
If the line $4x-3y-8=0$ cuts the parabola ${{x}^{2}}+y-4=0$ at A and B, and PA.PB is equal to $\dfrac{k}{8}$ (where P=(0,2)), then find the value of k.
Answer
599.4k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given the equation of a parabola and a straight line and are asked to find the distance of the points of intersection of the line and a fixed point P. Therefore, as the point of intersection of the line should lie on both the parabola and the line, we can simultaneously solve the equation of the line and the parabola and then find the distance from the points of intersection to the given point P(0, 2) using the formula for distance between two points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ $\left( d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}} \right)$ . We can then equate this value to $\dfrac{k}{8}$ and solve the resulting value of k to obtain the required answer.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The given equation of the parabola is ${{x}^{2}}+y-4=0......................................(1.1)$
And the equation of the straight line is
$\begin{align}
& 4x-3y-8=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3y=4x-8 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{4x-8}{3}............................(1.2) \\
\end{align}$
The parabola and the line are as shown in the following figure
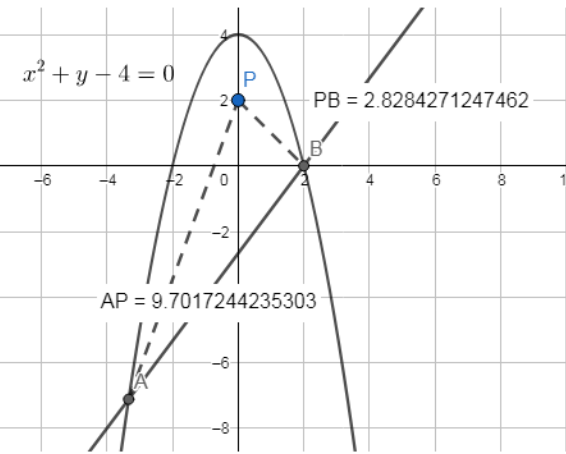
As the point of intersection should lie on both the straight line and the parabola, it should satisfy both equations for the line and the parabola. Thus, it should satisfy both (1.1) and (1.2). Therefore, putting the value of y from (1.2) in (1.1), we obtain
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+\dfrac{4x-8}{3}-4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+4x-8-3\times 4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+4x-20=0..................(1.3) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the formula for the solutions of a quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ is given by
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}....................(1.4)$
Therefore, using equation (1.4) in equation (1.3) with a=3, b=4 and c=-20, we obtain
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-4\times 3\times -20}}{2\times 3}=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{256}}{6}=\dfrac{-4\pm 16}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4-16}{6}=\dfrac{-10}{3}\text{ or }x=\dfrac{-4+16}{6}=\dfrac{+12}{6}=2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can use these values of x in (1.2) to find the corresponding values of y as
If $x=\dfrac{-10}{3}$ , then $y=\dfrac{4x-8}{3}=\dfrac{4\times \dfrac{-10}{3}-8}{3}=\dfrac{-64}{9}$
If $x=2$ , then $y=\dfrac{4x-8}{3}=\dfrac{4\times 2-8}{3}=\dfrac{8-8}{3}=0$
Therefore, the points of intersection are $A=\left( \dfrac{-10}{3},\dfrac{-64}{9} \right)$ and $B=\left( 2,0 \right)$ ………………………(1.5)
We know that the formula for finding the distance between 2 points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by$d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}..........................(1.6)$
Therefore, from (1.5) and (1.6), the distance between the point P(0,2) and A and B is given by
\[\begin{align}
& PA=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-10}{3}-0 \right)}^{2}}+\left( \dfrac{-64}{9}-2 \right)} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-10}{3} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{-82}{9} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{\left( \dfrac{100}{9} \right)+\left( \dfrac{6724}{81} \right)}=\sqrt{\dfrac{900+6724}{81}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{7624}{81}} \\
& =\dfrac{\sqrt{7624}}{9}...........................(1.7) \\
\end{align}\]
and
$\begin{align}
& PB=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{4+4} \\
& =2\sqrt{2}.....................(1.8) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, multiplying PA and PB, we obtain
$\begin{align}
& PA.PB=\sqrt{\dfrac{7624}{81}}\times 2\sqrt{2}=2\sqrt{\dfrac{7624\times 2}{81}} \\
& =2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{15248}}{9}......................(1.9) \\
\end{align}$
However, it is given that the $PA.PB=\dfrac{k}{8}$ , therefore equating it to (1.9), we obtain
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{k}{8}=\dfrac{2}{9}\times \sqrt{15248} \\
& \Rightarrow k=8\times \dfrac{2}{9}\times \sqrt{15248}\approx 219.52 \\
\end{align}$
Thus the required value of k is 219.52.
