
If we have the trigonometric function as \[\sin A\ = \dfrac{1}{3}\] and \[0 < A < 90\] then what is \[{\cos A}\] ?
Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, given that is \[\sin\ A\ = \dfrac{1}{3}\] then we need to find \[{\cos A}\]. By using trigonometric identities and ratios, we can find the \[{\cos A}\] . Also given a condition that \[0 < A < 90\] . First we can consider a right angle triangle. With the help of Pythagoras theorem, we can find the adjacent side and can easily solve the problem.
Pythagoras theorem :
Pythagoras theorem deals with the relationship between the sides of the right angle triangle. It states that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In a right angle triangle \[ABC\],
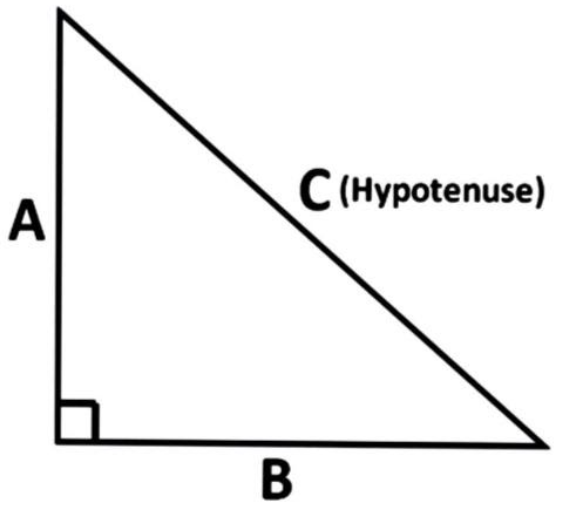
Where \[C\] is the hypotenuse, \[B\] is the base and \[A\] is the perpendicular.
According to Pythagoras theorem,
\[\left(\text{Hypotenuse} \right)^{2} = \left(\text{perpendicular} \right)^{2} + \left(\text{base} \right)^{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {C}^{2} = A^{2} + B^{2}\]
Formula used :
1.\[\sin\theta = \dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
2.\[\cos\theta = \dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given,
\[sin\ A\ = \dfrac{1}{3}\]
We know that
\[sin\theta = \dfrac{\text{opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\ \]
Thus we get,
\[\text{Opposite side} = 1\]
\[\text{Hypotenuse} = 3\]
Let us consider a right angle triangle \[{ABC}\],
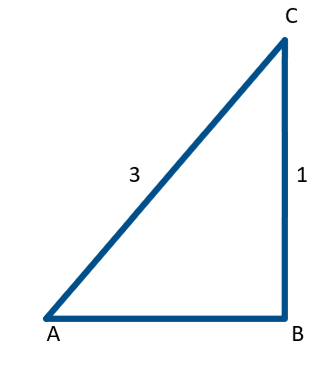
Here we need to find the adjacent side \[{AB}\],
By Pythagoras theorem,
\[BC^{2} = AB^{2} + AC^{2}\]
By substituting the known values
We get,
\[3^{2} = AB^{2} + 1^{2}\]
By simplifying,
We get,
\[AB^{2} = 9 – 1\]
By subtracting,
We get,
\[AB^{2} = 8\]
On taking square root on both sides,
We get,
\[AB = \sqrt{8}\]
Thus we get, \[AB = 2\sqrt{2}\]
Therefore the adjacent side is \[2\sqrt{2}\]
Now we can find \[{\cos A}\]
We know that,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By substituting the values,
We get,
\[\cos A = 2\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\]
Thus we get the value of \[\cos A = 2\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\]
Final answer :
The value of \[\cos A = 2\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\]
Note: The concept used to solve the given problem is trigonometric identities and ratios. Trigonometric identities are nothing but they involve trigonometric functions including variables and constants. The common technique used in this problem is the Pythagoras theorem with the use of trigonometric functions.
Pythagoras theorem :
Pythagoras theorem deals with the relationship between the sides of the right angle triangle. It states that in a right angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
In a right angle triangle \[ABC\],

Where \[C\] is the hypotenuse, \[B\] is the base and \[A\] is the perpendicular.
According to Pythagoras theorem,
\[\left(\text{Hypotenuse} \right)^{2} = \left(\text{perpendicular} \right)^{2} + \left(\text{base} \right)^{2}\]
\[\Rightarrow {C}^{2} = A^{2} + B^{2}\]
Formula used :
1.\[\sin\theta = \dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
2.\[\cos\theta = \dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given,
\[sin\ A\ = \dfrac{1}{3}\]
We know that
\[sin\theta = \dfrac{\text{opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\ \]
Thus we get,
\[\text{Opposite side} = 1\]
\[\text{Hypotenuse} = 3\]
Let us consider a right angle triangle \[{ABC}\],

Here we need to find the adjacent side \[{AB}\],
By Pythagoras theorem,
\[BC^{2} = AB^{2} + AC^{2}\]
By substituting the known values
We get,
\[3^{2} = AB^{2} + 1^{2}\]
By simplifying,
We get,
\[AB^{2} = 9 – 1\]
By subtracting,
We get,
\[AB^{2} = 8\]
On taking square root on both sides,
We get,
\[AB = \sqrt{8}\]
Thus we get, \[AB = 2\sqrt{2}\]
Therefore the adjacent side is \[2\sqrt{2}\]
Now we can find \[{\cos A}\]
We know that,
\[\cos \theta = \dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By substituting the values,
We get,
\[\cos A = 2\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\]
Thus we get the value of \[\cos A = 2\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\]
Final answer :
The value of \[\cos A = 2\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{3}\]
Note: The concept used to solve the given problem is trigonometric identities and ratios. Trigonometric identities are nothing but they involve trigonometric functions including variables and constants. The common technique used in this problem is the Pythagoras theorem with the use of trigonometric functions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




