
If the arms of one angle are respectively parallel to the arms of another angle, then the two angles are
A. neither equal nor supplementary
B. not equal but supplementary
C. equal but not supplementary
D. both equal and supplementary
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: To solve this problem, we should construct a diagram of the given situation and apply the properties of the angles between parallel lines and transversals. Using the alternate angle property which states that the angles corresponding to the transversal between two parallel lines are equal and the supplementary property which states that the inward angles are always supplementary, we can find the relation between the angles. In our case, two configurations are possible and we have checked both of them.
Complete step-by-step answer:
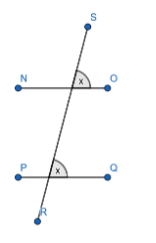
In our question, 2 configurations are possible. They are
Let us consider the configuration-1,
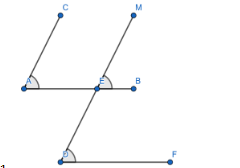
According to the question let us consider the lines AC is parallel to DM and AB is parallel to DF. We have to compare the angles, $ \angle CAB $ and $ \angle MDF $ .
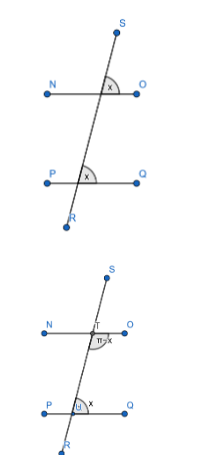
In the figure, NO is parallel to PQ, the angle between the lines SR and NO is equal to the angle between the lines SR and PQ. This is called the corresponding angles property.
Using this property, from configuration-1 , we can write
AB is parallel to DF and MD acts as the transversal. So
$ \angle MEB=\angle MDF $
Similarly, the lines AC and MD are parallel to each other. So
$ \angle CAB=\angle MEB $
Using these two relations, we can write
\[\angle MDF=\angle MEB=\angle CAB\]
So we can conclude that the two required angles $ \angle CAB $ and $ \angle MDF $ are equal.
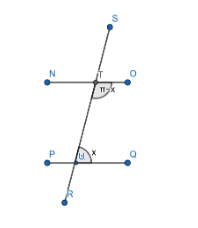
In the figure, NO is parallel to PQ, we can infer from the diagram that
$ \angle OTR+\angle SUQ=\pi $
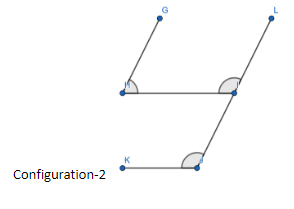
For configuration-2, according to the question let us consider the lines AC is parallel to DM and AB is parallel to DF. We have to compare the angles, $ \angle IJK $ and $ \angle GHI $ .
For configuration-2 using the above property, we can write
GH is parallel to LI and GI is the transversal , so
$ \angle GHI+\angle LIH=\pi \to \left( 1 \right) $
From the corresponding angles property, we know that
$ \angle LIH=\angle IJK $ .
Using this result in equation-1 we get
$ \angle GHI+\angle IJK=\pi $
So, the two required angles are supplementary.
$ \therefore $ The required two angles can either be equal or supplementary depending on the configuration of the lines.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Students might tend to choose the option containing equal but not supplementary because that is an obvious configuration that comes to mind. But, there is another configuration which leads to a result of two angles being supplementary and students should make a note of that configuration.
Complete step-by-step answer:

In our question, 2 configurations are possible. They are
Let us consider the configuration-1,


According to the question let us consider the lines AC is parallel to DM and AB is parallel to DF. We have to compare the angles, $ \angle CAB $ and $ \angle MDF $ .

In the figure, NO is parallel to PQ, the angle between the lines SR and NO is equal to the angle between the lines SR and PQ. This is called the corresponding angles property.
Using this property, from configuration-1 , we can write
AB is parallel to DF and MD acts as the transversal. So
$ \angle MEB=\angle MDF $
Similarly, the lines AC and MD are parallel to each other. So
$ \angle CAB=\angle MEB $
Using these two relations, we can write
\[\angle MDF=\angle MEB=\angle CAB\]
So we can conclude that the two required angles $ \angle CAB $ and $ \angle MDF $ are equal.

In the figure, NO is parallel to PQ, we can infer from the diagram that
$ \angle OTR+\angle SUQ=\pi $
For configuration-2, according to the question let us consider the lines AC is parallel to DM and AB is parallel to DF. We have to compare the angles, $ \angle IJK $ and $ \angle GHI $ .
For configuration-2 using the above property, we can write
GH is parallel to LI and GI is the transversal , so
$ \angle GHI+\angle LIH=\pi \to \left( 1 \right) $
From the corresponding angles property, we know that
$ \angle LIH=\angle IJK $ .
Using this result in equation-1 we get
$ \angle GHI+\angle IJK=\pi $
So, the two required angles are supplementary.
$ \therefore $ The required two angles can either be equal or supplementary depending on the configuration of the lines.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Students might tend to choose the option containing equal but not supplementary because that is an obvious configuration that comes to mind. But, there is another configuration which leads to a result of two angles being supplementary and students should make a note of that configuration.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




