
If the function $f\left( x \right)=\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right],x\in R$ where $\left[ x \right]$ denotes the greatest integer function, then:
A. Both $\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$ and $\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$ exist but are not equal
B. $\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$ exist but $\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$ doesn’t exist
C. $\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$ exist but $\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)$ doesn’t exist
D. f is continuous at $x=4$
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we should know the definition of greatest integer function. The greatest integer function $\left[ x \right]$ is defined as the greatest integer value which is $\le x$. Mathematically, $\left[ x \right]\le x$. Here when we are approaching from ${{4}^{-}}$, $3 < x < 4\Rightarrow 0<\dfrac{x}{4} < 1$. $\left[ x \right]$ is equal to 3 as 3 is the greatest integer less than x. $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=0$ as 0 is the greatest integer less than $\dfrac{x}{4}$. We can do a similar analysis for the right limit and the functional value to check which option is correct.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The greatest integer function $\left[ x \right]$ is defined as the greatest integer value which is $\le x$.
Mathematically, we can write it as $\left[ x \right]\le x$.
We are given the function $f\left( x \right)=\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right],x\in R$ and we are asked about the left and right limit at $x=4$ and eventually, the continuity of the function at $x=4$.
Let us consider $\left[ x \right]$ at $x=4$.
When $x=4$, as x is an integer, $\left[ x \right]=x=4$
When $x<4$, let us take an example of $x=3.99$. The greatest integer less than x is 3. So, $\left[ x \right]=\left[ {{4}^{-}} \right]=3\text{ }\forall x$ is valid within the range $x\approx {{4}^{-}}$
When $x>4$, let us take an example of $x=4.01$. The greatest integer less than x is 4. So, $\left[ x \right]=\left[ {{4}^{+}} \right]\text{=4 }\forall x$ is valid within the range \[x\approx {{4}^{+}}\]
Let us consider $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$ at $x=4$.
When $x=4\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}=1$, as $\dfrac{x}{4}$ is an integer, $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\left[ 1 \right]=1$
When $x<4\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}<1$, let us take an example of $x=3.99\Rightarrow \dfrac{3.99}{4}<1\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}\approx {{1}^{-}}$. The greatest integer less than x is 0. So, $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\left[ {{1}^{-}} \right]=0\text{ }\forall x$ is valid within the range $x\approx {{4}^{-}}$
When $x>4$, let us take an example of $x=4.01\Rightarrow \dfrac{4.01}{4}>1\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}\approx {{1}^{+}}$. The greatest integer less than x is 1. So, $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\left[ {{1}^{+}} \right]=1\text{ }\forall x$ is valid within the range \[x\approx {{4}^{+}}\]
Using the above values of $\left[ x \right]$ and $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$, we can evaluate the left limit, right limit aand the functional value of $f\left( x \right)$ at $x=4$.
Left limit = $\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$
From the above relations, we can write that
$\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,3-0=3$
Left limit = 3
Right limit = $\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$
From the above relations, we can write that
$\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,4-1=3$
Right limit = 3
Functional value at x = 4
$f\left( 4 \right)=\left[ 4 \right]-\left[ \dfrac{4}{4} \right]=\left[ 4 \right]-\left[ 1 \right]=3$
We got the result as Left limit = Right limit = Functional value.
So, the function is continuous at x = 4.
$\therefore $ The answer is option-D.
Note: Some students make a mistake while evaluating the value of $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$ at ${{4}^{-}}$. They think that at ${{4}^{-}}$ also the value $\dfrac{x}{4}$ is equal to 1 and they get the left limit as 2. When we are evaluating the greatest integer function, we should be careful about the range in which we are applying the relation. The below graph gives a graphical view of the function f(x) used in the question. A graphical approach is also useful to solve these type of questions
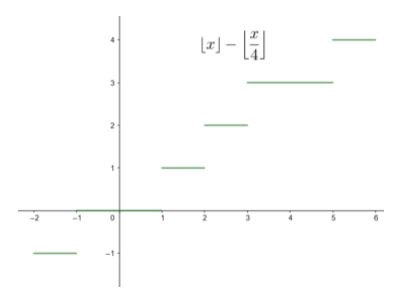
We can see that the function is discontinuous at the integers which are not multiples of 4. The function is continuous elsewhere.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The greatest integer function $\left[ x \right]$ is defined as the greatest integer value which is $\le x$.
Mathematically, we can write it as $\left[ x \right]\le x$.
We are given the function $f\left( x \right)=\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right],x\in R$ and we are asked about the left and right limit at $x=4$ and eventually, the continuity of the function at $x=4$.
Let us consider $\left[ x \right]$ at $x=4$.
When $x=4$, as x is an integer, $\left[ x \right]=x=4$
When $x<4$, let us take an example of $x=3.99$. The greatest integer less than x is 3. So, $\left[ x \right]=\left[ {{4}^{-}} \right]=3\text{ }\forall x$ is valid within the range $x\approx {{4}^{-}}$
When $x>4$, let us take an example of $x=4.01$. The greatest integer less than x is 4. So, $\left[ x \right]=\left[ {{4}^{+}} \right]\text{=4 }\forall x$ is valid within the range \[x\approx {{4}^{+}}\]
Let us consider $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$ at $x=4$.
When $x=4\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}=1$, as $\dfrac{x}{4}$ is an integer, $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\left[ 1 \right]=1$
When $x<4\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}<1$, let us take an example of $x=3.99\Rightarrow \dfrac{3.99}{4}<1\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}\approx {{1}^{-}}$. The greatest integer less than x is 0. So, $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\left[ {{1}^{-}} \right]=0\text{ }\forall x$ is valid within the range $x\approx {{4}^{-}}$
When $x>4$, let us take an example of $x=4.01\Rightarrow \dfrac{4.01}{4}>1\Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{4}\approx {{1}^{+}}$. The greatest integer less than x is 1. So, $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\left[ {{1}^{+}} \right]=1\text{ }\forall x$ is valid within the range \[x\approx {{4}^{+}}\]
Using the above values of $\left[ x \right]$ and $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$, we can evaluate the left limit, right limit aand the functional value of $f\left( x \right)$ at $x=4$.
Left limit = $\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$
From the above relations, we can write that
$\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\underset{x\to {{4}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,3-0=3$
Left limit = 3
Right limit = $\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,f\left( x \right)=\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$
From the above relations, we can write that
$\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left[ x \right]-\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]=\underset{x\to {{4}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,4-1=3$
Right limit = 3
Functional value at x = 4
$f\left( 4 \right)=\left[ 4 \right]-\left[ \dfrac{4}{4} \right]=\left[ 4 \right]-\left[ 1 \right]=3$
We got the result as Left limit = Right limit = Functional value.
So, the function is continuous at x = 4.
$\therefore $ The answer is option-D.
Note: Some students make a mistake while evaluating the value of $\left[ \dfrac{x}{4} \right]$ at ${{4}^{-}}$. They think that at ${{4}^{-}}$ also the value $\dfrac{x}{4}$ is equal to 1 and they get the left limit as 2. When we are evaluating the greatest integer function, we should be careful about the range in which we are applying the relation. The below graph gives a graphical view of the function f(x) used in the question. A graphical approach is also useful to solve these type of questions

We can see that the function is discontinuous at the integers which are not multiples of 4. The function is continuous elsewhere.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




