
If true enter1, else enter 0.
A species with one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical.
Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Homolytic cleavage i.e. the reaction which involves the breaking of the covalent bond in such a way that each atom separates with the electron of the shared pair and results in the formation of the neutral species i.e. the free radicals.
Complete step by step answer:
-A free radical is an atom or group of atoms having an odd or unpaired electron. It is denoted by putting a dot (·) against the symbol of the atom or group of atoms. E.g.· stands for chlorine free radicle etc.
-They are electrical neutral species which are usually formed by the homolytic cleavage (i.e. the cleavage in which the a covalent bond is equally shared between the two bonded atom and they gets separated with each atom having once electron of the covalent bond) of the molecules in reactions taking place in gas phase or in non-polar solvents. E.g.:
Cl—Cl $\to $ 2Cl·
Chlorine free radicals
-Due to the presence of unpaired electrons i.e. odd electrons, they are paramagnetic in nature. They are highly short- lived species. They are extremely reactive and as soon as they are formed, they immediately participate in the further reaction and their greater reactivity is due to the tendency of the odd-electron in them to get paired up.
Note: The free radicals which contain the carbon atom, their state of hybridization is not clearly known and it is indicated that most of alkyl free radicals such as methyl radicals are actually planar.
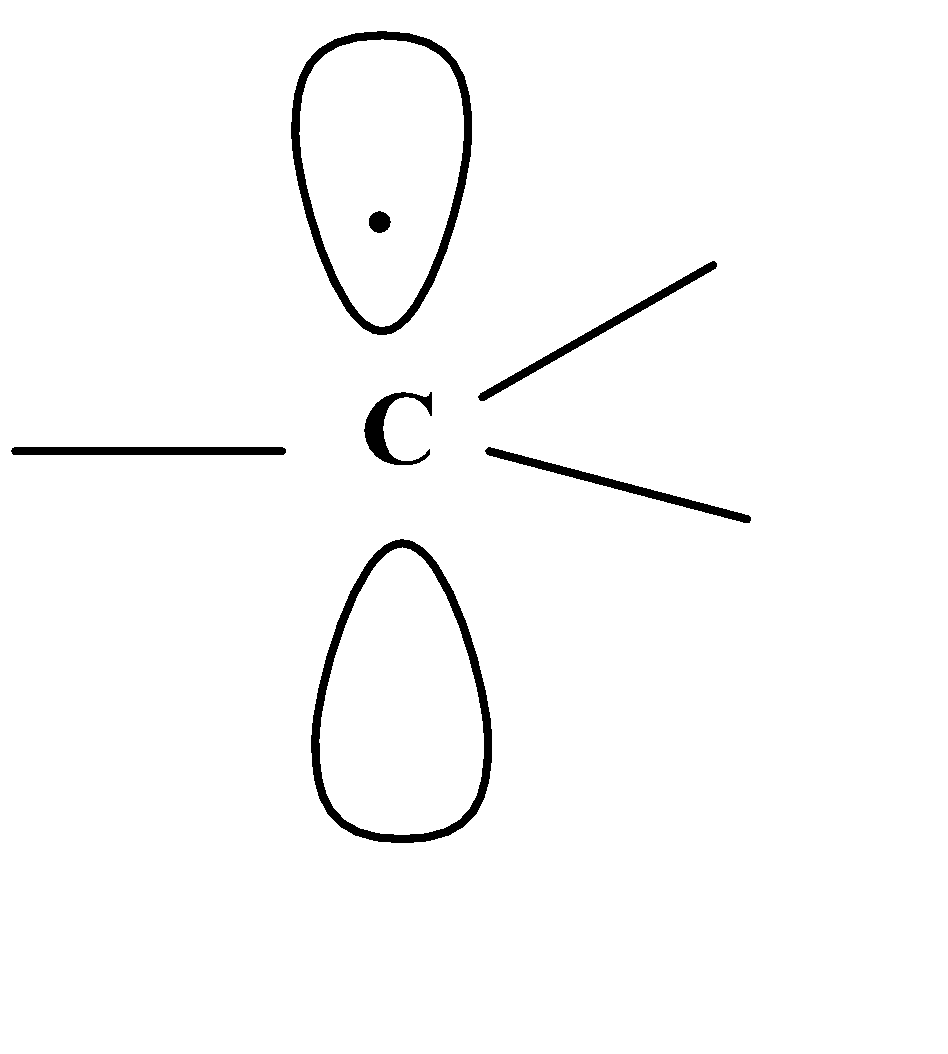
This means that carbon atom which carries odd electron has $\text{s}{{\text{p}} ^ {2}} $ hybridization and the other three hybrid orbitals are involved in bond formation with other atoms and the unhybridized p- orbital is at the right angle to plane and carries the odd electron.
Complete step by step answer:
-A free radical is an atom or group of atoms having an odd or unpaired electron. It is denoted by putting a dot (·) against the symbol of the atom or group of atoms. E.g.· stands for chlorine free radicle etc.
-They are electrical neutral species which are usually formed by the homolytic cleavage (i.e. the cleavage in which the a covalent bond is equally shared between the two bonded atom and they gets separated with each atom having once electron of the covalent bond) of the molecules in reactions taking place in gas phase or in non-polar solvents. E.g.:
Cl—Cl $\to $ 2Cl·
Chlorine free radicals
-Due to the presence of unpaired electrons i.e. odd electrons, they are paramagnetic in nature. They are highly short- lived species. They are extremely reactive and as soon as they are formed, they immediately participate in the further reaction and their greater reactivity is due to the tendency of the odd-electron in them to get paired up.
Note: The free radicals which contain the carbon atom, their state of hybridization is not clearly known and it is indicated that most of alkyl free radicals such as methyl radicals are actually planar.

This means that carbon atom which carries odd electron has $\text{s}{{\text{p}} ^ {2}} $ hybridization and the other three hybrid orbitals are involved in bond formation with other atoms and the unhybridized p- orbital is at the right angle to plane and carries the odd electron.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




