
If the value of charge density of a dielectric sphere with a cavity (as shown in the figure) is $ $ $ \rho $ . Find the electrostatic self energy.
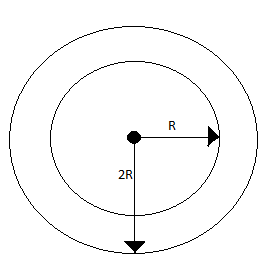

Answer
525.9k+ views
Hint :Here we should know that the energy in creating a charged spherical sphere is known as the electrostatic self energy. Self energy is also known as electrostatic interaction energy which is the attractive or repulsive interaction between objects having electric charges. In order to solve the given question we will be using the formula for electrostatic self energy and charge density and find the value of electrostatic self energy.
$ U=\dfrac{3{{Q}^{2}}}{20\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}R} $
Where $ R $ is the radius of a uniformly charged sphere of charge $ Q $ .
$ \rho =\dfrac{3Q}{4\pi {{R}^{3}}} $
Where $ \rho $ is the constant charge density.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here self energy is resulted due to the interaction energy of charges which constitute the thick spherical shell.
Suppose the core of outer radius $ r $ having charge $ Q $ , there will be a layer of infinitesimal thickness $ dr $ with charge $ dq $ .
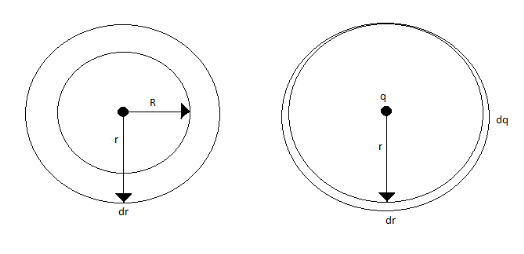
Here the radius of the shell created will be the radius of the outer shell minus the radius of the cavity $ {{(r-R)}^{3}} $ .
Since core can be assumed to be a point charge at the centre with charge $ q=\rho \cdot \dfrac{4}{3}\pi ({{r}^{3}}-{{R}^{3}}) $
$ \therefore $ Electrostatic interaction energy of point charge and the layer is given by
$ dU=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{q\cdot dq}{r} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{\rho \dfrac{4}{3}\pi ({{r}^{3}}-{{R}^{3}})\cdot \rho 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}{r} $
$ U=\int\limits_{R}^{2R}{\dfrac{{{\rho }^{2}}}{3{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}({{r}^{3}}-{{R}^{3}}r)\cdot dr} $
$ U=\dfrac{{{\rho }^{2}}4\pi }{3{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}[\dfrac{{{r}^{5}}}{5}-\dfrac{{{R}^{3}}{{r}^{2}}}{2}]_{R}^{2R} $
$ U=\dfrac{94}{15}\dfrac{{{\rho }^{2}}\pi {{R}^{5}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} $
Therefore this is the required answer.
Note :
In electrostatics, self energy of a particular charge distribution is the energy required to assemble the constituent charge distribution from infinity to that particular given configuration, without accelerating the charges. It is simply called the electrostatic potential energy reserved in the system of charges.
$ U=\dfrac{3{{Q}^{2}}}{20\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}R} $
Where $ R $ is the radius of a uniformly charged sphere of charge $ Q $ .
$ \rho =\dfrac{3Q}{4\pi {{R}^{3}}} $
Where $ \rho $ is the constant charge density.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Here self energy is resulted due to the interaction energy of charges which constitute the thick spherical shell.
Suppose the core of outer radius $ r $ having charge $ Q $ , there will be a layer of infinitesimal thickness $ dr $ with charge $ dq $ .

Here the radius of the shell created will be the radius of the outer shell minus the radius of the cavity $ {{(r-R)}^{3}} $ .
Since core can be assumed to be a point charge at the centre with charge $ q=\rho \cdot \dfrac{4}{3}\pi ({{r}^{3}}-{{R}^{3}}) $
$ \therefore $ Electrostatic interaction energy of point charge and the layer is given by
$ dU=\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{q\cdot dq}{r} $
$ =\dfrac{1}{4\pi {{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\dfrac{\rho \dfrac{4}{3}\pi ({{r}^{3}}-{{R}^{3}})\cdot \rho 4\pi {{r}^{2}}dr}{r} $
$ U=\int\limits_{R}^{2R}{\dfrac{{{\rho }^{2}}}{3{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}({{r}^{3}}-{{R}^{3}}r)\cdot dr} $
$ U=\dfrac{{{\rho }^{2}}4\pi }{3{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}[\dfrac{{{r}^{5}}}{5}-\dfrac{{{R}^{3}}{{r}^{2}}}{2}]_{R}^{2R} $
$ U=\dfrac{94}{15}\dfrac{{{\rho }^{2}}\pi {{R}^{5}}}{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} $
Therefore this is the required answer.
Note :
In electrostatics, self energy of a particular charge distribution is the energy required to assemble the constituent charge distribution from infinity to that particular given configuration, without accelerating the charges. It is simply called the electrostatic potential energy reserved in the system of charges.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




