
If $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ , find the values of other trigonometric ratios.
Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint: Consider a right angled $ \Delta ABC $ , right angled at B. Use Pythagoras theorem then find the values of $ \cos \theta , \tan \theta $ and their inverse $ \csc \theta,\sec \theta $ and $ \cot \theta $
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider a right angled triangle ABC. We know the Pythagoras theorem, also known as Pythagoras theorem; it is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the 3 sides of a right triangle.
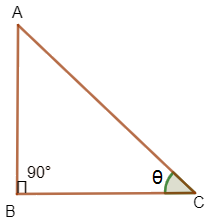
It states that the area of the squares whose sides is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
$ A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} $
We have been given, $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ .
In the triangle ABC, $ \angle B=90{}^\circ $
And take $ \angle C=\theta $
Here, $ \sin \theta = $ opposite side/hypotenuse = $ \dfrac{AB}{BC} $
$ \cos \theta = $ Adjacent side/hypotenuse = $ \dfrac{BC}{AC} $
Given, $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $
AB=3 and AC=5
Using the Pythagoras theorem, $ A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} $
$ \begin{align}
& {{5}^{2}}={{3}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow BC=\sqrt{25-9}=\sqrt{16}=4 \\
& \therefore \cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5} \\
\end{align} $
$ \tan \theta = $ Opposite side/adjacent side= $ \dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{3}{4} $
$ \csc\theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{5}}=\dfrac{5}{3} $
$ \begin{align}
& \sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{4}{5}}=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
& \cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}}=\dfrac{4}{3} \\
& \therefore \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5},\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5},\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4} \\
& \csc\theta =\dfrac{5}{3},\sec \theta =\dfrac{5}{4},\cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align} $
Note: There are three types of special right triangle, 30-60-90 triangle, 45-45-90 triangle and Pythagoras triple triangles. This problem was based on trigonometric ratios. So we just need to remember all the formulas of trigonometric ratio in the form of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us consider a right angled triangle ABC. We know the Pythagoras theorem, also known as Pythagoras theorem; it is a fundamental relation in Euclidean geometry among the 3 sides of a right triangle.

It states that the area of the squares whose sides is the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the areas of the squares on the other two sides.
$ A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} $
We have been given, $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $ .
In the triangle ABC, $ \angle B=90{}^\circ $
And take $ \angle C=\theta $
Here, $ \sin \theta = $ opposite side/hypotenuse = $ \dfrac{AB}{BC} $
$ \cos \theta = $ Adjacent side/hypotenuse = $ \dfrac{BC}{AC} $
Given, $ \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5} $
AB=3 and AC=5
Using the Pythagoras theorem, $ A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}} $
$ \begin{align}
& {{5}^{2}}={{3}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow B{{C}^{2}}={{5}^{2}}-{{3}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow BC=\sqrt{25-9}=\sqrt{16}=4 \\
& \therefore \cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5} \\
\end{align} $
$ \tan \theta = $ Opposite side/adjacent side= $ \dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{3}{4} $
$ \csc\theta =\dfrac{1}{\sin \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{5}}=\dfrac{5}{3} $
$ \begin{align}
& \sec \theta =\dfrac{1}{\cos \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{4}{5}}=\dfrac{5}{4} \\
& \cot \theta =\dfrac{1}{\tan \theta }=\dfrac{1}{\dfrac{3}{4}}=\dfrac{4}{3} \\
& \therefore \sin \theta =\dfrac{3}{5},\cos \theta =\dfrac{4}{5},\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4} \\
& \csc\theta =\dfrac{5}{3},\sec \theta =\dfrac{5}{4},\cot \theta =\dfrac{4}{3} \\
\end{align} $
Note: There are three types of special right triangle, 30-60-90 triangle, 45-45-90 triangle and Pythagoras triple triangles. This problem was based on trigonometric ratios. So we just need to remember all the formulas of trigonometric ratio in the form of perpendicular, base and hypotenuse.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Who was Subhash Chandra Bose Why was he called Net class 10 english CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE




