
If the vertices of triangle ABC are A$(3,4)$, B$(5\sin t,5\cos t)$, and C$(5\cos t, - 5\sin t)$. Find the locus of the orthocentre of triangle ABC.
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: As we know that a locus (place) is a set of all the points as a curve, line or surface e.t.c. whose location is determined by one or more specified conditions we can understand it with the help of diagram given below:
And, orthocentre is the point where three altitudes of a triangle meet and, an altitude is a line that goes through the vertex and makes a right angle to its opposite side. We can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below.
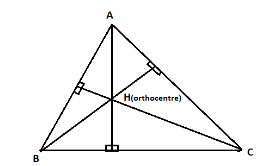
So, to find the locus of the orthocentre for the given triangle ABC, first of all we will let that the origin O(0,0) is at the equal distance from the vertices of the triangle which are A, B, and C as given in the question we can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below:
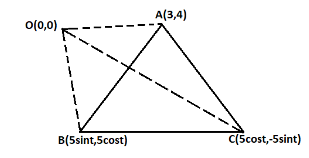
To find the distances between the origin (O) and the vertexes (A, B, and, C) we will use the formula to which is mentioned below:
Formula used:
Distance between two points which are $X = ({x_1},{y_1})$ and $Y = ({x_2},{y_2})$ is:
$XY = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $……………………..(1)
After finding the distances we will come to know that the distance between the origin and all the vertices are the same means, $OA = OB = OC$. Hence we can say that O is the circumcentre (the point at which the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle intersect which is at the equidistance from the vertices of the triangle). Now, we will let the orthocentre H (h,k) to find the centroid for the given triangle ABC and As we know, centroid (G) divides the orthocentre (H) and origin (O) in the ratio 2 : 1. We can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below.

Now, on comparing the orthocentre (H) with the centroid (G) we can find the locus of the orthocentre by adding the squares of both of the terms obtained.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
Vertex of triangle ABC are A$(3,4)$, B$(5\sin t,5\cos t)$, and C$(5\cos t, - 5\sin t)$.
Step 1: let the origin for the given triangle is O (0,0) and are at equal distance from the points A, B, and C (which are the vertices of the given triangle ABC).
So, first of all we will find the distance between the origin O(0,0) and the vertex A(3,4). To find the distance between two points we will use the formula ……….(1)
$OA = \sqrt {{{(3 - 0)}^2} + {{(4 - 0)}^2}} $
On solving the equation obtained,
$
OA = \sqrt {{{(3)}^2} + {{(4)}^2}} \\
OA = \sqrt {9 + 16} \\
OA = \sqrt {25} \\
OA = 5 \\
$
Hence the distance between points O and A is 5units.
Same as, we will find the distance between the origin O, and the vertex$B(5\sin t,5\cos t)$.
$OB = \sqrt {{{(5\sin t - 0)}^2} + {{(5\cos t - 0)}^2}} $
On solving the equation obtained,
$
OB = \sqrt {{{(5\sin t)}^2} + {{(5\cos t)}^2}} \\
OB = \sqrt {25{{\sin }^2}t + 25{{\cos }^2}t} \\
OB = \sqrt {25({{\sin }^2}t + {{\cos }^2}t)} \\
$
As we know that, ${\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t = 1$ so,
$
OB = \sqrt {25 \times 1} \\
OB = 5 \\
$
Hence the distance between points O and B is 5units.
Same as, we will find the distance between the origin O, and the vertex $C(5\cos t, - 5\sin t)$.
$OC = \sqrt {{{(5\cos t - 0)}^2} + ( - 5\sin t - 0)} $
On solving the equation obtained,
$
OC = \sqrt {{{(5\cos t)}^2} + ( - 5\sin t} {)^2} \\
OC = \sqrt {25{{\cos }^2}t + 25{{\sin }^2}t} \\
OC = \sqrt {25({{\cos }^2}t + {{\sin }^2}t)} \\
$
As we know, ${\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t = 1$so,
$
OC = \sqrt {25 \times 1} \\
OC = 5 \\
$
Hence the distance between points O and C is 5units.
