
If the two vertices of the triangle are $\left( -4,4 \right),\left( -1,5 \right)$ and the centroid is $\left( 6,-5 \right)$, then find the third vertex.
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: We first find the coordinates of the midpoint M of side joining the given vertices $B\left( -4,4 \right),C\left( -1,5 \right)$ using the section formula for internal division with ratio 1:1. We then assume the coordinate of the third vertex as $A\left( x,y \right)$ . We know that centroid O$\left( 6,-5 \right)$ divides AM with ratio 2:1. We use the section formula again and find the unknowns $x,y$.\[\]
Complete step-by-step solution:
A median is a line joining the vertex of the triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side. The centroid of a triangle is the point of intersection of the medians.
Section Formula: Any point $P(x,y)$ which divides a line segment internally $\overline{AB}$ in a ratio$AP:PB=m:n$ with endpoints $A({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{2}})\text{ and B(}{{\text{x}}_{2}}\text{,}{{\text{y}}_{2}}\text{)}$ then the coordinates of P are
\[x=\dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},y=\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n}\]
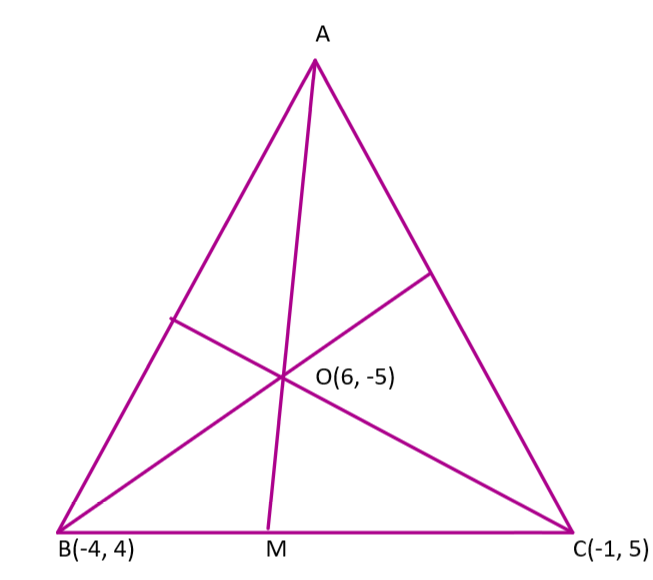
We denote the given vertices as $B\left( -4,4 \right),C\left( -1,5 \right)$. We denote the midpoint of BC as M. We join AM, now AM is median. We know that midpoint divides any line segment in a ratio 1:1. So M divides BC with ratio 1:1. We have the coordinates of M using section formula as
\[M=\left( \dfrac{-4+\left( -1 \right)}{2},\dfrac{4+5}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{-5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\]
We denote the centroid as O whose coordinates are given in the question as $\left( 6,-5 \right)$. We also know that the centroid divides the median in a ratio 2:1 where distance from vertex to the centroid is twice the distance from the to the midpoint on the opposite side to the said vertex. We assume the coordinate of A as $\left( x,y \right)$. We have O dividing A$\left( x,y \right)=\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and M $\left( \dfrac{-5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)=\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ with ratio $m:n=2:1$. We use section formula and have,
\[\begin{align}
& 6=\dfrac{2\times \left( \dfrac{5}{2} \right)+1\times x}{3},-5=\dfrac{2\times \dfrac{9}{2}+1\times y}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow 18=5+x,-15=9+y \\
& \Rightarrow x=13,y=-24 \\
\end{align}\]
So the coordinates of the third vertex A is $A\left( 13,-24 \right)$
Note: We need to be careful of the confusion of internal division for external division which is given by $x=\dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}-n{{x}_{1}}}{m-n},y=\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}-n{{y}_{1}}}{m-n}$. We can alternatively solve directly using the coordinates of centroid $\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}}{3} \right)$ where $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right),\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ are coordinates of the vertices of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
A median is a line joining the vertex of the triangle to the midpoint of the opposite side. The centroid of a triangle is the point of intersection of the medians.
Section Formula: Any point $P(x,y)$ which divides a line segment internally $\overline{AB}$ in a ratio$AP:PB=m:n$ with endpoints $A({{x}_{1}},{{y}_{2}})\text{ and B(}{{\text{x}}_{2}}\text{,}{{\text{y}}_{2}}\text{)}$ then the coordinates of P are
\[x=\dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}+n{{x}_{1}}}{m+n},y=\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}+n{{y}_{1}}}{m+n}\]

We denote the given vertices as $B\left( -4,4 \right),C\left( -1,5 \right)$. We denote the midpoint of BC as M. We join AM, now AM is median. We know that midpoint divides any line segment in a ratio 1:1. So M divides BC with ratio 1:1. We have the coordinates of M using section formula as
\[M=\left( \dfrac{-4+\left( -1 \right)}{2},\dfrac{4+5}{2} \right)=\left( \dfrac{-5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)\]
We denote the centroid as O whose coordinates are given in the question as $\left( 6,-5 \right)$. We also know that the centroid divides the median in a ratio 2:1 where distance from vertex to the centroid is twice the distance from the to the midpoint on the opposite side to the said vertex. We assume the coordinate of A as $\left( x,y \right)$. We have O dividing A$\left( x,y \right)=\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and M $\left( \dfrac{-5}{2},\dfrac{9}{2} \right)=\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ with ratio $m:n=2:1$. We use section formula and have,
\[\begin{align}
& 6=\dfrac{2\times \left( \dfrac{5}{2} \right)+1\times x}{3},-5=\dfrac{2\times \dfrac{9}{2}+1\times y}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow 18=5+x,-15=9+y \\
& \Rightarrow x=13,y=-24 \\
\end{align}\]
So the coordinates of the third vertex A is $A\left( 13,-24 \right)$
Note: We need to be careful of the confusion of internal division for external division which is given by $x=\dfrac{m{{x}_{2}}-n{{x}_{1}}}{m-n},y=\dfrac{m{{y}_{2}}-n{{y}_{1}}}{m-n}$. We can alternatively solve directly using the coordinates of centroid $\left( \dfrac{{{x}_{1}}+{{x}_{2}}+{{x}_{3}}}{3},\dfrac{{{y}_{1}}+{{y}_{2}}+{{y}_{3}}}{3} \right)$ where $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right),\left( {{x}_{3}},{{y}_{3}} \right)$ are coordinates of the vertices of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

Who was Subhash Chandra Bose Why was he called Net class 10 english CBSE




