
If the conduction-electron density in copper wire is $n$, the area of cross-section of wire is $A$ and the average drift speed of electron ${{V}_{d}}$, then the resultant number of electrons crossing a cross-section of the wire in a unit time interval $t$ will be given as,
$\begin{align}
& A.n{{V}_{d}}At \\
& B.ne{{V}_{d}}At \\
& C.ne{{V}_{d}}A \\
& D.n{{V}_{d}}A \\
\end{align}$
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: The distance travelled by the electrons can be calculated by taking the product of the drift velocity and time taken. The volume of this cylinder will be the product of the area of cross section and the distance travelled by the electron. The net number of electrons crossing the area of cross section wire will be the product of the conduction electron density and the volume of the cylinder. These all may help you to solve this question.
Complete answer:
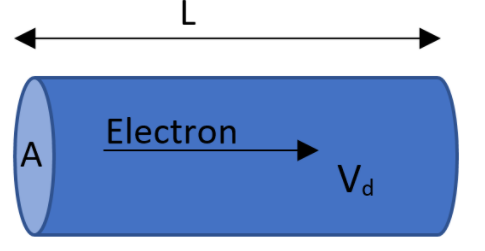
Let the length of the elementary cylindrical wire can be taken as $L$. The distance covered by the electrons in a time $t$can be written as,
$L={{V}_{d}}t$
Volume of this cylinder can be found as,
$V=AL$
Where $A$be the area of cross section. Substituting the values in it will give,
$V=A{{V}_{d}}t$
Therefore the resultant number of electrons crossing the wire can be written as,
$N=nV$
Where $n$be the conduction electron density in the copper wire. Substituting the volume in it will give,
$N=n{{V}_{d}}At$
Therefore the answer has been obtained.
The answer is given as option A.
Note:
Subatomic particles such as electrons can move in different directions all the time. If electrons are provided with an electric field, then they do move randomly, and gradually they drift into one direction, in the direction of the electric field applied. The resultant velocity at which these electrons are drifting in one direction is called drift velocity. This drift velocity of an electron for a unit electric field is called the mobility of the electron.
Complete answer:
Let the length of the elementary cylindrical wire can be taken as $L$. The distance covered by the electrons in a time $t$can be written as,
$L={{V}_{d}}t$
Volume of this cylinder can be found as,
$V=AL$
Where $A$be the area of cross section. Substituting the values in it will give,
$V=A{{V}_{d}}t$
Therefore the resultant number of electrons crossing the wire can be written as,
$N=nV$
Where $n$be the conduction electron density in the copper wire. Substituting the volume in it will give,
$N=n{{V}_{d}}At$
Therefore the answer has been obtained.
The answer is given as option A.

Note:
Subatomic particles such as electrons can move in different directions all the time. If electrons are provided with an electric field, then they do move randomly, and gradually they drift into one direction, in the direction of the electric field applied. The resultant velocity at which these electrons are drifting in one direction is called drift velocity. This drift velocity of an electron for a unit electric field is called the mobility of the electron.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




