
If the formula for the sine of a sum of angles C and D is given by
$\sin (C+D)=\sin C.\cos D+\cos C.\sin D$, then the value of $\sin {{75}^{\circ }}$ is?
a)$\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{2}}\left( \sqrt{3}+1 \right)$
b) $\dfrac{1}{2}\left( \sqrt{3}-1 \right)$
c) $\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$
d)$\dfrac{1}{2}$
Answer
620.1k+ views
Hint: We should try to write ${{75}^{\circ }}$as a sum of angles whose sine and cosine values are known. Then, we can use the formula given in the question to find $\sin {{75}^{\circ }}$ in terms of the sine and cosine values of the other two angles.
Complete Complete step by step answer:
We can write ${{75}^{\circ }}$ as the sum of ${{45}^{\circ }}\text{ and 3}{{0}^{\circ }}$, i.e.
${{75}^{\circ }}={{45}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }}$
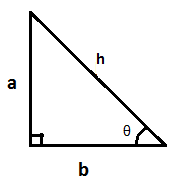
Now, from the definition of sine cosine function, we know that, in a right angled triangle having sides a and b and hypotenuse h as shown in figure 1,
$\sin (\theta )=\dfrac{\text{length of side facing the angle theta}}{\text{length of the hypotanuse}}=\dfrac{a}{h}$
and $\cos (\theta )=\dfrac{\text{length of side adjacent to the angle theta}}{\text{length of the hypotanuse}}=\dfrac{b}{h}$
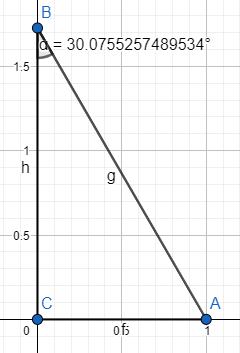
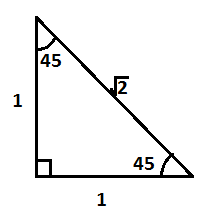
To find the sine and cosine of ${{45}^{\circ }}\text{ and 3}{{0}^{\circ }}$, we can draw the triangles shown in figure 2 and figure 3.
So, $\sin ({{30}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ and }\cos ({{30}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ (from fig2)
And $\sin ({{45}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\text{ and }\cos ({{45}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ (from fig3)
Now, using the formula given in the question and using the values as derived above,
$\begin{align}
& \sin (75{}^\circ )=\sin (45{}^\circ +30{}^\circ )=\sin (45{}^\circ )\cos (30{}^\circ )+\sin (30{}^\circ )\cos (45{}^\circ ) \\
& =\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}.\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)+\left( \dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
This answer matches option (a) of the question and thus option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: While finding the sines and cosines of various angles, we should try to write them in terms of ${{30}^{\circ }}$, ${{60}^{\circ }}$ and ${{45}^{\circ }}$ as their trigonometric ratios can be easily found out from figures 1 and 2.
In many cases, the angles have a value more than ${{360}^{\circ }}$. In that case, we can subtract a multiple of ${{360}^{\circ }}$ from the original angle and find the sine and cosine of it as adding or subtracting ${{360}^{\circ }}$ does not change the value of sine or cosine.
Complete Complete step by step answer:



We can write ${{75}^{\circ }}$ as the sum of ${{45}^{\circ }}\text{ and 3}{{0}^{\circ }}$, i.e.
${{75}^{\circ }}={{45}^{\circ }}+{{30}^{\circ }}$
Now, from the definition of sine cosine function, we know that, in a right angled triangle having sides a and b and hypotenuse h as shown in figure 1,
$\sin (\theta )=\dfrac{\text{length of side facing the angle theta}}{\text{length of the hypotanuse}}=\dfrac{a}{h}$
and $\cos (\theta )=\dfrac{\text{length of side adjacent to the angle theta}}{\text{length of the hypotanuse}}=\dfrac{b}{h}$
To find the sine and cosine of ${{45}^{\circ }}\text{ and 3}{{0}^{\circ }}$, we can draw the triangles shown in figure 2 and figure 3.
So, $\sin ({{30}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ and }\cos ({{30}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}$ (from fig2)
And $\sin ({{45}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\text{ and }\cos ({{45}^{\circ }})=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$ (from fig3)
Now, using the formula given in the question and using the values as derived above,
$\begin{align}
& \sin (75{}^\circ )=\sin (45{}^\circ +30{}^\circ )=\sin (45{}^\circ )\cos (30{}^\circ )+\sin (30{}^\circ )\cos (45{}^\circ ) \\
& =\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}.\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \right)+\left( \dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2\sqrt{2}} \\
\end{align}$
This answer matches option (a) of the question and thus option (a) is the correct answer.
Note: While finding the sines and cosines of various angles, we should try to write them in terms of ${{30}^{\circ }}$, ${{60}^{\circ }}$ and ${{45}^{\circ }}$ as their trigonometric ratios can be easily found out from figures 1 and 2.
In many cases, the angles have a value more than ${{360}^{\circ }}$. In that case, we can subtract a multiple of ${{360}^{\circ }}$ from the original angle and find the sine and cosine of it as adding or subtracting ${{360}^{\circ }}$ does not change the value of sine or cosine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A large number of liquid drops each of radius r coalesce class 11 physics CBSE

The period of a conical pendulum in terms of its length class 11 physics CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

In a fight of 600km an aircraft was slowed down du-class-11-maths-CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

A solution of a substance X is used for white washing class 11 chemistry CBSE




