
If the length of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the line whose intercepts on the axes are a and b be p, then
1) ${a^2} + {b^2} = \dfrac{1}{{{p^2}}}$
2) ${a^2} + {b^2} = {p^2}$
3) $\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{b^2}}} = \dfrac{2}{{{p^2}}}$
4)$\dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{b^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{p^2}}}$
Answer
516.3k+ views
Hint: We can start by writing the equation of a line intercepts. It is given that the length of the perpendiculars are a, b and p. So, we can substitute these in the length of the perpendicular equation. By doing so, we can determine the relationship between a, b and p.
The basic formula used in the problem are:
$\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1$
Where $a$is used to represent $x$intercept and $b$is to represent $y$intercept.
$d = \left| {\dfrac{c}{{\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)}}} \right|$
Complete step-by-step solution:
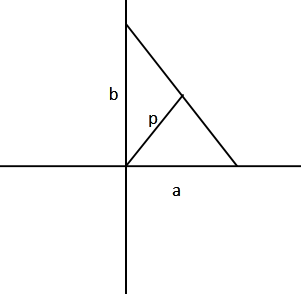
Let us consider the line in the form, $ax + by + c = 0$
The equation of a line in the intercept form is
$\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1$
Rearranging this equation,
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} - 1 = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow bx + ay - ab = 0 \cr} $
We know that the length of the perpendicular from the origin $\left( {0,0} \right)$to the given line $ax + by + c = 0$is given by, $d = \left| {\dfrac{c}{{\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)}}} \right|$
It is given that the perpendicular from origin to the given line is p.
$ \Rightarrow p = \left| {\dfrac{{ab}}{{\sqrt {\left( {{b^2} + {a^2}} \right)} }}} \right|$
Squaring on both sides, we get,
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {p^2} = \dfrac{{{a^2}{b^2}}}{{\left( {{b^2} + {a^2}} \right)}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{b^2}}} \cr} $
The final answer is $\dfrac{1}{{{p^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{b^2}}}$
Hence, the correct option is (4).
Additional Information:
On a graph, the point where the line crosses both the x-axis and the y-axis is called an intercept. The point of intersection of the line with the x-axis gives the x-intercept. The point of intersection of the line with the y-axis gives the y-intercept.
Note: The intercept equation and the perpendicular drawn to the line are two different equations. The equation for line and the equation for its intercept are similar, be careful while using them. Since the points are already given, substitute them for the known equations.
The basic formula used in the problem are:
$\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1$
Where $a$is used to represent $x$intercept and $b$is to represent $y$intercept.
$d = \left| {\dfrac{c}{{\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)}}} \right|$
Complete step-by-step solution:

Let us consider the line in the form, $ax + by + c = 0$
The equation of a line in the intercept form is
$\dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1$
Rearranging this equation,
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} - 1 = 0 \cr
& \Rightarrow bx + ay - ab = 0 \cr} $
We know that the length of the perpendicular from the origin $\left( {0,0} \right)$to the given line $ax + by + c = 0$is given by, $d = \left| {\dfrac{c}{{\left( {{a^2} + {b^2}} \right)}}} \right|$
It is given that the perpendicular from origin to the given line is p.
$ \Rightarrow p = \left| {\dfrac{{ab}}{{\sqrt {\left( {{b^2} + {a^2}} \right)} }}} \right|$
Squaring on both sides, we get,
$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {p^2} = \dfrac{{{a^2}{b^2}}}{{\left( {{b^2} + {a^2}} \right)}} \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{b^2}}} \cr} $
The final answer is $\dfrac{1}{{{p^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{1}{{{b^2}}}$
Hence, the correct option is (4).
Additional Information:
On a graph, the point where the line crosses both the x-axis and the y-axis is called an intercept. The point of intersection of the line with the x-axis gives the x-intercept. The point of intersection of the line with the y-axis gives the y-intercept.
Note: The intercept equation and the perpendicular drawn to the line are two different equations. The equation for line and the equation for its intercept are similar, be careful while using them. Since the points are already given, substitute them for the known equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




