
If the real function \[f:X\to \left[ 2,6 \right]\] , where \[f\left( x \right)=\sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x+4\] is one-one onto then possible X among the following is
(A) \[\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{2},\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right]\]
(B) \[\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right]\]
(C) \[\left[ \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right]\]
(D) \[\left[ -\pi ,\pi \right]\]
Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Transform the given function, \[f\left( x \right)=\sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x+4\] as \[f\left( x \right)=2.\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x \right)+4\] . Now, simplify it using the formula \[\sin \left( A-B \right)=\sin A\cos B-\sin B\cos A\] . The maximum and minimum value of the sine function is 1 and -1 respectively. We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=1\] and \[\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1\] . Using this get the values of x corresponding to which the function \[y=f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4\] , has the maximum and minimum value. Now, plot the graph of the function and get those intervals of x in which y has different values corresponding to different values of x.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have the function,
\[f\left( x \right)=\sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x+4\] ……………………………(1)
It is given that the range of this function is \[\left[ 2,6 \right]\] . It means that the minimum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 2 and the maximum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 6.
First of all, we need to simplify the function \[f\left( x \right)\] .
Transforming equation (1), we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2.\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x \right)+4\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\sin 2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\cos 2x \right)+4\] ………………………………….(2)
We know that, \[\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\] and \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\] …………………………..(3)
Now, from equation (2) and equation (3), we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left\{ \sin 2x\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\cos 2x \right\}+4\] …………………………..(4)
We know the formula, \[\sin \left( A-B \right)=\sin A\cos B-\sin B\cos A\] …………………………..(5)
Now, replacing A by 2x and B by \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\] in equation (5), we get
\[sin\left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\sin 2x\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\cos 2x\] ………………………….(6)
From equation (4) and equation (6), we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4\] ………………………..(7)
We know that the maximum value of the sine function is 1.
So, the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is maximum when the value of \[\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\] is equal to 1 and we know that
\[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=1\] . Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow \sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) \right)\] ……………………………………(8)
We know the property, \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin y \right)=y\] ………………………………..(9)
From equation (8) and equation (9), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{4\pi }{6} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] …………………….(10)
At \[x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] , the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is maximum, and the maximum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2.\dfrac{\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)+4\] ………………..(11)
We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=1\] ……………………(12)
From equation (11) and equation (12), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left( 1 \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=6\]
The maximum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 6 …………………………..(13)
We know that the maximum value of sine function is -1.
So, the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is minimum when the value of \[\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\] is equal to -1 and we know that
\[\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1\] . Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow \sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right) \right)\] ……………………………………(14)
We know the property, \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin y \right)=y\] ………………………………..(15)
From equation (14) and equation (15), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=\left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=-\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{-2\pi }{6} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-\pi }{6}\] …………………….(16)
At \[x=\dfrac{-\pi }{6}\] , the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is minimum, and the minimum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2.\dfrac{-\pi }{6}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)+4\] ………………..(17)
We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1\] ……………………(18)
From equation (17) and equation (18), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left( -1 \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\]
The minimum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 2 …………………………..(19)
Now, plotting graph of the function \[y=f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4\] , we get
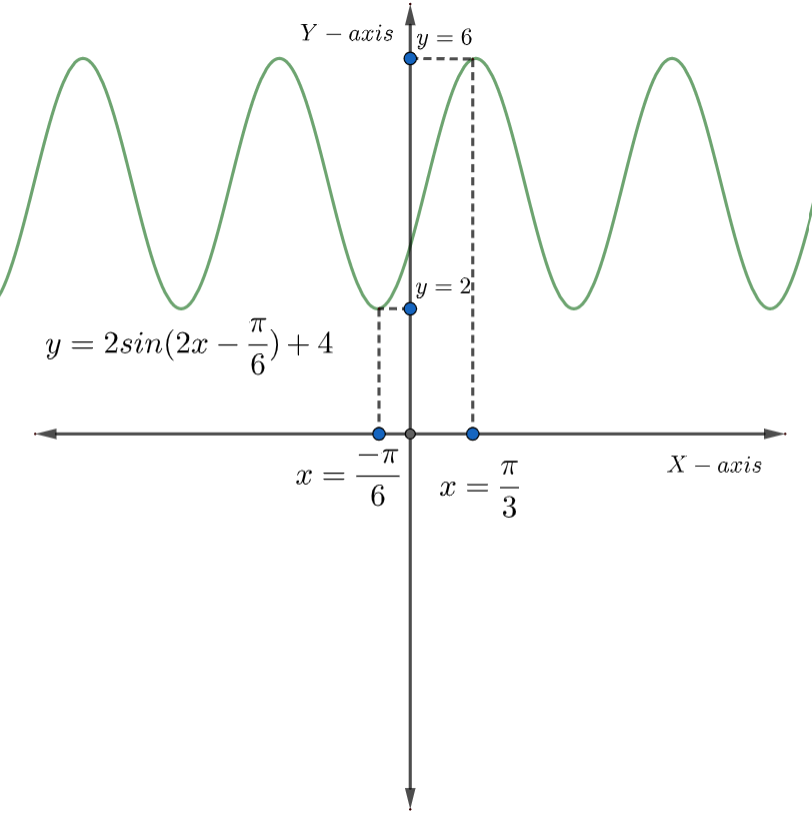
We know that one-one onto functions doesn’t have the same value of y for different values of x.
