
If the length of the wire is doubled, the strain produced will be given as,
$\begin{align}
& A.0.5 \\
& B.1 \\
& C.0.25 \\
& D.2 \\
\end{align}$
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The longitudinal stress is given as the ratio of the change in the length of the wire to the original length of the wire. As it is mentioned like the wire and the length has been varied, the strain produced will be longitudinal strain itself. And the value will not be having any units as the strain is a dimensionless quantity. Hope this may help you to solve this question.
Formula used:
The longitudinal stress is given as,
$S=\dfrac{\Delta L}{{{L}_{old}}}$
Where $\Delta L$ be the change in length and ${{L}_{old}}$ be the original length of the wire.
Complete step by step answer:
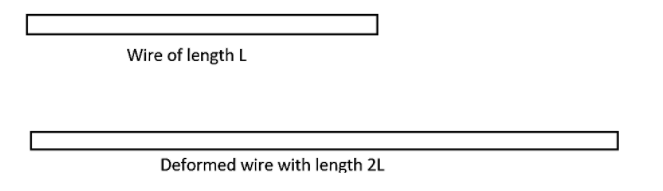
As we look into the question, we can see that the terms given in the questions can be written as,
The original length of the wire can be mentioned as $L$.
${{L}_{old}}=L$
And now this length has been changed to double of its value which means that the length now becomes,
${{L}_{new}}=2L$
Therefore the change in length can be taken as the difference between these two lengths. That is we can write that,
$\Delta L={{L}_{new}}-{{L}_{old}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\Delta L=2L-L=L$
Now we have to find the longitudinal strain acting on the wire. It is given as the ratio of the change in length of the wire to the actual or the original length of the wire. This can be expressed in the form of an equation given as,
$S=\dfrac{\Delta L}{{{L}_{old}}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$S=\dfrac{L}{L}=1$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Stress is defined as the force acting on a surface per unit area. Stress can be the reason for the strain, when it is having the force to overcome the strength of the surface that is under stress. Strain is a variation in shape or size due to the applied forces.
Formula used:
The longitudinal stress is given as,
$S=\dfrac{\Delta L}{{{L}_{old}}}$
Where $\Delta L$ be the change in length and ${{L}_{old}}$ be the original length of the wire.
Complete step by step answer:

As we look into the question, we can see that the terms given in the questions can be written as,
The original length of the wire can be mentioned as $L$.
${{L}_{old}}=L$
And now this length has been changed to double of its value which means that the length now becomes,
${{L}_{new}}=2L$
Therefore the change in length can be taken as the difference between these two lengths. That is we can write that,
$\Delta L={{L}_{new}}-{{L}_{old}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$\Delta L=2L-L=L$
Now we have to find the longitudinal strain acting on the wire. It is given as the ratio of the change in length of the wire to the actual or the original length of the wire. This can be expressed in the form of an equation given as,
$S=\dfrac{\Delta L}{{{L}_{old}}}$
Substituting the values in it will give,
$S=\dfrac{L}{L}=1$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Stress is defined as the force acting on a surface per unit area. Stress can be the reason for the strain, when it is having the force to overcome the strength of the surface that is under stress. Strain is a variation in shape or size due to the applied forces.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




