
If we have a trigonometric expression as $\left[ 2\cos x \right]+\left[ \sin x \right]=-3$ then the range of the function $f\left( x \right)=\sin x+\sqrt{3}\cos x$ in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$ is (where $\left[ \cdot \right]$ denotes greatest integer function).
\[\begin{align}
& A.\left( 2,-1 \right) \\
& B.\left( -1,\dfrac{-1}{2} \right) \\
& C.\left( -2,-1 \right) \\
& D.\text{None of these} \\
\end{align}\]
Answer
570.6k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will first find possible values of [2cosx] and [sinx] such that their sum is equal to -3 using the range of cosx and sinx which is [-1,1]. Using values of [2cosx] and [sinx] we will find the range of cosx and sinx in this sum. Using the range of cosx and sinx, we will find the range of x for both functions in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$ and then find a common range from both to get a range of x. At last, we will use the range of x to find the range of f(x).
Complete step-by-step solution
Here, we are given that $\left[ 2\cos x \right]+\left[ \sin x \right]=-3$.
As we know that, values of cosx and sinx lie between [-1,1] therefore to make the sum of $\left[ 2\cos x \right]+\left[ \sin x \right]$ as -3 we need the value of sinx as -1. Also the value of cosx will be -1. But the value of [2cosx] will be -2. Therefore,
$\left[ 2\cos x \right]=-2\text{ and }\left[ \sin x \right]=-1$.
Since we are dealing with the greatest integer here, the value of [2cosx] will be -2 if 2cosx will be anywhere between -2 and -1. (According to the definition of greatest integer). We cannot include -2, because we need value more than -2 and less than or equal to -1. Therefore, $-2\le 2\cos x < -1$.
Dividing by 2, $-1\le \cos x\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{-1}{2}$.
Since, we need range in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$ so let us draw graph of cosx in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$ which is given by,
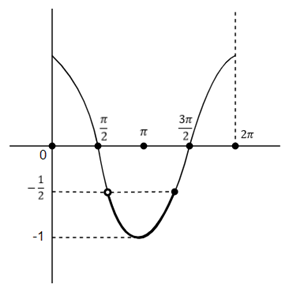
As we can see, the darker line in the graph is our required range, so the range will be between values of x when cosx is equal to $\dfrac{-1}{2}$ in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$.
We know that, $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\cos \dfrac{4\pi }{3}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$ in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$.
Therefore, the range of x will be between $\dfrac{2\pi }{3}\text{ and }\dfrac{4\pi }{3}$.
Hence, for cosx $x\in \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3},\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$. (We cannot take $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}\text{ and }\cos \dfrac{4\pi }{3}$ as these are equal to $\dfrac{-1}{2}$ which is not included).
Now, $\left[ \sin x \right]=-1$ means that sinx will be between 0 and -1. So sinx will be less than 0 and greater than or equal to -1. $\therefore -1\le \sin x\text{ }<\text{ }0$.
As we are dealing with negative values of sinx, we know that sinx is negative in the third and fourth quadrant, so the value of x will be between $\pi \text{ and }2\pi $.
Hence, sinx \[x\in \left( \pi ,2\pi \right)\]. We cannot include $\pi \text{ and }2\pi $ because $\sin \pi =\sin 2\pi =0$ and 0 is not included. Now, we need a common range of x.
Hence, taking intersection of $\left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3},\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)\text{ and }\left( \pi ,2\pi \right)$.
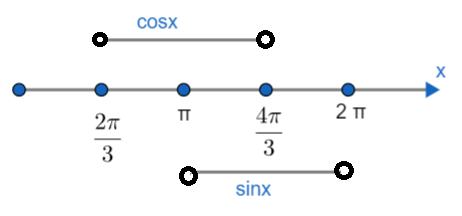
Region common to both will be $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$.
Hence, the range of x is $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$.
Now, we need to find the range of $f\left( x \right)=\sin x+\sqrt{3}\cos x$.
Let us first simplify f(x), $f\left( x \right)=\sin x+\sqrt{3}\cos x$.
Multiplying and dividing by 2, we get: $f\left( x \right)=2\left( \dfrac{1}{2}\sin x+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cos x \right)$.
As we know, $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\text{ and }\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{1}{2}$ so we get: $f\left( x \right)=2\left( \sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}\sin x+\cos x\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$.
Now function becomes of the form $\sin A\sin B+ \cos A\cos B$. We know that, $\cos \left( A-B \right)=\sin A\sin B+ \cos A\cos B$ so we get:
$f\left( x \right)=2\left( \cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)$.
Now, let us find the range of $2\left( \cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)$.
Since the range of x is $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$.
So we can write it as $\pi \text{ }<\text{ }x\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{4\pi }{3}$.
Subtracting $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$ we get:
$\begin{align}
& \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{4\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{x-\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{7\pi }{6} \\
\end{align}$.
Now to take value of $\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$ let us look at graph,
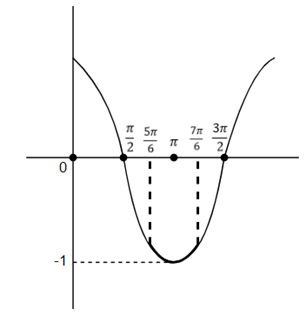
Hence, our range will be the darker part, since the minimum value will be -1 so $\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\ge -1$.
Also the minimum value will be either $\cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{6} \right),\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6} \right)$.
Let us evaluate them,
$\begin{align}
& \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{6} \right)=\cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{-\cos \pi }{6}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6} \right)=\cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{-\cos \pi }{6}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
So the maximum value of $\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}$.
Hence $\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}$. (We cannot take value of $\cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{6} \right),\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6} \right)$ in range because of open bracket)
Hence $-1\le \cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}$.
Multiplying by 2, $-2\le 2\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\text{ }<\text{ }-\sqrt{3}$.
Since $f\left( x \right)=2\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$ so, $-2\le f\left( x \right)\text{ }<\text{ }-\sqrt{3}$.
Hence the range of f(x) is $\left[ -2,-\sqrt{3} \right)$.
Hence, none of the options are correct.
So option D is the correct answer.
Note: Students should note that the greatest integer (x) rounds down a real number to the nearest integer. Here x could be less than or equal to ${{x}_{7}}$. Students should always draw graphs for calculating range. They should keep in mind all the trigonometric formulas before solving the sum. Take care of open and closed intervals.
Complete step-by-step solution
Here, we are given that $\left[ 2\cos x \right]+\left[ \sin x \right]=-3$.
As we know that, values of cosx and sinx lie between [-1,1] therefore to make the sum of $\left[ 2\cos x \right]+\left[ \sin x \right]$ as -3 we need the value of sinx as -1. Also the value of cosx will be -1. But the value of [2cosx] will be -2. Therefore,
$\left[ 2\cos x \right]=-2\text{ and }\left[ \sin x \right]=-1$.
Since we are dealing with the greatest integer here, the value of [2cosx] will be -2 if 2cosx will be anywhere between -2 and -1. (According to the definition of greatest integer). We cannot include -2, because we need value more than -2 and less than or equal to -1. Therefore, $-2\le 2\cos x < -1$.
Dividing by 2, $-1\le \cos x\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{-1}{2}$.
Since, we need range in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$ so let us draw graph of cosx in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$ which is given by,

