
If the normal at (1, 2) on the parabola${{y}^{2}}=4x$meets the parabola again at the point$\left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right)$then t is equal to:
Answer
609.3k+ views
Hint: First of all find the slope of the normal at (1, 2) on the parabola. Now, we know the point (1, 2) and the slope of the normal. We can write the equation of a normal then find the intersection of the normal and parabola. You will find 2 solutions one is given (1, 2) and the other one is the answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the below diagram, a parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ is drawn along with the normal passing through point A (1, 2) and again meet the parabola at point $ B\left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ .
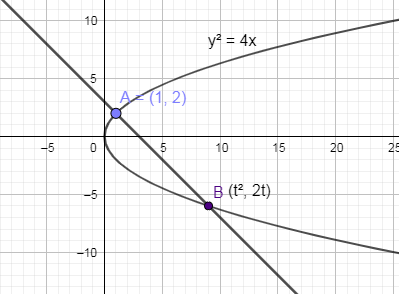
The slope of the tangent of parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ is derived as follows:
$ {{y}^{2}}=4x $
Taking derivative with respect to x on both the sides will get:
$ \begin{align}
& 2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=4 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{2}{y} \\
\end{align} $
Now, we know that tangent and normal are perpendicular to each other so let’s take the slope of a tangent as $ {{m}_{1}} $ and the slope of a normal as $ {{m}_{2}} $ so the relation between tangent and normal is given below:
$ {{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}=-1 $
So, the slope of the normal is $ -\dfrac{1}{{{m}_{1}}} $ .
The slope of normal is $ -\dfrac{y}{2} $ . Satisfying the point (1, 2) in the slope of normal then slope is equal to -1.
The equation of a normal at (1, 2) with a slope -1 is:
y – 2 = -1(x – 1)
$ \Rightarrow $ y – 2 = -x + 1
$ \Rightarrow $ x + y = 3
Solving the equation of a normal and parabola we get,
$ x+y=3 $ ………… Eq. (1)
$ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ ………… Eq. (2)
Substituting the value of x from eq. (2) in eq. (1) we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}+y=3 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+4y=12 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+6y-2y-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y\left( y+6 \right)-2\left( y+6 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y+6 \right)\left( y-2 \right)=0 \\
\end{align} $
Two solutions are getting y = 2, -6 from the above calculation. From the two solutions y = 2 is the point at which normal is drawn and y = -6 is the intersection of normal on parabola.
Substituting y = -6 in eq. (1) we get,
$ x=9 $
So, the intersection point of a normal on the parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ is (9, -6).
In question, the point of intersection is given in the form of $ \left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ . Comparing $ \left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ with (9, -6), the value of t= -3.
Hence, the value of t in $ \left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ is -3.
Note: We can verify the point of intersection is correct or not by satisfying the point (9, -6) in the equation of a parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ .
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the below diagram, a parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ is drawn along with the normal passing through point A (1, 2) and again meet the parabola at point $ B\left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ .

The slope of the tangent of parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ is derived as follows:
$ {{y}^{2}}=4x $
Taking derivative with respect to x on both the sides will get:
$ \begin{align}
& 2y\dfrac{dy}{dx}=4 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{dy}{dx}=\dfrac{2}{y} \\
\end{align} $
Now, we know that tangent and normal are perpendicular to each other so let’s take the slope of a tangent as $ {{m}_{1}} $ and the slope of a normal as $ {{m}_{2}} $ so the relation between tangent and normal is given below:
$ {{m}_{1}}{{m}_{2}}=-1 $
So, the slope of the normal is $ -\dfrac{1}{{{m}_{1}}} $ .
The slope of normal is $ -\dfrac{y}{2} $ . Satisfying the point (1, 2) in the slope of normal then slope is equal to -1.
The equation of a normal at (1, 2) with a slope -1 is:
y – 2 = -1(x – 1)
$ \Rightarrow $ y – 2 = -x + 1
$ \Rightarrow $ x + y = 3
Solving the equation of a normal and parabola we get,
$ x+y=3 $ ………… Eq. (1)
$ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ ………… Eq. (2)
Substituting the value of x from eq. (2) in eq. (1) we get,
$ \begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{y}^{2}}}{4}+y=3 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+4y=12 \\
& \Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}+6y-2y-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y\left( y+6 \right)-2\left( y+6 \right)=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( y+6 \right)\left( y-2 \right)=0 \\
\end{align} $
Two solutions are getting y = 2, -6 from the above calculation. From the two solutions y = 2 is the point at which normal is drawn and y = -6 is the intersection of normal on parabola.
Substituting y = -6 in eq. (1) we get,
$ x=9 $
So, the intersection point of a normal on the parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ is (9, -6).
In question, the point of intersection is given in the form of $ \left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ . Comparing $ \left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ with (9, -6), the value of t= -3.
Hence, the value of t in $ \left( {{t}^{2}},2t \right) $ is -3.
Note: We can verify the point of intersection is correct or not by satisfying the point (9, -6) in the equation of a parabola $ {{y}^{2}}=4x $ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




