
If the normal to the ellipse $3{{x}^{2}}+4{{y}^{2}}=12$ at a point P on it is parallel to the line $2x+y=4$ and the tangent to the ellipse at P passes through Q(4, 4) then PQ is equal to?
(a) $\dfrac{\sqrt{221}}{2}$
(b) $\dfrac{\sqrt{157}}{2}$
(c) $\dfrac{\sqrt{61}}{2}$
(d) $\dfrac{5\sqrt{5}}{2}$
Answer
586.2k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will draw the figure of the ellipse $3{{x}^{2}}+4{{y}^{2}}=12$ and draw a normal to the ellipse with the slope same that as of the given line, as we know that the slopes of parallel lines are equal. This normal will intersect the ellipse at point P. We will also draw a tangent at the same point P, which has point Q on it. We will find the relation between coordinates of P by finding the slope of the ellipse by differentiation and find an equation. We have the slope of the tangent and we have point Q on it. We will thus find the equation of tangent is slope-point form. Thus, to find the coordinates of P, we will solve these equations. Once we have coordinates of P, we can find the distance PQ with the help of distance formula.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The ellipse given to us is $3{{x}^{2}}+4{{y}^{2}}=12$ and the line given to us is $2x+y=4$. To find the slope of the normal at point P on the ellipse which is parallel to line $2x+y=4$, we need to find the slope of the line, as slopes of parallel lines are equal.
To find the slope of $2x+y=4$, we will write the equation in slope-intercept form $y=mx+c$, where m is the slope.
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+4$
Therefore, slope of the normal will be –2.
The slope of the tangent will satisfy the condition of slopes of perpendicular lines as normal and tangent are at right angles. The condition of slopes is given as ${{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}=-1$, where ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the two slopes.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{m}_{n}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{-1}{-2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Let P be any point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ on the ellipse.
Now, we will draw the figure of the ellipse and the tangent and normal at any point P$\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ with the slopes –2 and $\dfrac{1}{2}$ respectively.
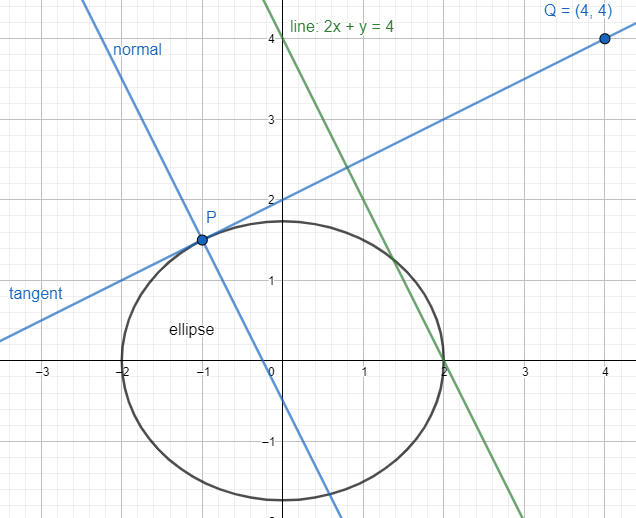
Now, to find a relation between ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$, we will differentiate the equation of the ellipse and equate it to zero to find the slope at any point P$\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d\left( 3{{x}^{2}}+4{{y}^{2}}-12 \right)}{dx}=\left[ 6{{x}_{1}}+8{{y}_{1}}\dfrac{dy}{dx} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow 6{{x}_{1}}+8{{y}_{1}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-6{{x}_{1}}}{8{{y}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}$
But we know that slope of tangent is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-3{{x}_{1}}}{4{{y}_{1}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{y}_{1}}=-3{{x}_{1}}......\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
We also know that the tangent passes through point Q(4, 4). Therefore, equation of tangent in slope-point form will be as follows:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( y-4 \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( x-4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2y-8=x-4 \\
& \Rightarrow x-2y+4=0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that P$\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ lies on this line.
