
If vapour pressures of pure liquids A & Bare 300 and 800 torr respectively at ${{25}^{0}}C$. When these two liquids are mixed at this temperature to form a solution in which mole percentage of B is 92, then the total vapour pressure is observed to be 0.95 atm. Which of the following is true for this solution:
A. $\Delta {{V}_{mix}}>0$
B. $\Delta {{H}_{mix}}<0$
C. $\Delta {{V}_{mix}}=0$
D. $\Delta {{H}_{mix}}=0$
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: The concept of Raoult’s Law is needed for this question. The expected total pressure could be found out using the data given in the question and Raoult’s law formula, and then it can be compared with the real vapour pressure.
Complete Solution :
In order to answer this question, we need to learn about Raoult’s Law. Raoult's law states that, the vapour pressure of a solution which contains a solute that is non volatile is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent. For a solution containing non-volatile solute, at a given temperature, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to mole fraction of the solute. It states that for a solution of two or more miscible volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution at a given temperature is directly proportional to its mole fraction. The solutions which obey Raoult's law are ideal solutions. In this case, the vapour pressure of the solution always lies in the middle, the vapour pressure of the pure components. The cases of non-ideal solutions are:
- Positive Deviation solutions: In this type of deviations, the partial vapour pressure of each component (say A and B) of solution is greater than the vapour pressure as expected according to Raoult's law. This type of deviations are shown by the solutions in which solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions are weaker than solvent-solute interactions. Since in solution, the interactions among molecules becomes weaker, therefore, their escaping tendency increases which results in the increase in their partial vapour pressures. In such solutions total vapour pressure of the solution is also greater than the vapour pressure required according to the Raoult's Law. Here,$\Delta {{H}_{mix}}>0,\Delta {{V}_{mix}}>0$
- Negative deviation solutions: In this type of deviations the partial vapour pressure of each component of solution is less than t vapour pressure as expected according to Raoult law. This type of deviations are shown by the solution in which solvent-solvent and solute-solute interaction are weaker than solvent-solute interactions.In such solutions total vapour pressure of the solution is also less than the vapour pressure expected according to Raoult's law. Here,$\Delta {{V}_{mix}}<0,\Delta {{H}_{mix}}<0$.
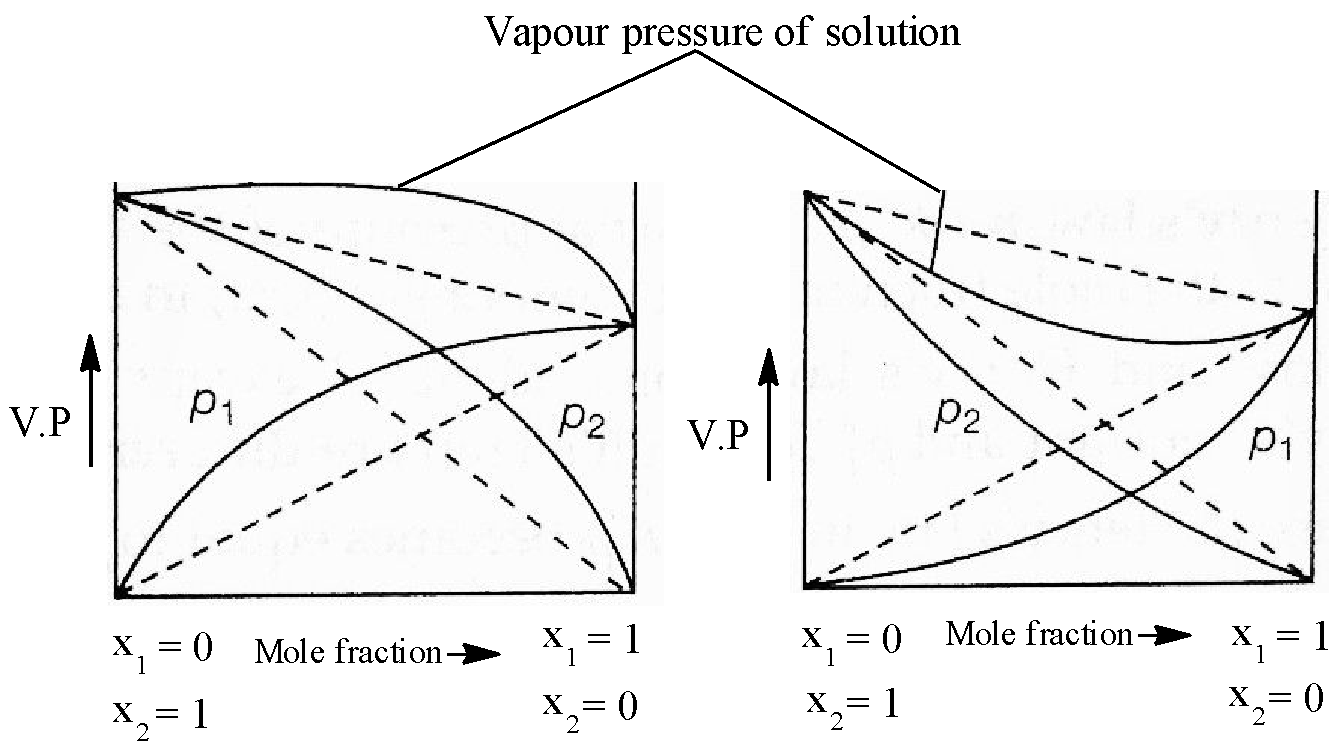
- We know that ${{p}_{T}}={{p}_{A}}^{0}{{x}_{A}}+{{p}_{B}}^{0}{{x}_{B}}$, where ${{p}_{T}}$ is total pressure and ${{P}_{A}},{{P}_{B}},{{x}_{A}},{{x}_{B}}$ represent partial pressures and mole fraction of A and B respectively. Now, substituting the data given in the question, we have:
\[{{p}_{T}} = 300\times 0.8+800\times 0.92 = 976 torr = 1.2 atm\]
- However this is the expected vapour pressure. The total vapour pressure is given to be 0.95 atm. This represents negative deviation from Raoult’s Law. So,$\Delta {{H}_{mix}}<0,\Delta {{V}_{mix}}<0$, So, the correct answer is “OptionA and B”.
