
If the trigonometric sine ratio $\sin x=\dfrac{4}{5}$, how do you find the value of $\cos x$?
Answer
564.9k+ views
Hint: We know that the $\sin $ of an angle is equal to the ratio of the opposite side of the angle and the hypotenuse of the right-angle triangle. In the problem we have the value of $\sin x$ as $\dfrac{4}{5}$. So, we will equate the both the values of $\sin x$. Now we will get the length of the opposite side of the triangle and the length of the hypotenuse. In a right-angled triangle, we have the relation between the side lengths as $hy{{p}^{2}}=sid{{e_1}^{2}}+sid{{e_2}^{2}}$. From this relation we will calculate the length of the adjacent side of the $x$. After getting all the side lengths in the triangle we will calculate the $\cos x$ by taking the ratio of adjacent sides to the hypotenuse of the right-angle triangle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that,
$\sin x=\dfrac{4}{5}$
We know that $\sin x=\dfrac{\text{Opposite to }x}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$, then we will get
$\dfrac{\text{Opposite to }x}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{4}{5}$
Assuming a proportional constant $k$, then we will get
$\text{Opposite side to }x=4k$
$\text{Hypotenuse}=5k$.
Now the triangle with the above-mentioned side lengths is given below
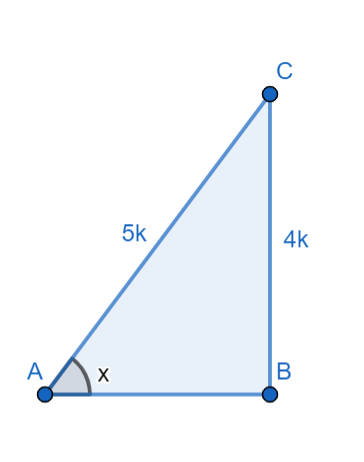
From the Pythagoras theorem we can write
$\begin{align}
& A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 5k \right)}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+{{\left( 4k \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 25{{k}^{2}}-16{{k}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{9{{k}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=3k \\
\end{align}$
Now we have all the side lengths in the triangle. Now the value of $\cos x$ is given by
$\begin{align}
& \cos x=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent to }x}{\text{Hypotenuse}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{AB}{AC} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{3k}{5k} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{3}{5} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the value of $\cos x$ is $\dfrac{3}{5}$.
Note: We can solve this problem in another method. We have trigonometric identity ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$. Substituting $\sin x=\dfrac{4}{5}$ in the above identity, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{4}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}x=1-\dfrac{16}{25} \\
\end{align}$
Taking LCM in the RHS, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{25-16}{25}$
Applying square root on both sides of the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{25}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{3}{5} \\
\end{align}$
From both the methods we got the same result.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given that,
$\sin x=\dfrac{4}{5}$
We know that $\sin x=\dfrac{\text{Opposite to }x}{\text{Hypotenuse}}$, then we will get
$\dfrac{\text{Opposite to }x}{\text{Hypotenuse}}=\dfrac{4}{5}$
Assuming a proportional constant $k$, then we will get
$\text{Opposite side to }x=4k$
$\text{Hypotenuse}=5k$.
Now the triangle with the above-mentioned side lengths is given below

From the Pythagoras theorem we can write
$\begin{align}
& A{{C}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{\left( 5k \right)}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+{{\left( 4k \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow 25{{k}^{2}}-16{{k}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{9{{k}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=3k \\
\end{align}$
Now we have all the side lengths in the triangle. Now the value of $\cos x$ is given by
$\begin{align}
& \cos x=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent to }x}{\text{Hypotenuse}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{AB}{AC} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{3k}{5k} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{3}{5} \\
\end{align}$
Hence the value of $\cos x$ is $\dfrac{3}{5}$.
Note: We can solve this problem in another method. We have trigonometric identity ${{\sin }^{2}}x+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1$. Substituting $\sin x=\dfrac{4}{5}$ in the above identity, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& {{\left( \dfrac{4}{5} \right)}^{2}}+{{\cos }^{2}}x=1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}x=1-\dfrac{16}{25} \\
\end{align}$
Taking LCM in the RHS, then we will get
$\Rightarrow {{\cos }^{2}}x=\dfrac{25-16}{25}$
Applying square root on both sides of the above equation, then we will get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\sqrt{\dfrac{9}{25}} \\
& \Rightarrow \cos x=\dfrac{3}{5} \\
\end{align}$
From both the methods we got the same result.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Who was Subhash Chandra Bose Why was he called Net class 10 english CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE




