
If the bisectors of angles of ∠ ABC and ∠ ACB of a triangle ABC meet at point O, then prove that ∠ BOC $ = {90^o} + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A$.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: A bisector is described that cuts an object into two equal parts. It is used to line segments and angles. The bisectors of an angles means a line that splits an angle into two equal angles. To find the value of ∠ BOC, firstly we have to draw an angle bisector of∠ B and ∠ C.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Angle bisector is a line which divides any angle into two parts. After drawing an angle bisector, we have to use the angle property of a triangle.
Angle sum property of a triangle is the sum of internal angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degree. This is called the angle sum property of triangles. Using angle sum property, we find ∠ B +∠ C and with the help of this, we calculate ∠ BOC.
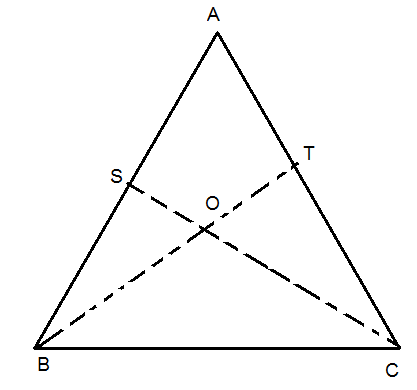
To prove ∠ BOC =$ = {90^o} + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A$
Construction :- Firstly we draw angle bisector from B and C. let BT and CS be the angle bisector of ∠ B and ∠ C. let BT and CS meet at O. Now, by angle sum property of the triangle .
Sum of internal angles of triangle =180degree
Therefore, sum of internal angles of $\vartriangle ABC = {180^o}$
∴ ∠ A+∠ B+∠ C =${180^o}$
Taking ∠ A to the right hand side, we get
$\angle B + \angle C = {180^o} + \angle A...............(i)$
We take it as equation (i)
Now BT and CS form a triangle BOC. Since BT and CS are angle bisector of ∠ B and ∠ C respectively.
Therefore ∠ OBC is equal to half of angle ∠ B and ∠ OCB is equal to half of ∠ C.
∴ \[
\angle OBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle B \\
\Rightarrow \angle OCB = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle C \\
].....................(ii)\]
Again we use angle sum property in Δ BOC.
Sum of the internal angles of $\vartriangle BOC = {180^o}$
That is $\angle OBC + \angle OCB + \angle BOC = {180^o}................(iii)$
We use value of equation (ii) in (iii), we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\angle B + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle C + \angle BOC = {180^o} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}[\angle B + \angle C] + \angle BOC = {180^o}..................(iv) \\
$
Using the value of equation (i) in equation (iv)
$\dfrac{1}{2}[{180^o} - \angle A] + \angle BOC = {180^o}$
$
\dfrac{1}{2}\angle {180^o} - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {180^o} \\
\Rightarrow {90^o} - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {180^o} \\
\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {(180 - 90)^o} \\
\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {90^o} \\
\Rightarrow \angle BOC = {90^o} + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A \\
$
Hence, the result is proved.
Note: A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes of geometry. There are some properties of triangle:
→ a triangle has three sides’ three vertices and three angles.
→The sum of interior angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degree.
→ Length of two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
→Area of the triangle is equal to half the product of base and height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Angle bisector is a line which divides any angle into two parts. After drawing an angle bisector, we have to use the angle property of a triangle.
Angle sum property of a triangle is the sum of internal angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degree. This is called the angle sum property of triangles. Using angle sum property, we find ∠ B +∠ C and with the help of this, we calculate ∠ BOC.

To prove ∠ BOC =$ = {90^o} + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A$
Construction :- Firstly we draw angle bisector from B and C. let BT and CS be the angle bisector of ∠ B and ∠ C. let BT and CS meet at O. Now, by angle sum property of the triangle .
Sum of internal angles of triangle =180degree
Therefore, sum of internal angles of $\vartriangle ABC = {180^o}$
∴ ∠ A+∠ B+∠ C =${180^o}$
Taking ∠ A to the right hand side, we get
$\angle B + \angle C = {180^o} + \angle A...............(i)$
We take it as equation (i)
Now BT and CS form a triangle BOC. Since BT and CS are angle bisector of ∠ B and ∠ C respectively.
Therefore ∠ OBC is equal to half of angle ∠ B and ∠ OCB is equal to half of ∠ C.
∴ \[
\angle OBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle B \\
\Rightarrow \angle OCB = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle C \\
].....................(ii)\]
Again we use angle sum property in Δ BOC.
Sum of the internal angles of $\vartriangle BOC = {180^o}$
That is $\angle OBC + \angle OCB + \angle BOC = {180^o}................(iii)$
We use value of equation (ii) in (iii), we get
$
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}\angle B + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle C + \angle BOC = {180^o} \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}[\angle B + \angle C] + \angle BOC = {180^o}..................(iv) \\
$
Using the value of equation (i) in equation (iv)
$\dfrac{1}{2}[{180^o} - \angle A] + \angle BOC = {180^o}$
$
\dfrac{1}{2}\angle {180^o} - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {180^o} \\
\Rightarrow {90^o} - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {180^o} \\
\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {(180 - 90)^o} \\
\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A + \angle BOC = {90^o} \\
\Rightarrow \angle BOC = {90^o} + \dfrac{1}{2}\angle A \\
$
Hence, the result is proved.
Note: A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes of geometry. There are some properties of triangle:
→ a triangle has three sides’ three vertices and three angles.
→The sum of interior angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degree.
→ Length of two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
→Area of the triangle is equal to half the product of base and height.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




