
If two zeroes of a polynomial ${{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35$ are $2\pm \sqrt{3}$ find other zeroes.
Answer
574.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given an equation of degree 4 along with two of its zeroes and we have to find the remaining zeroes. Since equation is of degree 4, therefore it will have 4 zeroes and thus we need to find other two zeroes. For this, we will use given two zeroes to form factors and thus an equation of degree 2 which will divide the given equation. We will obtain another equation of degree 2 which will give us another 2 zeroes and hence those zeroes will be the zeroes of given equation of degree 4. To solve the quadratic equation (equation of degree 2) formed later, we will use split the middle term method.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are given equation as ${{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35$ and two of its zeroes are $2+\sqrt{3}\text{ and }2-\sqrt{3}$. We have to find other zeroes of the equation.
As we can see, equation is of degree 4, therefore, there will be total 4 zeroes and we need to find two remaining zeroes. Let $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35$.
Let us now use given roots to form an equation.
Since $x=2+\sqrt{3}$ is a zero of given equation p(x).
Therefore, $\left( x-\left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right) \right)$ is factor of equation p(x).
$\Rightarrow x-2-\sqrt{3}$ is factor.
Similarly, $x=2-\sqrt{3}$ is a zero of given equation p(x).
Therefore, $\left( x-\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right) \right)$ is factor of equation p(x).
$\Rightarrow x-2+\sqrt{3}$ is factor.
Now, $\left( x-2-\sqrt{3} \right)\text{ and }\left( x-2+\sqrt{3} \right)$ are both factors, so their product will also be a factor.
Hence, $\left( \left( x-2 \right)-\sqrt{3} \right)\left( \left( x-2 \right)+\sqrt{3} \right)$ is a factor.
We know, $\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ therefore we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}-4x-3 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+4-4x-3 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-4x+1 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, ${{x}^{2}}-4x+1$ is a factor of p(x).
Now let us divide p(x) by ${{x}^{2}}-4x+1$ to find other equation which is a factor of p(x).
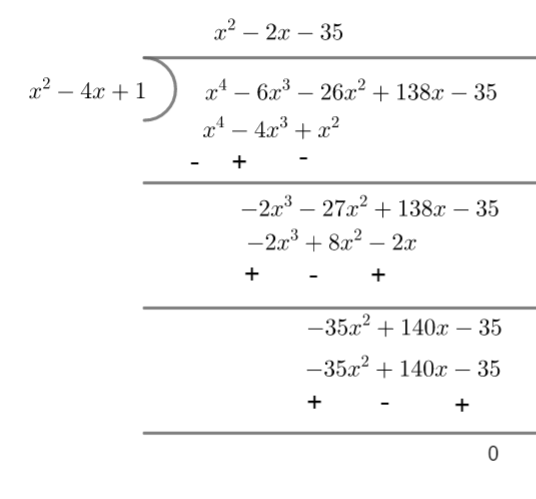
Now, we have got an equation of degree 2 as ${{x}^{2}}-2x-35$.
By Euclid's division algorithm, we see that
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35=\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)\]
Hence, $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)$ is a factor of p(x).
Therefore, zeroes of the equation will be roots of p(x).
So let us find zeroes of equation $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)$ using split the middle term method.
For splitting the middle term method equation $\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)$ we have to find two numbers whose sum is b and whose product is c.
In $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)$ we have to find two numbers whose sum is -2 and product is -35.
As we can see, -7 and 5 are numbers whose sum is -2 (-7+5=2) and product is -35$\left( 7\times \left( -5 \right) \right)$. So our equation becomes
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+\left( -7+5 \right)x-35=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-7x+5x-35=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\left( x-7 \right)+5\left( x-7 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x+5 \right)\left( x-7 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, x+5 = 0 and x-7 = 0, x = -5 and x = 7.
Hence, two zeroes of this equation are -5, 7.
Hence, two remaining zeros of the given equation p(x) are -5, 7.
