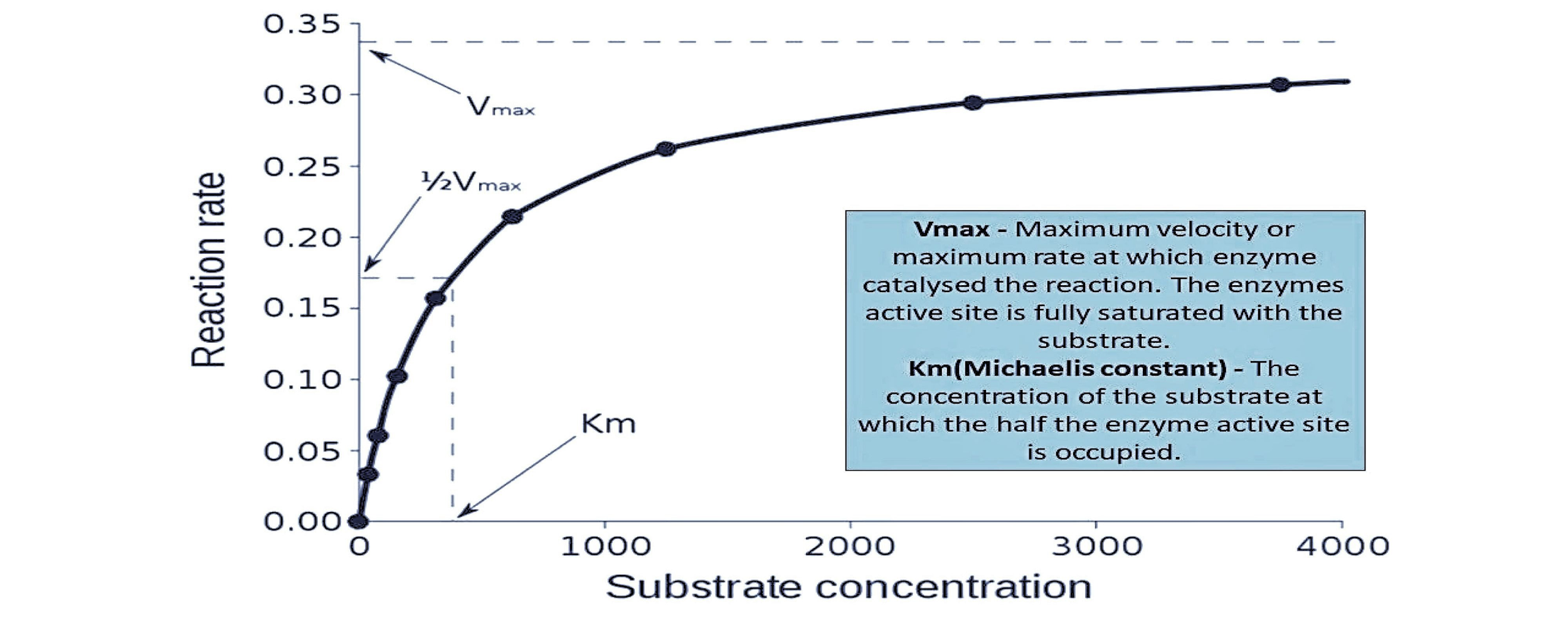
One of the important parameters affecting the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is the concentration of the substrate [S]. The initial velocity V0 gradually increases with increasing substrate concentration during the enzyme-substrate reaction. Finally, a point is reached, beyond which the [S] will not depend on the increase in VO. When we draw a graph with the concentration of substrates on the X-axis and corresponding velocity on the Y-axis. From the graph, it can be observed that a corresponding increase in the VO occurs as the substrate concentration increases. However, the velocity remains constant without any further increase beyond a particular concentration of the substrate. This maximum velocity of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction under the saturation of the substrate is called the maximum velocity of the Vmax.
Note: In humans, enzymes play a very important role in maintaining the body function. If there is a defect in the enzyme action, then it leads to diseases. Phenylketonuria ( PKU) is an inborn metabolism error that results in reduced amino acid phenylalanine metabolism. It is due to the nonfunctional enzyme that cannot metabolize phenylalanine. Untreated, PKU leads to intellectual disability, behavioral problems, seizures, and mental disorders.
Complete answer:
The rate of chemical reaction increases as the concentration of the substrates increases. Enzymes become saturated when the concentration of substrates is high. If we plot a substrate concentration graph on the X-axis, and the velocity in the Y-axis it is found that, as the substrate concentration increases, a corresponding increase in the reaction occurs. It thus forms an arc-shaped curve.
Enzymes are protein molecules that serve as biological catalysts that increase the reaction rate without altering the overall reaction. They are long-chain amino acids connected by peptide bonds. Enzymes are seen in all living cells, and they control the metabolic processes in which nutrients are converted into energy and new cells. The substrates are the reactants of the enzyme-catalyzed reactions. The enzyme is highly specific and operates on a specific substrate to produce a specific product. The enzyme-catalyzed reaction mechanism can be studied by determining the reaction rate and its changes in response to changes in substrate concentration, the concentration of enzymes, pH, temperature, etc. This is known as enzyme kinetics. The substrate binds to an enzyme at a specific site called the active site.

One of the important parameters affecting the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction is the concentration of the substrate [S]. The initial velocity V0 gradually increases with increasing substrate concentration during the enzyme-substrate reaction. Finally, a point is reached, beyond which the [S] will not depend on the increase in VO. When we draw a graph with the concentration of substrates on the X-axis and corresponding velocity on the Y-axis. From the graph, it can be observed that a corresponding increase in the VO occurs as the substrate concentration increases. However, the velocity remains constant without any further increase beyond a particular concentration of the substrate. This maximum velocity of the enzyme-catalyzed reaction under the saturation of the substrate is called the maximum velocity of the Vmax.
Note: In humans, enzymes play a very important role in maintaining the body function. If there is a defect in the enzyme action, then it leads to diseases. Phenylketonuria ( PKU) is an inborn metabolism error that results in reduced amino acid phenylalanine metabolism. It is due to the nonfunctional enzyme that cannot metabolize phenylalanine. Untreated, PKU leads to intellectual disability, behavioral problems, seizures, and mental disorders.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




