
If \[\tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3}\] , then \[\sin \theta \] is
A. \[ - \dfrac{4}{5}\] but not \[\dfrac{4}{5}\]
B. \[ - \dfrac{4}{5}\] or \[\dfrac{4}{5}\]
C. \[\dfrac{4}{5}\] but not \[ - \dfrac{4}{5}\]
D. None of these
Answer
508.2k+ views
Hint: Here in this question we have to find the value of \[\sin \theta \]. As they are given the value of \[\tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3}\]. By using the Pythagoras theorem we determine the value of another side. As we know that the definition of the trigonometric ratios \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], \[\cos \alpha = \dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}\] and \[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}\], we are going to determine the value of \[\sin \theta \].
Complete step by step answer:
Trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. There are six trigonometric ratios, sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant and cotangent which can be abbreviated as sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec and cot. Now consider the given question, \[\tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3}\]. According to the ASTC rule the tangent trigonometric ratio is negative in the second quadrant and fourth quadrant. If the tangent trigonometric ratio is present in the second quadrant.
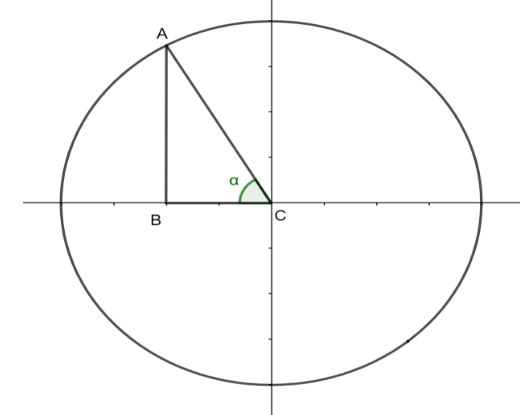
Usually the trigonometric ratios are defined as \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], \[\cos \alpha = \dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}\] and \[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}\]
From the figure tan trigonometric ratio can be written as
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\]
The value of AB = 4 and the value of BC = 3. By using the Pythagoras theorem, we can determine the value of AC.
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = {4^2} + {3^2}\]
On squaring we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = 16 + 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = 25\]
Taking square root we get the value of AC is
\[ \Rightarrow AC = 5\]
Now we determine the value of \[\sin \theta \]
As we know that \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Since it is present in the second quadrant, the sine trigonometric ratio will be positive.
Therefore \[\sin \theta = + \dfrac{4}{5}\]
If the tangent trigonometric ratio is present in the fourth quadrant.
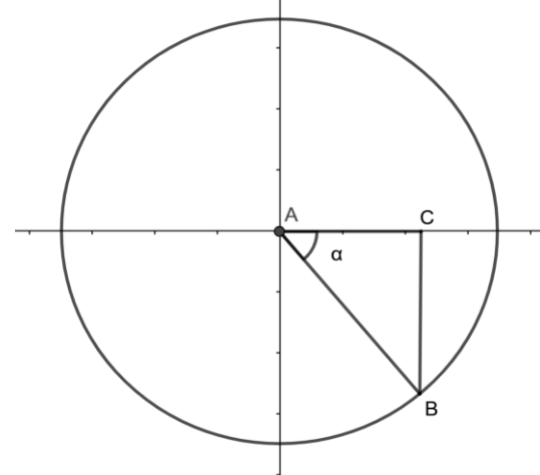
From the figure tan trigonometric ratio can be written as
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}\]
The value of BC = 4 and the value of AC = 3. By using the Pythagoras theorem, we can determine the value of AB.
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{C^2} + B{C^2}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {4^2} + {3^2}\]
On squaring we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 16 + 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 25\]
Taking square root we get the value of AB is
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 5\]
Now we determine the value of \[\sin \theta \]
As we know that \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Since it is present in the fourth quadrant, the sine trigonometric ratio will be negative
Therefore \[\sin \theta = - \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Hence the value of \[\sin \theta = - \dfrac{4}{5}\] or \[\sin \theta = + \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Therefore the option B is correct.
Note: The ASTC rule defined as All Sine Tangent Cosine trigonometric ratios are positive in the first, second, third and fourth quadrant respectively. It is not enough to find the value, we have considered the quadrant also. We have to remember the Pythagoras theorem where it is used to find the value of the other side.
Complete step by step answer:
Trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. There are six trigonometric ratios, sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant and cotangent which can be abbreviated as sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec and cot. Now consider the given question, \[\tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3}\]. According to the ASTC rule the tangent trigonometric ratio is negative in the second quadrant and fourth quadrant. If the tangent trigonometric ratio is present in the second quadrant.

Usually the trigonometric ratios are defined as \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], \[\cos \alpha = \dfrac{{adjacent}}{{hypotenuse}}\] and \[\tan \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{adjacent}}\]
From the figure tan trigonometric ratio can be written as
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}}\]
The value of AB = 4 and the value of BC = 3. By using the Pythagoras theorem, we can determine the value of AC.
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = {4^2} + {3^2}\]
On squaring we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = 16 + 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow A{C^2} = 25\]
Taking square root we get the value of AC is
\[ \Rightarrow AC = 5\]
Now we determine the value of \[\sin \theta \]
As we know that \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Since it is present in the second quadrant, the sine trigonometric ratio will be positive.
Therefore \[\sin \theta = + \dfrac{4}{5}\]
If the tangent trigonometric ratio is present in the fourth quadrant.

From the figure tan trigonometric ratio can be written as
\[ \Rightarrow \tan \theta = - \dfrac{4}{3} = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AC}}\]
The value of BC = 4 and the value of AC = 3. By using the Pythagoras theorem, we can determine the value of AB.
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = A{C^2} + B{C^2}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {4^2} + {3^2}\]
On squaring we have
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 16 + 9\]
\[ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = 25\]
Taking square root we get the value of AB is
\[ \Rightarrow AB = 5\]
Now we determine the value of \[\sin \theta \]
As we know that \[\sin \alpha = \dfrac{{opposite}}{{hypotenuse}}\], we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{{BC}}{{AB}}\]
On substituting the values we have
\[ \Rightarrow \sin \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Since it is present in the fourth quadrant, the sine trigonometric ratio will be negative
Therefore \[\sin \theta = - \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Hence the value of \[\sin \theta = - \dfrac{4}{5}\] or \[\sin \theta = + \dfrac{4}{5}\]
Therefore the option B is correct.
Note: The ASTC rule defined as All Sine Tangent Cosine trigonometric ratios are positive in the first, second, third and fourth quadrant respectively. It is not enough to find the value, we have considered the quadrant also. We have to remember the Pythagoras theorem where it is used to find the value of the other side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