As all the distances obtained between the origin O and vertexes (A, B, and C) are equal,
$OA = OB = OC = 5$units so, we can say that O is the circumcentre (the point at which the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle intersect which is at the equidistance from the vertices of the triangle)
Step 2: Now, let H (h,k) be the Orthocentre (the point where three altitudes of a triangle meet and an altitude is a line that goes through the vertex and makes a right angle to the opposite side) of the triangle ABC, and G is the centroid (is the intersection of the three medians, or the average of the three vertices) of the triangle ABC.
Hence, centroid of the given triangle ABC is:
$G = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t}}{3},\dfrac{{4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t}}{3}} \right)$……………………….(2)
As we know, centroid (G) divides the orthocentre (H) and origin (O) in the ration 2 : 1. We can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below.
Step 3: Now, we will find the coordinate of G (centroid)
So, $G = \left( {\dfrac{h}{3},\dfrac{k}{3}} \right)$……………………….(3)
Step 4: Now, we will compare (1) and (2),
$\left( {\dfrac{h}{3},\dfrac{k}{3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t}}{3},\dfrac{{4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t}}{3}} \right)$
On comparing both sides we will obtain the orthocentre (H),
$\dfrac{h}{3} = \dfrac{{3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t}}{3}$
$h = 3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t$
Same as,
$
\dfrac{k}{3} = \dfrac{{4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t}}{3} \\
k = 4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t \\
$
Hence obtained orthocentre (H) is $(h,k) = (3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t,4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t)$
Step 5: Now, with the help of orthocentre (H) we will find the locus of the given triangle ABC. So, first of all we will rearrange the obtained orthocentre.
$(h - 3) = 5(\sin t + \cos t)$…………………(4)
$(k - 4) = 5(\cos t - \sin t)$…………………(5)
Step 6: Now, we will add both the square of equations (4) and (5)
$
{(h - 3)^2} + {(k - 4)^2} = {\left[ {5\left( {\sin t + \cos t} \right)} \right]^2} + {\left[ {5\left( {\cos t - \sin t} \right)} \right]^2} \\
\\
$
Now, to solve the obtained equation we will use the formulas given below,
$
{(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab \\
{(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab \\
$
$
({h^2} + {3^2} - 2 \times 3 \times h) + ({k^2} + {4^2} + 2 \times 4 \times k) = 25({\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t + 2 \times \sin t \times \cos t) + 25({\cos ^2}t + {\sin ^2}t - 2 \times \cos t \times \sin t) \\
{h^{^2}} + 9 - 6h + {k^2} + 16 + 8k = 25(1 + 2\sin t\cos t) + 25(1 - 2\sin t\cos t) \\
{h^2} - 6h + {k^2} + 8k + 25 = 25\left( {1 + 2\sin t\cos t + 1 - 2\sin t\cos t} \right) \\
$On rearranging all the terms of obtained equation,
$
{h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k + 25 = 25 \times 2 \\
{h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k = 50 - 25 \\
{h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k - 25 = 0 \\
$
So, locus of orthocentre of triangle ABC is: ${h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k - 25 = 0$
Hence, we have obtained the locus of the orthocentre of the given triangle ABC, which is: ${h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k - 25 = 0$.
Note: Make sure all the distances between the origin and vertices of the given triangle are the same so that O (origin) is the circumcentre.
Centroid (G) divides the orthocentre (H) and origin (O) in the ration 2 : 1.
Use ${\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t = 1$ to solve the equation easily.
Make sure to use the right points to find the distances and other points.