As we can see, the darker line in the graph is our required range, so the range will be between values of x when cosx is equal to $\dfrac{-1}{2}$ in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$.
We know that, $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\cos \dfrac{4\pi }{3}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$ in $\left[ 0,2\pi \right]$.
Therefore, the range of x will be between $\dfrac{2\pi }{3}\text{ and }\dfrac{4\pi }{3}$.
Hence, for cosx $x\in \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3},\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$. (We cannot take $\cos \dfrac{2\pi }{3}\text{ and }\cos \dfrac{4\pi }{3}$ as these are equal to $\dfrac{-1}{2}$ which is not included).
Now, $\left[ \sin x \right]=-1$ means that sinx will be between 0 and -1. So sinx will be less than 0 and greater than or equal to -1. $\therefore -1\le \sin x\text{ }<\text{ }0$.
As we are dealing with negative values of sinx, we know that sinx is negative in the third and fourth quadrant, so the value of x will be between $\pi \text{ and }2\pi $.
Hence, sinx \[x\in \left( \pi ,2\pi \right)\]. We cannot include $\pi \text{ and }2\pi $ because $\sin \pi =\sin 2\pi =0$ and 0 is not included. Now, we need a common range of x.
Hence, taking intersection of $\left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3},\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)\text{ and }\left( \pi ,2\pi \right)$.

Region common to both will be $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$.
Hence, the range of x is $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$.
Now, we need to find the range of $f\left( x \right)=\sin x+\sqrt{3}\cos x$.
Let us first simplify f(x), $f\left( x \right)=\sin x+\sqrt{3}\cos x$.
Multiplying and dividing by 2, we get: $f\left( x \right)=2\left( \dfrac{1}{2}\sin x+\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\cos x \right)$.
As we know, $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\text{ and }\sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}=\dfrac{1}{2}$ so we get: $f\left( x \right)=2\left( \sin \dfrac{\pi }{6}\sin x+\cos x\cos \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$.
Now function becomes of the form $\sin A\sin B+ \cos A\cos B$. We know that, $\cos \left( A-B \right)=\sin A\sin B+ \cos A\cos B$ so we get:
$f\left( x \right)=2\left( \cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)$.
Now, let us find the range of $2\left( \cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right) \right)$.
Since the range of x is $\left( \pi ,\dfrac{4\pi }{3} \right)$.
So we can write it as $\pi \text{ }<\text{ }x\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{4\pi }{3}$.
Subtracting $\dfrac{\pi }{6}$ we get:
$\begin{align}
& \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{4\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{5\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{x-\pi }{6}\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{7\pi }{6} \\
\end{align}$.
Now to take value of $\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$ let us look at graph,

Hence, our range will be the darker part, since the minimum value will be -1 so $\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\ge -1$.
Also the minimum value will be either $\cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{6} \right),\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6} \right)$.
Let us evaluate them,
$\begin{align}
& \cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{6} \right)=\cos \left( \pi -\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{-\cos \pi }{6}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6} \right)=\cos \left( \pi +\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{-\cos \pi }{6}=\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
So the maximum value of $\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}$.
Hence $\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}$. (We cannot take value of $\cos \left( \dfrac{5\pi }{6} \right),\cos \left( \dfrac{7\pi }{6} \right)$ in range because of open bracket)
Hence $-1\le \cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\text{ }<\text{ }\dfrac{-\sqrt{3}}{2}$.
Multiplying by 2, $-2\le 2\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\text{ }<\text{ }-\sqrt{3}$.
Since $f\left( x \right)=2\cos \left( x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)$ so, $-2\le f\left( x \right)\text{ }<\text{ }-\sqrt{3}$.
Hence the range of f(x) is $\left[ -2,-\sqrt{3} \right)$.
Hence, none of the options are correct.
So option D is the correct answer.
Note: Students should note that the greatest integer (x) rounds down a real number to the nearest integer. Here x could be less than or equal to ${{x}_{7}}$. Students should always draw graphs for calculating range. They should keep in mind all the trigonometric formulas before solving the sum. Take care of open and closed intervals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




