
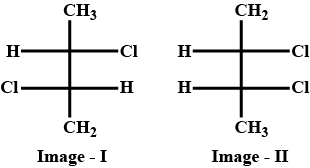
If the optical rotation produced by ref. Image 1 is \[ + 36^\circ \] , then the optical rotation Produced by ref. Image 2 is?

Answer
573k+ views
Hint: The above molecules are meso isomers of each other. Meso forms are optically inactive that means they show no rotation.
Complete step by step solution:
Optical isomers have the same physical and chemical properties but they differ in their behaviour towards plane polarized light. An optically active compound is the one which can rotate plane polarized light. Those which can rotate PPL (plane polarized light) towards right are known as dextrorotatory compounds (d form) and those which can rotate PPL towards left are known as laevorotatory (l form). The angles by which dextrorotatory compounds rotate PPL towards right are represented with + sign. On the other hand angle by which laevorotatory compounds rotate PPL towards left are represented by – sign. The compounds which fail to rotate PPL are known as optically inactive. Optically active compounds have dissymmetry, chirality and are non super imposable mirror images of each other. For example: 2-Hydroxypropanal Propanoic Acid or lactic acid is an optically active compound.
Stereoisomers which are mirror images of each other are known as enantiomers. Diastereomers are stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other. Meso compounds are those compounds which have chiral carbon but still they are optically inactive due to internal compensation. Racemic mixture is the one which has equal concentration of d & l form compounds and also racemic mixture are optically inactive.
According to the question, as we can see in image 1 the given compound have chirality and dissymmetry (have no centre of symmetry and no plane of symmetry) it is optically active and as given its optical rotation is \[ + 36^\circ \] which means it is the d form or Dextrorotatory. The compound given in image 2 is its meso form. The meso form is optically inactive.
Thus, the correct answer is zero optical rotation.
Note:
The prediction of optical behaviour of a compound is only done by experimental explanations. Compounds with only 1 chiral carbon are always optically active.
Complete step by step solution:
Optical isomers have the same physical and chemical properties but they differ in their behaviour towards plane polarized light. An optically active compound is the one which can rotate plane polarized light. Those which can rotate PPL (plane polarized light) towards right are known as dextrorotatory compounds (d form) and those which can rotate PPL towards left are known as laevorotatory (l form). The angles by which dextrorotatory compounds rotate PPL towards right are represented with + sign. On the other hand angle by which laevorotatory compounds rotate PPL towards left are represented by – sign. The compounds which fail to rotate PPL are known as optically inactive. Optically active compounds have dissymmetry, chirality and are non super imposable mirror images of each other. For example: 2-Hydroxypropanal Propanoic Acid or lactic acid is an optically active compound.
Stereoisomers which are mirror images of each other are known as enantiomers. Diastereomers are stereoisomers which are not mirror images of each other. Meso compounds are those compounds which have chiral carbon but still they are optically inactive due to internal compensation. Racemic mixture is the one which has equal concentration of d & l form compounds and also racemic mixture are optically inactive.
According to the question, as we can see in image 1 the given compound have chirality and dissymmetry (have no centre of symmetry and no plane of symmetry) it is optically active and as given its optical rotation is \[ + 36^\circ \] which means it is the d form or Dextrorotatory. The compound given in image 2 is its meso form. The meso form is optically inactive.
Thus, the correct answer is zero optical rotation.
Note:
The prediction of optical behaviour of a compound is only done by experimental explanations. Compounds with only 1 chiral carbon are always optically active.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