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}-2{{y}_{1}}+4=0$
We will execute substitution from (1) to find ${{x}_{1}}$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}-\left( -3{{x}_{1}} \right)+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{x}_{1}}+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{y}_{1}}=-3\left( -1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, coordinates of P are $\left( -1,\dfrac{3}{2} \right)$ .
We will use distance formula $d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$ to find the distance between P and Q.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\sqrt{{{\left( 4-\left( -1 \right) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4-\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{5}^{2}}}{{{2}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\dfrac{\sqrt{4\left( {{5}^{2}} \right)+{{5}^{2}}}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\dfrac{5\sqrt{5}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option (d)”.
Note: This is a lengthy but simple problem which employs concepts of coordinate geometry and basics of differentiation. It is advisable to always draw the figure for better understanding of the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The ellipse given to us is $3{{x}^{2}}+4{{y}^{2}}=12$ and the line given to us is $2x+y=4$. To find the slope of the normal at point P on the ellipse which is parallel to line $2x+y=4$, we need to find the slope of the line, as slopes of parallel lines are equal.
To find the slope of $2x+y=4$, we will write the equation in slope-intercept form $y=mx+c$, where m is the slope.
$\Rightarrow y=-2x+4$
Therefore, slope of the normal will be –2.
The slope of the tangent will satisfy the condition of slopes of perpendicular lines as normal and tangent are at right angles. The condition of slopes is given as ${{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}=-1$, where ${{m}_{1}}$ and ${{m}_{2}}$ are the two slopes.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{m}_{n}}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{-1}{-2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{t}}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Let P be any point $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ on the ellipse.
Now, we will draw the figure of the ellipse and the tangent and normal at any point P$\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ with the slopes –2 and $\dfrac{1}{2}$ respectively.

Now, to find a relation between ${{x}_{1}}$ and ${{y}_{1}}$, we will differentiate the equation of the ellipse and equate it to zero to find the slope at any point P$\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{d\left( 3{{x}^{2}}+4{{y}^{2}}-12 \right)}{dx}=\left[ 6{{x}_{1}}+8{{y}_{1}}\dfrac{dy}{dx} \right] \\
& \Rightarrow 6{{x}_{1}}+8{{y}_{1}}\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-6{{x}_{1}}}{8{{y}_{1}}} \\
\end{align}$
But we know that slope of tangent is $\dfrac{1}{2}$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{-3{{x}_{1}}}{4{{y}_{1}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{y}_{1}}=-3{{x}_{1}}......\left( 1 \right) \\
\end{align}$
We also know that the tangent passes through point Q(4, 4). Therefore, equation of tangent in slope-point form will be as follows:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left( y-4 \right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\left( x-4 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2y-8=x-4 \\
& \Rightarrow x-2y+4=0 \\
\end{align}$
We know that P$\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ lies on this line.
$\Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}-2{{y}_{1}}+4=0$
We will execute substitution from (1) to find ${{x}_{1}}$.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}-\left( -3{{x}_{1}} \right)+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{x}_{1}}+4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}_{1}}=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{y}_{1}}=-3\left( -1 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}_{1}}=\dfrac{3}{2} \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, coordinates of P are $\left( -1,\dfrac{3}{2} \right)$ .
We will use distance formula $d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}} \right)}^{2}}}$ to find the distance between P and Q.
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\sqrt{{{\left( 4-\left( -1 \right) \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 4-\dfrac{3}{2} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\sqrt{{{5}^{2}}+\dfrac{{{5}^{2}}}{{{2}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\dfrac{\sqrt{4\left( {{5}^{2}} \right)+{{5}^{2}}}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow \overline{PQ}=\dfrac{5\sqrt{5}}{2} \\
\end{align}$
So, the correct answer is “Option (d)”.
Note: This is a lengthy but simple problem which employs concepts of coordinate geometry and basics of differentiation. It is advisable to always draw the figure for better understanding of the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




