
If \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+2ay+a+3=0\] represents a real circle with non – zero radius, then most appropriate is?
A. $a\in \left( -\infty ,-1 \right)$
B. $a\in \left( -1,2 \right)$
C. $a\in \left( 2,\infty \right)$
D. $a\in \left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left( 2,\infty \right)$
Answer
606.6k+ views
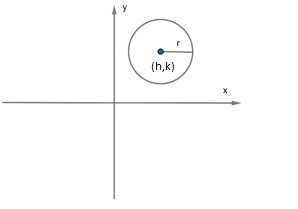
Hint: We will start by using the fact that a circle with radius r and centre at $\left( h,k \right)$ is ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$. Then we will convert the given equation in the similar form and use the fact that the quantity inside a square root can’t be negative to find the range of a.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have the equation of a circle as ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+2ay+a+3=0$ and the circle had non – zero radius. Now, we know that the general equation of a circle with centre at $\left( h,k \right)$ and radius r is ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$.
Now, we have the equation of a circle as ${{x}^{2}}-2x+{{y}^{2}}+2ay+a+3=0$.
Now, we will complete the square with respect to x and y by adding and subtracting the $\dfrac{1}{2}$ of the coefficient of x and y. So, we have,
${{x}^{2}}-2x+{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2ay+{{a}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}+a+3=0$
Now, we know that,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \\
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \\
\end{align}$
So, applying this to the above equation, we have,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}-1+{{\left( y+a \right)}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}+a+3=0 \\
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+a \right)}^{2}}+a-{{a}^{2}}+2=0 \\
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+a \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-a-2 \\
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-\left( -a \right) \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-a-2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, on comparing with ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$ we have the radius of circle as $r=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-a-2}$.
Now, we know that the quantity inside a square root is always non – negative. So, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}-a-2\ge 0 \\
& {{a}^{2}}-2a+a-2\ge 0 \\
& a\left( a-2 \right)+1\left( a-2 \right)\ge 0 \\
& \left( a+1 \right)\left( a-2 \right)\ge 0 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have the point at which ${{a}^{2}}-a-2=0$ as $a=2,a=-1$. Now, we represent this range on a number line and the sign depicting the nature of ${{a}^{2}}-a-2$.
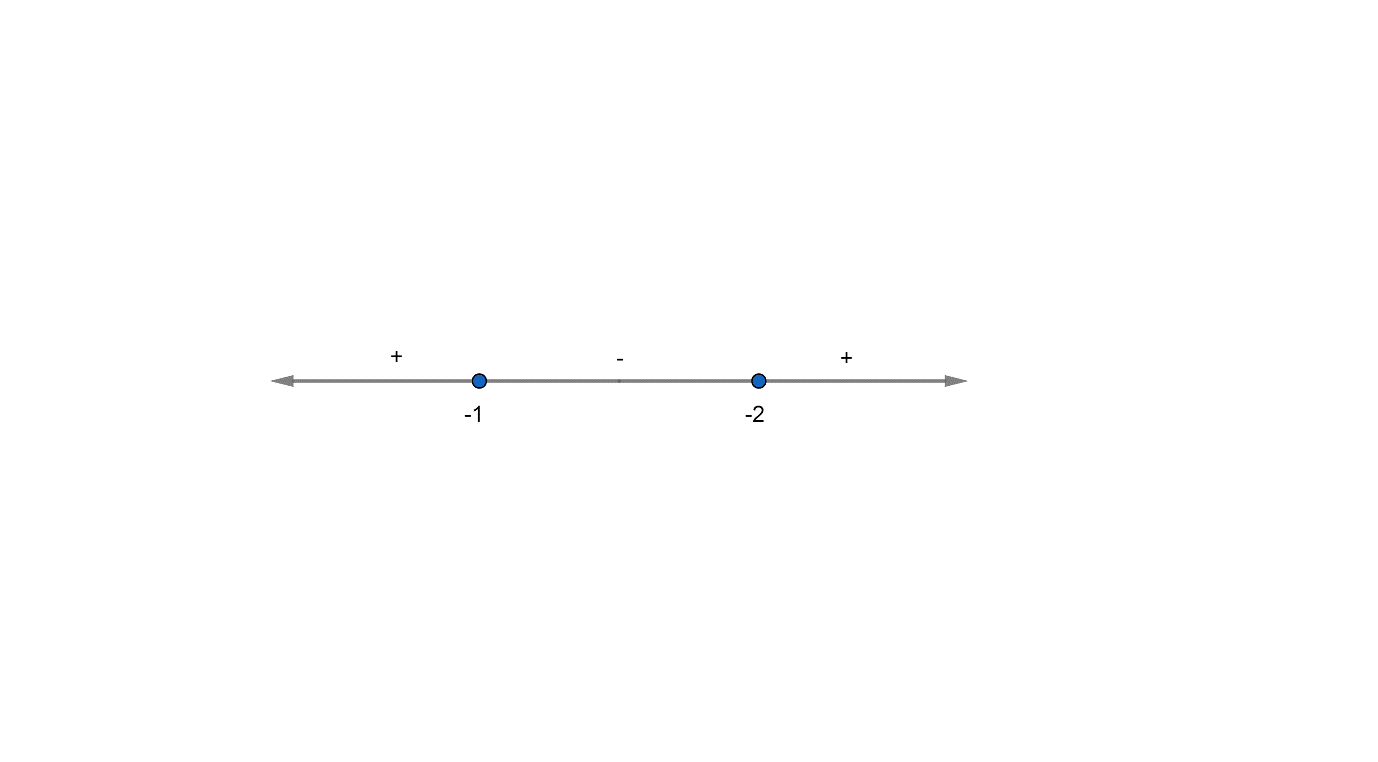
So, we have,
$\left( a+1 \right)\left( a-2 \right)\ge 0$ for $a\in \left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left( 2,\infty \right)$