Note: We should note that in equation (1.5), we could have also chosen the points A and B as $A=\left( 2,0 \right)$ and $B=\left( \dfrac{-10}{3},\dfrac{-64}{9} \right)$ as we are just given that A and b are the points of intersection. However, the final answer would remain unchanged as the value of k depends on the product of PA and PB and the product (PA.PB) would remain the same if we interchange the points A and B.
Complete step-by-step solution -
The given equation of the parabola is ${{x}^{2}}+y-4=0......................................(1.1)$
And the equation of the straight line is
$\begin{align}
& 4x-3y-8=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3y=4x-8 \\
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{4x-8}{3}............................(1.2) \\
\end{align}$
The parabola and the line are as shown in the following figure

As the point of intersection should lie on both the straight line and the parabola, it should satisfy both equations for the line and the parabola. Thus, it should satisfy both (1.1) and (1.2). Therefore, putting the value of y from (1.2) in (1.1), we obtain
$\begin{align}
& {{x}^{2}}+\dfrac{4x-8}{3}-4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+4x-8-3\times 4=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3{{x}^{2}}+4x-20=0..................(1.3) \\
\end{align}$
Now, we know that the formula for the solutions of a quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ is given by
$x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}....................(1.4)$
Therefore, using equation (1.4) in equation (1.3) with a=3, b=4 and c=-20, we obtain
$\begin{align}
& x=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-4\times 3\times -20}}{2\times 3}=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{256}}{6}=\dfrac{-4\pm 16}{6} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{-4-16}{6}=\dfrac{-10}{3}\text{ or }x=\dfrac{-4+16}{6}=\dfrac{+12}{6}=2 \\
\end{align}$
Now, we can use these values of x in (1.2) to find the corresponding values of y as
If $x=\dfrac{-10}{3}$ , then $y=\dfrac{4x-8}{3}=\dfrac{4\times \dfrac{-10}{3}-8}{3}=\dfrac{-64}{9}$
If $x=2$ , then $y=\dfrac{4x-8}{3}=\dfrac{4\times 2-8}{3}=\dfrac{8-8}{3}=0$
Therefore, the points of intersection are $A=\left( \dfrac{-10}{3},\dfrac{-64}{9} \right)$ and $B=\left( 2,0 \right)$ ………………………(1.5)
We know that the formula for finding the distance between 2 points $\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)$ and $\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)$ is given by$d=\sqrt{{{\left( {{x}_{1}}-{{x}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( {{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}} \right)}^{2}}}..........................(1.6)$
Therefore, from (1.5) and (1.6), the distance between the point P(0,2) and A and B is given by
\[\begin{align}
& PA=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-10}{3}-0 \right)}^{2}}+\left( \dfrac{-64}{9}-2 \right)} \\
& =\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{-10}{3} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{-82}{9} \right)}^{2}}} \\
& =\sqrt{\left( \dfrac{100}{9} \right)+\left( \dfrac{6724}{81} \right)}=\sqrt{\dfrac{900+6724}{81}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{7624}{81}} \\
& =\dfrac{\sqrt{7624}}{9}...........................(1.7) \\
\end{align}\]
and
$\begin{align}
& PB=\sqrt{{{\left( 2-0 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 0-2 \right)}^{2}}}=\sqrt{4+4} \\
& =2\sqrt{2}.....................(1.8) \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, multiplying PA and PB, we obtain
$\begin{align}
& PA.PB=\sqrt{\dfrac{7624}{81}}\times 2\sqrt{2}=2\sqrt{\dfrac{7624\times 2}{81}} \\
& =2\times \dfrac{\sqrt{15248}}{9}......................(1.9) \\
\end{align}$
However, it is given that the $PA.PB=\dfrac{k}{8}$ , therefore equating it to (1.9), we obtain
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{k}{8}=\dfrac{2}{9}\times \sqrt{15248} \\
& \Rightarrow k=8\times \dfrac{2}{9}\times \sqrt{15248}\approx 219.52 \\
\end{align}$
Thus the required value of k is 219.52.
Note: We should note that in equation (1.5), we could have also chosen the points A and B as $A=\left( 2,0 \right)$ and $B=\left( \dfrac{-10}{3},\dfrac{-64}{9} \right)$ as we are just given that A and b are the points of intersection. However, the final answer would remain unchanged as the value of k depends on the product of PA and PB and the product (PA.PB) would remain the same if we interchange the points A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