And, orthocentre is the point where three altitudes of a triangle meet and, an altitude is a line that goes through the vertex and makes a right angle to its opposite side. We can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below.

So, to find the locus of the orthocentre for the given triangle ABC, first of all we will let that the origin O(0,0) is at the equal distance from the vertices of the triangle which are A, B, and C as given in the question we can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below:

To find the distances between the origin (O) and the vertexes (A, B, and, C) we will use the formula to which is mentioned below:
Formula used:
Distance between two points which are $X = ({x_1},{y_1})$ and $Y = ({x_2},{y_2})$ is:
$XY = \sqrt {{{({x_2} - {x_1})}^2} + {{({y_2} - {y_1})}^2}} $……………………..(1)
After finding the distances we will come to know that the distance between the origin and all the vertices are the same means, $OA = OB = OC$. Hence we can say that O is the circumcentre (the point at which the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle intersect which is at the equidistance from the vertices of the triangle). Now, we will let the orthocentre H (h,k) to find the centroid for the given triangle ABC and As we know, centroid (G) divides the orthocentre (H) and origin (O) in the ratio 2 : 1. We can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below.

Now, on comparing the orthocentre (H) with the centroid (G) we can find the locus of the orthocentre by adding the squares of both of the terms obtained.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given,
Vertex of triangle ABC are A$(3,4)$, B$(5\sin t,5\cos t)$, and C$(5\cos t, - 5\sin t)$.
Step 1: let the origin for the given triangle is O (0,0) and are at equal distance from the points A, B, and C (which are the vertices of the given triangle ABC).
So, first of all we will find the distance between the origin O(0,0) and the vertex A(3,4). To find the distance between two points we will use the formula ……….(1)
$OA = \sqrt {{{(3 - 0)}^2} + {{(4 - 0)}^2}} $
On solving the equation obtained,
$
OA = \sqrt {{{(3)}^2} + {{(4)}^2}} \\
OA = \sqrt {9 + 16} \\
OA = \sqrt {25} \\
OA = 5 \\
$
Hence the distance between points O and A is 5units.
Same as, we will find the distance between the origin O, and the vertex$B(5\sin t,5\cos t)$.
$OB = \sqrt {{{(5\sin t - 0)}^2} + {{(5\cos t - 0)}^2}} $
On solving the equation obtained,
$
OB = \sqrt {{{(5\sin t)}^2} + {{(5\cos t)}^2}} \\
OB = \sqrt {25{{\sin }^2}t + 25{{\cos }^2}t} \\
OB = \sqrt {25({{\sin }^2}t + {{\cos }^2}t)} \\
$
As we know that, ${\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t = 1$ so,
$
OB = \sqrt {25 \times 1} \\
OB = 5 \\
$
Hence the distance between points O and B is 5units.
Same as, we will find the distance between the origin O, and the vertex $C(5\cos t, - 5\sin t)$.
$OC = \sqrt {{{(5\cos t - 0)}^2} + ( - 5\sin t - 0)} $
On solving the equation obtained,
$
OC = \sqrt {{{(5\cos t)}^2} + ( - 5\sin t} {)^2} \\
OC = \sqrt {25{{\cos }^2}t + 25{{\sin }^2}t} \\
OC = \sqrt {25({{\cos }^2}t + {{\sin }^2}t)} \\
$
As we know, ${\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t = 1$so,
$
OC = \sqrt {25 \times 1} \\
OC = 5 \\
$
Hence the distance between points O and C is 5units.
As all the distances obtained between the origin O and vertexes (A, B, and C) are equal,
$OA = OB = OC = 5$units so, we can say that O is the circumcentre (the point at which the perpendicular bisectors of the sides of a triangle intersect which is at the equidistance from the vertices of the triangle)
Step 2: Now, let H (h,k) be the Orthocentre (the point where three altitudes of a triangle meet and an altitude is a line that goes through the vertex and makes a right angle to the opposite side) of the triangle ABC, and G is the centroid (is the intersection of the three medians, or the average of the three vertices) of the triangle ABC.
Hence, centroid of the given triangle ABC is:
$G = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t}}{3},\dfrac{{4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t}}{3}} \right)$……………………….(2)
As we know, centroid (G) divides the orthocentre (H) and origin (O) in the ration 2 : 1. We can also understand it with the help of the diagram given below.
Step 3: Now, we will find the coordinate of G (centroid)
So, $G = \left( {\dfrac{h}{3},\dfrac{k}{3}} \right)$……………………….(3)
Step 4: Now, we will compare (1) and (2),
$\left( {\dfrac{h}{3},\dfrac{k}{3}} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t}}{3},\dfrac{{4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t}}{3}} \right)$
On comparing both sides we will obtain the orthocentre (H),
$\dfrac{h}{3} = \dfrac{{3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t}}{3}$
$h = 3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t$
Same as,
$
\dfrac{k}{3} = \dfrac{{4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t}}{3} \\
k = 4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t \\
$
Hence obtained orthocentre (H) is $(h,k) = (3 + 5\sin t + 5\cos t,4 + 5\cos t - 5\sin t)$
Step 5: Now, with the help of orthocentre (H) we will find the locus of the given triangle ABC. So, first of all we will rearrange the obtained orthocentre.
$(h - 3) = 5(\sin t + \cos t)$…………………(4)
$(k - 4) = 5(\cos t - \sin t)$…………………(5)
Step 6: Now, we will add both the square of equations (4) and (5)
$
{(h - 3)^2} + {(k - 4)^2} = {\left[ {5\left( {\sin t + \cos t} \right)} \right]^2} + {\left[ {5\left( {\cos t - \sin t} \right)} \right]^2} \\
\\
$
Now, to solve the obtained equation we will use the formulas given below,
$
{(a - b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab \\
{(a + b)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab \\
$
$
({h^2} + {3^2} - 2 \times 3 \times h) + ({k^2} + {4^2} + 2 \times 4 \times k) = 25({\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t + 2 \times \sin t \times \cos t) + 25({\cos ^2}t + {\sin ^2}t - 2 \times \cos t \times \sin t) \\
{h^{^2}} + 9 - 6h + {k^2} + 16 + 8k = 25(1 + 2\sin t\cos t) + 25(1 - 2\sin t\cos t) \\
{h^2} - 6h + {k^2} + 8k + 25 = 25\left( {1 + 2\sin t\cos t + 1 - 2\sin t\cos t} \right) \\
$On rearranging all the terms of obtained equation,
$
{h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k + 25 = 25 \times 2 \\
{h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k = 50 - 25 \\
{h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k - 25 = 0 \\
$
So, locus of orthocentre of triangle ABC is: ${h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k - 25 = 0$
Hence, we have obtained the locus of the orthocentre of the given triangle ABC, which is: ${h^2} + {k^2} - 6h + 8k - 25 = 0$.
Note: Make sure all the distances between the origin and vertices of the given triangle are the same so that O (origin) is the circumcentre.
Centroid (G) divides the orthocentre (H) and origin (O) in the ration 2 : 1.
Use ${\sin ^2}t + {\cos ^2}t = 1$ to solve the equation easily.
Make sure to use the right points to find the distances and other points.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