And we can see in the graph that when \[x\in \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] then, y has different values corresponding to different values of x. The interval \[x\in \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] also includes the range of y.
Therefore, the given function is one-one onto when \[x\in \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] .
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In this question, one might think to take the periodicity of the sine function that is, \[\left( 0,2\pi \right)\] as the interval for the one-one onto function. This is wrong because in the interval \[\left( 0,2\pi \right)\] the graph includes the same range on the y-axis between the x-range which is a contradiction for one-one onto function.
Complete step by step answer:
According to the question, we have the function,
\[f\left( x \right)=\sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x+4\] ……………………………(1)
It is given that the range of this function is \[\left[ 2,6 \right]\] . It means that the minimum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 2 and the maximum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 6.
First of all, we need to simplify the function \[f\left( x \right)\] .
Transforming equation (1), we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2.\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \sqrt{3}\sin 2x-\cos 2x \right)+4\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left( \dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\sin 2x-\dfrac{1}{2}\cos 2x \right)+4\] ………………………………….(2)
We know that, \[\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\] and \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\] …………………………..(3)
Now, from equation (2) and equation (3), we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left\{ \sin 2x\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\cos 2x \right\}+4\] …………………………..(4)
We know the formula, \[\sin \left( A-B \right)=\sin A\cos B-\sin B\cos A\] …………………………..(5)
Now, replacing A by 2x and B by \[\left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\] in equation (5), we get
\[sin\left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\sin 2x\cos \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)-\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\cos 2x\] ………………………….(6)
From equation (4) and equation (6), we get
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4\] ………………………..(7)
We know that the maximum value of the sine function is 1.
So, the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is maximum when the value of \[\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\] is equal to 1 and we know that
\[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=1\] . Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow \sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) \right)\] ……………………………………(8)
We know the property, \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin y \right)=y\] ………………………………..(9)
From equation (8) and equation (9), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=\left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{4\pi }{6} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] …………………….(10)
At \[x=\dfrac{\pi }{3}\] , the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is maximum, and the maximum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2.\dfrac{\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{2\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)+4\] ………………..(11)
We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=1\] ……………………(12)
From equation (11) and equation (12), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left( 1 \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=6\]
The maximum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 6 …………………………..(13)
We know that the maximum value of sine function is -1.
So, the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is minimum when the value of \[\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)\] is equal to -1 and we know that
\[\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1\] . Therefore,
\[\Rightarrow \sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)=\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}={{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right) \right)\] ……………………………………(14)
We know the property, \[{{\sin }^{-1}}\left( \sin y \right)=y\] ………………………………..(15)
From equation (14) and equation (15), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6}=\left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=-\dfrac{\pi }{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{6} \\
& \Rightarrow 2x=\dfrac{-2\pi }{6} \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-\pi }{6}\] …………………….(16)
At \[x=\dfrac{-\pi }{6}\] , the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is minimum, and the minimum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2.\dfrac{-\pi }{6}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{3}-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)+4\] ………………..(17)
We know that \[\sin \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{2} \right)=-1\] ……………………(18)
From equation (17) and equation (18), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\left( -1 \right)+4 \\
& \Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=-2+4 \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow f\left( x \right)=2\]
The minimum value of the function \[f\left( x \right)\] is equal to 2 …………………………..(19)
Now, plotting graph of the function \[y=f\left( x \right)=2\sin \left( 2x-\dfrac{\pi }{6} \right)+4\] , we get

We know that one-one onto functions doesn’t have the same value of y for different values of x.
And we can see in the graph that when \[x\in \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] then, y has different values corresponding to different values of x. The interval \[x\in \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] also includes the range of y.
Therefore, the given function is one-one onto when \[x\in \left( \dfrac{-\pi }{6},\dfrac{\pi }{3} \right)\] .
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In this question, one might think to take the periodicity of the sine function that is, \[\left( 0,2\pi \right)\] as the interval for the one-one onto function. This is wrong because in the interval \[\left( 0,2\pi \right)\] the graph includes the same range on the y-axis between the x-range which is a contradiction for one-one onto function.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




