
If two distinct chords drawn from the point \[\left( a,b \right)\] of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-ax-by=0\](where \[ab\ne 0\]) are bisected by the x-axis, then the roots of the quadratic equation \[b{{x}^{2}}-ax+2b=0\] are necessarily.
A. imaginary
B. real and equal
C. real and unequal
D. rational
Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we have to find the nature of the given roots from the given data. We can first draw the circle with two distinct chords, we can then find the coordinates and substitute in the given equation. We can see that we are given two distinct chords where there will be two distinct values, where discriminant will be greater than 0. Using that we can find the nature of the given root.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the given equation of the circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-ax-by=0\]where two distinct chords drawn from the point \[\left( a,b \right)\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-ax-by=0\](\[ab\ne 0\]) are bisected by the x-axis.
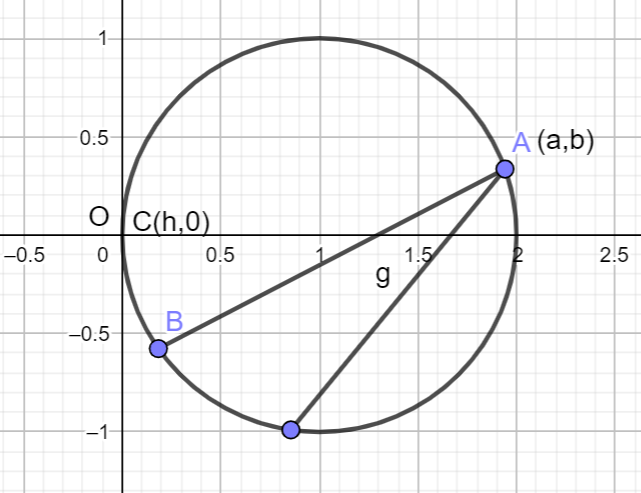
We can see that the point \[A\left( a,b \right)\] and C is the midpoint, where the coordinate is \[C\left( h,0 \right)\].
Then we can say that the coordinate of B is \[\left( -a+2h,-b \right)\].
We can substitute this coordinate in the given equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( -a+2h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -b \right)}^{2}}=a\left( -a+2h \right)+b\left( -b \right)\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+4{{h}^{2}}-4ah+{{b}^{2}}=-{{a}^{2}}+2ah-{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{h}^{2}}-3ah+{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=0....(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that, if there are two distinct chords which are bisected at x-axis then, there will be two distinct values of h satisfying equation (1).
Therefore, we can say that the discriminant of this quadratic equation must be greater than 0.
\[\Rightarrow D>0\]
We can now use the discriminant formula for the equation (1), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -3a \right)}^{2}}-4\times 2\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)>0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}-8{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}>8{{b}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that we are given a root, \[b{{x}^{2}}-ax+2b=0\].
We can now find the discriminant of the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow D'={{a}^{2}}-4\times \left( b \right)\left( 2b \right) \\
& \Rightarrow D'={{a}^{2}}-8{{b}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Here we can see that D’ is positive i.e. \[D'>0\].
Therefore, the roots of the given quadratic equation are real and equal.(B)
Note: Students should always remember that the formula for the discriminant is \[{{b}^{2}}-4ac\]. We should also remember that if the discriminant is greater than 0, the roots will be real and equal, if the discriminant is less than zero, we will have imaginary roots and if the discriminant is equal to zero, then the roots will be real and unequal.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that the given equation of the circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-ax-by=0\]where two distinct chords drawn from the point \[\left( a,b \right)\] and \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}-ax-by=0\](\[ab\ne 0\]) are bisected by the x-axis.

We can see that the point \[A\left( a,b \right)\] and C is the midpoint, where the coordinate is \[C\left( h,0 \right)\].
Then we can say that the coordinate of B is \[\left( -a+2h,-b \right)\].
We can substitute this coordinate in the given equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\left( -a+2h \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( -b \right)}^{2}}=a\left( -a+2h \right)+b\left( -b \right)\]
We can now simplify the above step, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}+4{{h}^{2}}-4ah+{{b}^{2}}=-{{a}^{2}}+2ah-{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{h}^{2}}-3ah+{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=0....(1) \\
\end{align}\]
We can see that, if there are two distinct chords which are bisected at x-axis then, there will be two distinct values of h satisfying equation (1).
Therefore, we can say that the discriminant of this quadratic equation must be greater than 0.
\[\Rightarrow D>0\]
We can now use the discriminant formula for the equation (1), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( -3a \right)}^{2}}-4\times 2\left( {{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}} \right)>0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}-8{{b}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}>8{{b}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We know that we are given a root, \[b{{x}^{2}}-ax+2b=0\].
We can now find the discriminant of the above equation, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow D'={{a}^{2}}-4\times \left( b \right)\left( 2b \right) \\
& \Rightarrow D'={{a}^{2}}-8{{b}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Here we can see that D’ is positive i.e. \[D'>0\].
Therefore, the roots of the given quadratic equation are real and equal.(B)
Note: Students should always remember that the formula for the discriminant is \[{{b}^{2}}-4ac\]. We should also remember that if the discriminant is greater than 0, the roots will be real and equal, if the discriminant is less than zero, we will have imaginary roots and if the discriminant is equal to zero, then the roots will be real and unequal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




