
If the normal at \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\]on the curve \[xy={{c}^{2}}\] meets the curve again at \[{{t}^{'}}\] , then
A. \[{{t}^{'}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}^{3}}}\]
B. \[{{t}^{'}}=\dfrac{-1}{t}\]
C. \[{{t}^{'}}=\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{2}}}\]
D. \[{{({{t}^{'}})}^{2}}=\dfrac{-1}{{{t}^{2}}}\]
Answer
576.6k+ views
Complete step-by-step solution:
We are given a curve \[xy={{c}^{2}}\] and normal at point \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\] meets the curve again at \[(c{{t}^{'}},\dfrac{c}{{{t}^{'}}})\] . In the below, we have drawn a hyperbola \[xy={{c}^{2}}\] and also draw a tangent and normal at point \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\] meets the curve again at \[(c{{t}^{'}},\dfrac{c}{{{t}^{'}}})\].
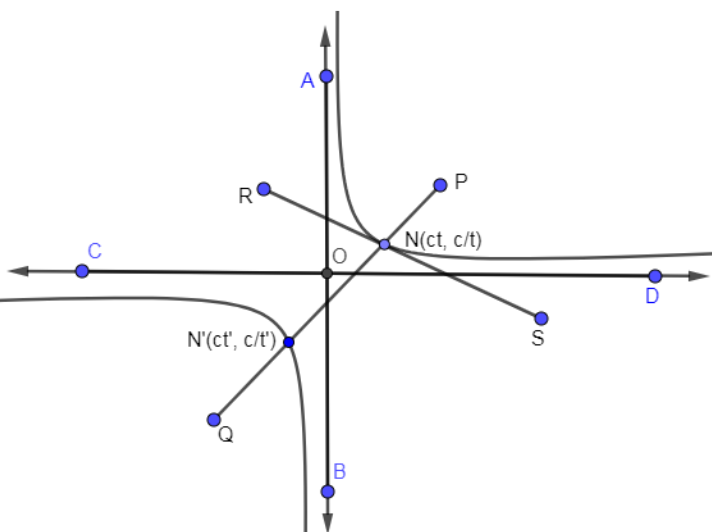
In the above diagram, RS is tangent at point N \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\] and PQ is the normal at point N \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\] which meets the hyperbola again at N’ \[(c{{t}^{'}},\dfrac{c}{{{t}^{'}}})\].
So, let's find the equation of normal, for that we first have to find the slope which is \[\dfrac{-dx}{dy}\]
So for that we will find \[\dfrac{dy}{dx}\] by differentiating \[xy={{c}^{2}}\] at point \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\]
On differentiating we get \[1y+x\dfrac{dy}{dx}=0\] which on solving gives
\[\dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{-y}{x}\]but we want value of\[\dfrac{-dx}{dy}\], which is equal to
\[\dfrac{-dx}{dy}=\dfrac{x}{y}\] , on putting value of point \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\]
\[\dfrac{-dx}{dy}=\dfrac{c{{t}^{2}}}{c}={{t}^{2}}\]
So, we have the point \[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\] passing through normal as well as slope of normal \[{{t}^{2}}\]
So, the equation of normal will be using property \[y-{{y}_{1}}=(x-{{x}_{1}})m\]
On putting \[x=ct,y=\dfrac{c}{t},m={{t}^{2}}\] , we get equation of normal as
\[y-\dfrac{c}{t}=(x-ct){{t}^{2}}\]
But it's given that it passes through point \[(c{{t}^{'}},\dfrac{c}{{{t}^{'}}})\] also
So, we will put this point in our equation
On putting \[x=c{{t}^{'}},y=\dfrac{c}{{{t}^{'}}}\] in equation \[y-\dfrac{c}{t}=(x-ct){{t}^{2}}\]
We get \[\dfrac{c}{{{t}^{'}}}-\dfrac{c}{t}=(c{{t}^{'}}-ct){{t}^{2}}\]
On solving gives \[\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{'}}}-\dfrac{1}{t}=({{t}^{'}}-t){{t}^{2}}\]
Which on further solving gives \[\dfrac{t-{{t}^{'}}}{t{{t}^{'}}}=({{t}^{'}}-t){{t}^{2}}\]
Cancelling \[({{t}^{'}}-t)\] we finally get \[{{t}^{'}}=-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{3}}}\]
Hence answer is \[{{t}^{'}}=-\dfrac{1}{{{t}^{3}}}\] option (A).
Note: Most of the students while in hurry take the slope of tangent and forgets to consider the slope of normal which results in the wrong answer. The equation of the tangent and normal at Point\[(ct,\dfrac{c}{t})\] of rectangular hyperbola by = c2 are \[x+y-{{t}^{2}}-2ct=0\]and \[x{{t}^{3}}-ty-c{{t}^{4}}+c=0\]respectively ,remember it directly
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




