
If the diagonal of the cube is $10\sqrt 3 $cm, find its surface area.
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: The above question wants the information of the surface area of the cube and the surface area of the cube is $6{a^2}$, where a is the side of the cube. So, we need to determine the relation of the diagonal of the cube with the side of the cube, so that we can determine the side and it will be easy to calculate the surface area of the cube.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given information is given below
\[
Side{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}cube{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}a{\text{ }}cm \\
Diagonal{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}cube{\text{ }} = 10\sqrt 3 cm \\
\]
The figure of the cube is given below
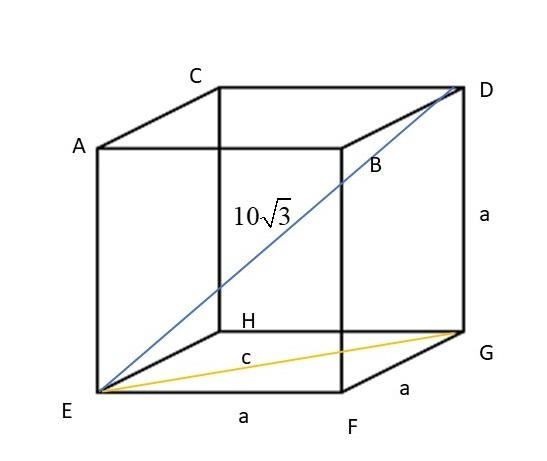
The above figure represents a cube, where the blue line represents the diagonal and the side of the cube is a. Now,
EFG is the right-angle triangle and let the value of EG be $c$, EF and FG is $a$
Now, by this we can get the relation of $c$ with $a$ which will be beneficial to determine the value of the surface area of the cube, since in a cube all sides are equal so that means all the sides of the cube will have the value $a$.
If we apply the Pythagoras’s theorem in the triangle EFG
$
{(EG)^2} = {(EF)^2} + {(FG)^2} \\
\\
$
Substituting the value of $EG = c,EF = FG = a$ in the above equation, we get
$
{c^2} = {a^2} + {a^2} \\
\\
$
On simplifying the above relation, we get
$c = \sqrt 2 a$
After getting the relation between $c$and $a$, we can move forward to determine the side of the cube so that we can determine the surface area of the cube.
Now, applying the Pythagoras theorem for triangle EDG
\[\]\[{(ED)^2} = {(EG)^2} + {(GD)^2}\]
Now, substituting the given values in the above equation
\[ED = 10\sqrt 3 ,EG = c,GD = a\]
We get
$(10{\sqrt {3)} ^2} = {c^2} + {a^2}$
Hence, from the above relation of $c$and $a$, we get
$
(10{\sqrt {3)} ^2} = {(\sqrt 2 a)^2} + {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(10\sqrt 3 )^2} = 2{a^2} + {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(10\sqrt 3 )^2} = 3{a^2} \\
\Rightarrow 10\sqrt 3 = \sqrt 3 a \\
\Rightarrow a = 10 \\
$
Now, after determining the side of the triangle we can easily determine the surface area of the cube
Surface area = $6{a^{^2}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Surface area = $6{(10)^{^2}}$ = 6(100) = 600
So, the surface area is $600c{m^2}$and the side of the cube is $10cm$
Note: The side of the square has a relation with the diagonal of the cube by the help of the diagonal we can determine the side of the cube that can be used to determine the surface area of the cube.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The given information is given below
\[
Side{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}cube{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}a{\text{ }}cm \\
Diagonal{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}the{\text{ }}cube{\text{ }} = 10\sqrt 3 cm \\
\]
The figure of the cube is given below

The above figure represents a cube, where the blue line represents the diagonal and the side of the cube is a. Now,
EFG is the right-angle triangle and let the value of EG be $c$, EF and FG is $a$
Now, by this we can get the relation of $c$ with $a$ which will be beneficial to determine the value of the surface area of the cube, since in a cube all sides are equal so that means all the sides of the cube will have the value $a$.
If we apply the Pythagoras’s theorem in the triangle EFG
$
{(EG)^2} = {(EF)^2} + {(FG)^2} \\
\\
$
Substituting the value of $EG = c,EF = FG = a$ in the above equation, we get
$
{c^2} = {a^2} + {a^2} \\
\\
$
On simplifying the above relation, we get
$c = \sqrt 2 a$
After getting the relation between $c$and $a$, we can move forward to determine the side of the cube so that we can determine the surface area of the cube.
Now, applying the Pythagoras theorem for triangle EDG
\[\]\[{(ED)^2} = {(EG)^2} + {(GD)^2}\]
Now, substituting the given values in the above equation
\[ED = 10\sqrt 3 ,EG = c,GD = a\]
We get
$(10{\sqrt {3)} ^2} = {c^2} + {a^2}$
Hence, from the above relation of $c$and $a$, we get
$
(10{\sqrt {3)} ^2} = {(\sqrt 2 a)^2} + {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(10\sqrt 3 )^2} = 2{a^2} + {a^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(10\sqrt 3 )^2} = 3{a^2} \\
\Rightarrow 10\sqrt 3 = \sqrt 3 a \\
\Rightarrow a = 10 \\
$
Now, after determining the side of the triangle we can easily determine the surface area of the cube
Surface area = $6{a^{^2}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Surface area = $6{(10)^{^2}}$ = 6(100) = 600
So, the surface area is $600c{m^2}$and the side of the cube is $10cm$
Note: The side of the square has a relation with the diagonal of the cube by the help of the diagonal we can determine the side of the cube that can be used to determine the surface area of the cube.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