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: It is important to note that we have used fact given in the question that the circle is real and has non – zero radius. Also, it is important to note that we have not taken the value of $a=-1\ and\ a=2$ because the value radius of the circle is zero which contradicts the fact that the circle is real with non – zero radius.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, we have the equation of a circle as ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-2x+2ay+a+3=0$ and the circle had non – zero radius. Now, we know that the general equation of a circle with centre at $\left( h,k \right)$ and radius r is ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$.

Now, we have the equation of a circle as ${{x}^{2}}-2x+{{y}^{2}}+2ay+a+3=0$.
Now, we will complete the square with respect to x and y by adding and subtracting the $\dfrac{1}{2}$ of the coefficient of x and y. So, we have,
${{x}^{2}}-2x+{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2ay+{{a}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}+a+3=0$
Now, we know that,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-2ab \\
& {{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+2ab \\
\end{align}$
So, applying this to the above equation, we have,
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}-1+{{\left( y+a \right)}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}+a+3=0 \\
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+a \right)}^{2}}+a-{{a}^{2}}+2=0 \\
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y+a \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-a-2 \\
& {{\left( x-1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-\left( -a \right) \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}-a-2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, on comparing with ${{\left( x-h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( y-k \right)}^{2}}={{r}^{2}}$ we have the radius of circle as $r=\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}-a-2}$.
Now, we know that the quantity inside a square root is always non – negative. So, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& {{a}^{2}}-a-2\ge 0 \\
& {{a}^{2}}-2a+a-2\ge 0 \\
& a\left( a-2 \right)+1\left( a-2 \right)\ge 0 \\
& \left( a+1 \right)\left( a-2 \right)\ge 0 \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we have the point at which ${{a}^{2}}-a-2=0$ as $a=2,a=-1$. Now, we represent this range on a number line and the sign depicting the nature of ${{a}^{2}}-a-2$.

So, we have,
$\left( a+1 \right)\left( a-2 \right)\ge 0$ for $a\in \left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left( 2,\infty \right)$
Hence, the correct option is (D).
Note: It is important to note that we have used fact given in the question that the circle is real and has non – zero radius. Also, it is important to note that we have not taken the value of $a=-1\ and\ a=2$ because the value radius of the circle is zero which contradicts the fact that the circle is real with non – zero radius.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




