
If the truth value of p is T, q is F, then truth values of (\[p\to q\]) and \[\left( q\to p \right)V\left( \nu p \right)\] are respectively.
a.F, F
b.F, T
c.T, F
d.T, T
Answer
619.8k+ views
Hint: In \[pVq\], V represents a non-exclusive or i.e. \[pVq\] is true when any of p, q is true and also when both are true. Draw the table of logical implication. Find the truth value of (\[p\to q\]), (\[q\to p\]) and (\[\nu p\]).
Complete step-by-step answer:
Substituting all the values, find the truth value.
The truth or falsehood of a proposition is called its truth value. In \[P\nu q,\]V represents a non-exclusive or i.e. \[p\nu q\] is true when any of p, q is true and also when both are true.
Here, (\[p\to q\]) implies that,
‘p’ implies ‘q’ means that if p is true, then q must also be true.
The true statement “p implies q” is also written “if p then q” or sometimes “q if p”. Statement p is called the premise of the implication and q is called the conclusion.
For eg: -\[P\to Q\] is logically equivalent to \[P\nu Q\]. “If a number is a multiple of 4, then it is even” is equivalent to a “number is not a multiple of 4 or (else) it is even”.
Now in the question it is given that the true value of p is T and the true value of q is F.
We need to find the value of (\[p\to q\]).
From the table of logical implication,
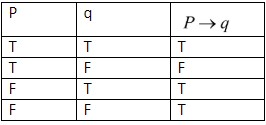
\[\therefore P\to q\] when P is T and q is F.
The 2nd case,
\[\therefore P\to q\] is F.
Similarly, to find \[q\to P\].
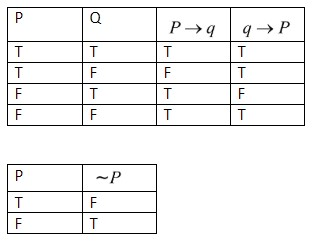
From the above table for the 2nd case, where the truth value of P is T and truth value of Q is F.
\[P\to q\]is F, \[q\to p\]is T and \[\sim p=F\]
We need to find \[\left( q\to p \right)V\left( \sim p \right)=F\].
i.e. if T V T comes then the truth value is T.
if T V F, then the truth value is F.
if F V F, then the truth value is F.
if F V T, then the truth value is F.
Hence, the correct answer is (a),
Note: You should remember or be able to construct the truth tables for the logical connectives. You will use these tables to construct tables for more complicated sentences. It’s easier to demonstrate what to do than to describe it in words. When you construct a truth table, you will have to consider all possible assignments of True (T) and False (F) to the component statement.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Substituting all the values, find the truth value.
The truth or falsehood of a proposition is called its truth value. In \[P\nu q,\]V represents a non-exclusive or i.e. \[p\nu q\] is true when any of p, q is true and also when both are true.
Here, (\[p\to q\]) implies that,
‘p’ implies ‘q’ means that if p is true, then q must also be true.
The true statement “p implies q” is also written “if p then q” or sometimes “q if p”. Statement p is called the premise of the implication and q is called the conclusion.
For eg: -\[P\to Q\] is logically equivalent to \[P\nu Q\]. “If a number is a multiple of 4, then it is even” is equivalent to a “number is not a multiple of 4 or (else) it is even”.
Now in the question it is given that the true value of p is T and the true value of q is F.
We need to find the value of (\[p\to q\]).
From the table of logical implication,

\[\therefore P\to q\] when P is T and q is F.
The 2nd case,
\[\therefore P\to q\] is F.
Similarly, to find \[q\to P\].

From the above table for the 2nd case, where the truth value of P is T and truth value of Q is F.
\[P\to q\]is F, \[q\to p\]is T and \[\sim p=F\]
We need to find \[\left( q\to p \right)V\left( \sim p \right)=F\].
i.e. if T V T comes then the truth value is T.
if T V F, then the truth value is F.
if F V F, then the truth value is F.
if F V T, then the truth value is F.
Hence, the correct answer is (a),
Note: You should remember or be able to construct the truth tables for the logical connectives. You will use these tables to construct tables for more complicated sentences. It’s easier to demonstrate what to do than to describe it in words. When you construct a truth table, you will have to consider all possible assignments of True (T) and False (F) to the component statement.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