Note: A solution that gets distilled at a particular temperature without any change in composition is called azeotrope. Positive deviation solutions show minimum boiling azeotrope whereas negative deviation solutions show maximum boiling azeotrope.
Complete Solution :
In order to answer this question, we need to learn about Raoult’s Law. Raoult's law states that, the vapour pressure of a solution which contains a solute that is non volatile is directly proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent. For a solution containing non-volatile solute, at a given temperature, the relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to mole fraction of the solute. It states that for a solution of two or more miscible volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution at a given temperature is directly proportional to its mole fraction. The solutions which obey Raoult's law are ideal solutions. In this case, the vapour pressure of the solution always lies in the middle, the vapour pressure of the pure components. The cases of non-ideal solutions are:
- Positive Deviation solutions: In this type of deviations, the partial vapour pressure of each component (say A and B) of solution is greater than the vapour pressure as expected according to Raoult's law. This type of deviations are shown by the solutions in which solute-solute and solvent-solvent interactions are weaker than solvent-solute interactions. Since in solution, the interactions among molecules becomes weaker, therefore, their escaping tendency increases which results in the increase in their partial vapour pressures. In such solutions total vapour pressure of the solution is also greater than the vapour pressure required according to the Raoult's Law. Here,$\Delta {{H}_{mix}}>0,\Delta {{V}_{mix}}>0$
- Negative deviation solutions: In this type of deviations the partial vapour pressure of each component of solution is less than t vapour pressure as expected according to Raoult law. This type of deviations are shown by the solution in which solvent-solvent and solute-solute interaction are weaker than solvent-solute interactions.In such solutions total vapour pressure of the solution is also less than the vapour pressure expected according to Raoult's law. Here,$\Delta {{V}_{mix}}<0,\Delta {{H}_{mix}}<0$.

- We know that ${{p}_{T}}={{p}_{A}}^{0}{{x}_{A}}+{{p}_{B}}^{0}{{x}_{B}}$, where ${{p}_{T}}$ is total pressure and ${{P}_{A}},{{P}_{B}},{{x}_{A}},{{x}_{B}}$ represent partial pressures and mole fraction of A and B respectively. Now, substituting the data given in the question, we have:
\[{{p}_{T}} = 300\times 0.8+800\times 0.92 = 976 torr = 1.2 atm\]
- However this is the expected vapour pressure. The total vapour pressure is given to be 0.95 atm. This represents negative deviation from Raoult’s Law. So,$\Delta {{H}_{mix}}<0,\Delta {{V}_{mix}}<0$, So, the correct answer is “OptionA and B”.
Note: A solution that gets distilled at a particular temperature without any change in composition is called azeotrope. Positive deviation solutions show minimum boiling azeotrope whereas negative deviation solutions show maximum boiling azeotrope.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




