
If x-a is a factor of $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$, the the value of b is
[a] 0
[b] 2
[c] 1
[d] 3
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: Use factor theorem. According to factor theorem, if x-a is a factor of p(x), then p(a) = 0. Use factor theorem and hence form an equation in b. Solve for b. The value of b gives the value such that x-a is a factor of p(x).
Complete step-by-step answer:
Alternatively, use synthetic division to determine at what value of b is x-a a factor of p(x).
We have $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$.
Since x-a is a factor of p(x), we have
$p\left( x \right)=\left( x-a \right)g\left( x \right)$ where g(x) is another polynomial of lower degree.
Put x = a, we get
$p\left( a \right)=\left( a-a \right)g\left( a \right)=0$
Hence, we have
p(a) =0.
Now, we have
$p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$
Put x = a in the expression of p(x), we get
$p\left( a \right)={{\left( a \right)}^{3}}-3{{a}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}a+b={{a}^{3}}-3{{a}^{3}}+2{{a}^{3}}+b=b$
Hence, p(a) = b
But p(a) = 0
Hence, we have
b =0
Hence the value of b at which x-a is a factor of p(x) is 0.
Hence option [a] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution: Best Method: Synthetic division.
In this method, we start by writing coefficients of the polynomial in order from the highest degree to the constant term. If in between some degree terms are missing, we set their coefficient as 0.
Hence $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3a{{x}^{3}}+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$ will be written as
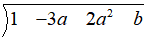
Now each the point which has to be substituted(say x= a) is written as follows
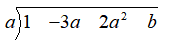
0 is placed below the first term
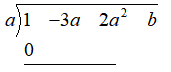
Now the terms under the same column are added. The sum is then multiplied with the root, and the product is written under the coefficient of the next term.
Hence, we have
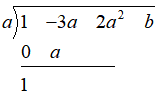
Continuing in this way we have the following
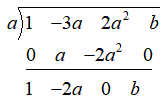
Since the last sum is b, we have $p\left( a \right)=b$.
Hence, b = 0 by factor theorem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Alternatively, use synthetic division to determine at what value of b is x-a a factor of p(x).
We have $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$.
Since x-a is a factor of p(x), we have
$p\left( x \right)=\left( x-a \right)g\left( x \right)$ where g(x) is another polynomial of lower degree.
Put x = a, we get
$p\left( a \right)=\left( a-a \right)g\left( a \right)=0$
Hence, we have
p(a) =0.
Now, we have
$p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3{{x}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$
Put x = a in the expression of p(x), we get
$p\left( a \right)={{\left( a \right)}^{3}}-3{{a}^{2}}a+2{{a}^{2}}a+b={{a}^{3}}-3{{a}^{3}}+2{{a}^{3}}+b=b$
Hence, p(a) = b
But p(a) = 0
Hence, we have
b =0
Hence the value of b at which x-a is a factor of p(x) is 0.
Hence option [a] is correct.
Note: Alternative solution: Best Method: Synthetic division.
In this method, we start by writing coefficients of the polynomial in order from the highest degree to the constant term. If in between some degree terms are missing, we set their coefficient as 0.
Hence $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{3}}-3a{{x}^{3}}+2{{a}^{2}}x+b$ will be written as
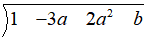
Now each the point which has to be substituted(say x= a) is written as follows
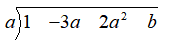
0 is placed below the first term
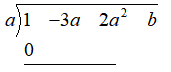
Now the terms under the same column are added. The sum is then multiplied with the root, and the product is written under the coefficient of the next term.
Hence, we have
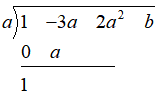
Continuing in this way we have the following
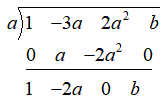
Since the last sum is b, we have $p\left( a \right)=b$.
Hence, b = 0 by factor theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




