
If we have the probability as \[P\left( A \right)=0.25\], \[P\left( B \right)=0.5\] and \[P\left( A\cap B \right)=0.14\] then \[P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)\] is equal to
(a) 0.61
(b) 0.39
(c) 0.48
(d) 0.11
Answer
579.9k+ views
Hint: For solving this problem we simply use the formulas of sets. Sets and probabilities have almost the same formulas. We consider the events as the sets and go for the problems to solve in sets and finally we again replace the sets into probabilities to get the required answer.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given some of the probabilities as
\[P\left( A \right)=0.25\]
\[P\left( B \right)=0.5\]
\[P\left( A\cap B \right)=0.14\]
Let us assume that the given events are some sets.
Here, there are two sets \[A, B\] that has the values as shown in the following Venn diagram
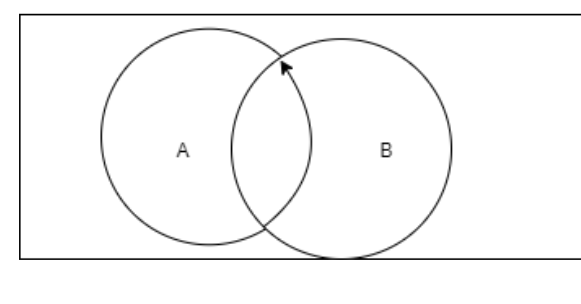
Here, the common part is denoted as \[A\cap B\]
We can say that the part not \[B\] is denoted as \[\bar{B}\]
Now, let us find \[A\cap \bar{B}\] from the Venn diagram shown above.
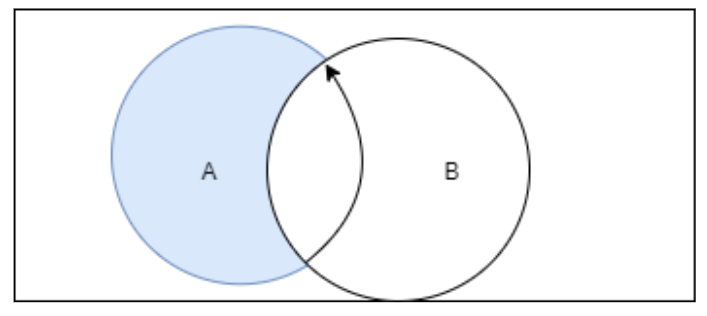
Here, we can see that the colored part is \[A\cap \bar{B}\] because it is the common part of ‘A’ and ‘not B’
Here, the colored part can be obtained by subtracting \[A\cap B\] from \[A\].
So, we can write
\[A\cap \bar{B}=A-\left( A\cap B \right)\]
So, as we got the required set let us convert these sets again back to probabilities.
Here, we can write
\[\Rightarrow P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)=P\left( A \right)-P\left( A\cap B \right)\]
By substituting the values of required probabilities in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)=0.25-0.14 \\
& \Rightarrow P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)=0.11 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)\] is 0.11
So, option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: This problem can be solved in other methods also.
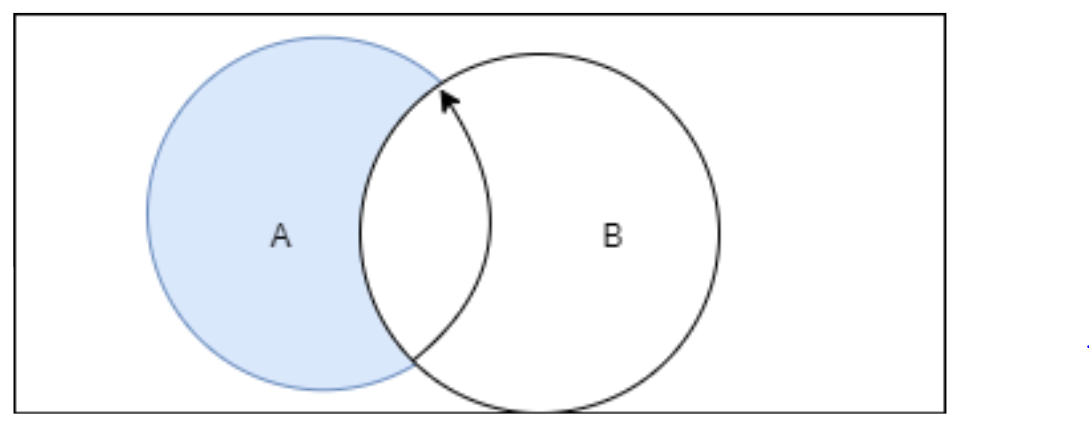
Here the coloured part can be written in the different way also like
\[A\cap \bar{B}=\left( A\cup B \right)-B\]
Now, we know that the union of two sets is given as
\[A\cup B=A+B-\left( A\cap B \right)\]
By substituting the values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A\cap \bar{B}=\left( A+B-\left( A\cap B \right) \right)-B \\
& \Rightarrow A\cap \bar{B}=A-\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Again we get the same equation as before.
Therefore our answer to option (d) is correct in this method also.
Complete step-by-step solution
We are given some of the probabilities as
\[P\left( A \right)=0.25\]
\[P\left( B \right)=0.5\]
\[P\left( A\cap B \right)=0.14\]
Let us assume that the given events are some sets.
Here, there are two sets \[A, B\] that has the values as shown in the following Venn diagram

Here, the common part is denoted as \[A\cap B\]
We can say that the part not \[B\] is denoted as \[\bar{B}\]
Now, let us find \[A\cap \bar{B}\] from the Venn diagram shown above.

Here, we can see that the colored part is \[A\cap \bar{B}\] because it is the common part of ‘A’ and ‘not B’
Here, the colored part can be obtained by subtracting \[A\cap B\] from \[A\].
So, we can write
\[A\cap \bar{B}=A-\left( A\cap B \right)\]
So, as we got the required set let us convert these sets again back to probabilities.
Here, we can write
\[\Rightarrow P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)=P\left( A \right)-P\left( A\cap B \right)\]
By substituting the values of required probabilities in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)=0.25-0.14 \\
& \Rightarrow P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)=0.11 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore the value of \[P\left( A\cap \bar{B} \right)\] is 0.11
So, option (d) is the correct answer.
Note: This problem can be solved in other methods also.

Here the coloured part can be written in the different way also like
\[A\cap \bar{B}=\left( A\cup B \right)-B\]
Now, we know that the union of two sets is given as
\[A\cup B=A+B-\left( A\cap B \right)\]
By substituting the values in above equation we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow A\cap \bar{B}=\left( A+B-\left( A\cap B \right) \right)-B \\
& \Rightarrow A\cap \bar{B}=A-\left( A\cap B \right) \\
\end{align}\]
Again we get the same equation as before.
Therefore our answer to option (d) is correct in this method also.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




