
If $\theta $ is an acute angle and $\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{2x}}$, then $\tan \theta $ is equal to
A. ${{x}^{2}}-1$
B. $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$
C. $\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+1}$
D. ${{x}^{2}}+1$
Answer
508.5k+ views
Hint: We first use the multiple angle formula $\cos \theta =1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$ to find the value of $\cos \theta $. We use the representation of a right-angle triangle with base and hypotenuse ratio being $\dfrac{1}{x}$ and the angle being $\theta $. We also take the trigonometric ratio formula to find the value of $\tan \theta $.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that $\theta $ is an acute angle and $\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{2x}}$.
From the multiple angle formula we know that $\cos \theta =1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$.
We put the values to get $\cos \theta =1-2{{\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{2x}} \right)}^{2}}=1-\dfrac{x-1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{x}$.
We know \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{base}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]. We can take the representation of a right-angle triangle with base and hypotenuse ratio being $\dfrac{1}{x}$ and the angle being $\theta $. The height and base were considered with respect to that particular angle $\theta $.
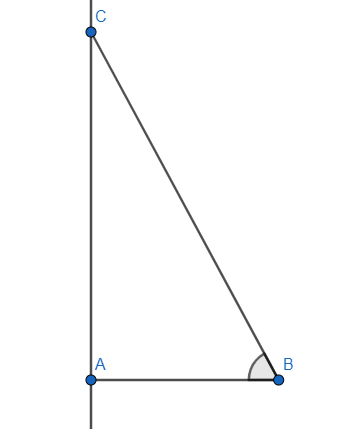
In this case we take $AB=1$ and keeping the ratio in mind we have $BC=x$ as the ratio has to be $\dfrac{1}{x}$. Now we apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of AC. $B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$.
So, $A{{C}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}-1$ which gives $AC=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$. We took positive value as $\theta $ is an acute angle.
We need to find $\tan \theta $. This ratio gives \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{height}}{\text{base}}\]. So, \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}{1}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}\].
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note:
We can also apply the trigonometric image form to get the value of $\tan \theta $.
The value $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{x}$ gives that \[\sec \theta =x\]. We know $\sec \theta =\sqrt{1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }$.
Putting the values, we get $\tan \theta =\sqrt{{{\sec }^{2}}\theta -1}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$.
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that $\theta $ is an acute angle and $\sin \dfrac{\theta }{2}=\sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{2x}}$.
From the multiple angle formula we know that $\cos \theta =1-2{{\sin }^{2}}\dfrac{\theta }{2}$.
We put the values to get $\cos \theta =1-2{{\left( \sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{2x}} \right)}^{2}}=1-\dfrac{x-1}{x}=\dfrac{1}{x}$.
We know \[\cos \theta =\dfrac{\text{base}}{\text{hypotenuse}}\]. We can take the representation of a right-angle triangle with base and hypotenuse ratio being $\dfrac{1}{x}$ and the angle being $\theta $. The height and base were considered with respect to that particular angle $\theta $.

In this case we take $AB=1$ and keeping the ratio in mind we have $BC=x$ as the ratio has to be $\dfrac{1}{x}$. Now we apply the Pythagoras’ theorem to find the length of AC. $B{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}$.
So, $A{{C}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}-1$ which gives $AC=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$. We took positive value as $\theta $ is an acute angle.
We need to find $\tan \theta $. This ratio gives \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{height}}{\text{base}}\]. So, \[\tan \theta =\dfrac{AC}{AB}=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}}{1}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}\].
Therefore, the correct option is (B).
Note:
We can also apply the trigonometric image form to get the value of $\tan \theta $.
The value $\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{x}$ gives that \[\sec \theta =x\]. We know $\sec \theta =\sqrt{1+{{\tan }^{2}}\theta }$.
Putting the values, we get $\tan \theta =\sqrt{{{\sec }^{2}}\theta -1}=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}-1}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