Note: Students should take care of signs while performing long division. Students can also use quadratic formula for finding zeroes of the equation ${{x}^{2}}-2x-35=0$. Quadratic formula for an equation $\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)$ is given as $\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$. In this question,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-\left( -2 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( -35 \right)}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2\pm \sqrt{4+140}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2\pm \sqrt{144}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2\pm 12}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2+12}{2}\text{ and }x=\dfrac{2-12}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, x = 7 and x = -5.
Complete step by step answer:
Here we are given equation as ${{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35$ and two of its zeroes are $2+\sqrt{3}\text{ and }2-\sqrt{3}$. We have to find other zeroes of the equation.
As we can see, equation is of degree 4, therefore, there will be total 4 zeroes and we need to find two remaining zeroes. Let $p\left( x \right)={{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35$.
Let us now use given roots to form an equation.
Since $x=2+\sqrt{3}$ is a zero of given equation p(x).
Therefore, $\left( x-\left( 2+\sqrt{3} \right) \right)$ is factor of equation p(x).
$\Rightarrow x-2-\sqrt{3}$ is factor.
Similarly, $x=2-\sqrt{3}$ is a zero of given equation p(x).
Therefore, $\left( x-\left( 2-\sqrt{3} \right) \right)$ is factor of equation p(x).
$\Rightarrow x-2+\sqrt{3}$ is factor.
Now, $\left( x-2-\sqrt{3} \right)\text{ and }\left( x-2+\sqrt{3} \right)$ are both factors, so their product will also be a factor.
Hence, $\left( \left( x-2 \right)-\sqrt{3} \right)\left( \left( x-2 \right)+\sqrt{3} \right)$ is a factor.
We know, $\left( a-b \right)\left( a+b \right)={{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}$ therefore we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( x-2 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{3} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+{{2}^{2}}-4x-3 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+4-4x-3 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-4x+1 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, ${{x}^{2}}-4x+1$ is a factor of p(x).
Now let us divide p(x) by ${{x}^{2}}-4x+1$ to find other equation which is a factor of p(x).

Now, we have got an equation of degree 2 as ${{x}^{2}}-2x-35$.
By Euclid's division algorithm, we see that
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{4}}-6{{x}^{3}}-26{{x}^{2}}+138x-35=\left( {{x}^{2}}-4x+1 \right)\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)\]
Hence, $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)$ is a factor of p(x).
Therefore, zeroes of the equation will be roots of p(x).
So let us find zeroes of equation $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)$ using split the middle term method.
For splitting the middle term method equation $\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)$ we have to find two numbers whose sum is b and whose product is c.
In $\left( {{x}^{2}}-2x-35 \right)$ we have to find two numbers whose sum is -2 and product is -35.
As we can see, -7 and 5 are numbers whose sum is -2 (-7+5=2) and product is -35$\left( 7\times \left( -5 \right) \right)$. So our equation becomes
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+\left( -7+5 \right)x-35=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-7x+5x-35=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x\left( x-7 \right)+5\left( x-7 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( x+5 \right)\left( x-7 \right)=0 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, x+5 = 0 and x-7 = 0, x = -5 and x = 7.
Hence, two zeroes of this equation are -5, 7.
Hence, two remaining zeros of the given equation p(x) are -5, 7.
Note: Students should take care of signs while performing long division. Students can also use quadratic formula for finding zeroes of the equation ${{x}^{2}}-2x-35=0$. Quadratic formula for an equation $\left( a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c \right)$ is given as $\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}$. In this question,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-\left( -2 \right)\pm \sqrt{{{\left( -2 \right)}^{2}}-4\left( 1 \right)\left( -35 \right)}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2\pm \sqrt{4+140}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2\pm \sqrt{144}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2\pm 12}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{2+12}{2}\text{ and }x=\dfrac{2-12}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, x = 7 and x = -5.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




