
If \[sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}{\text{ }},{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}0{\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{2}} \right)\] and \[cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5}{\text{ }},{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\pi {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}{\text{ }}} \right)\] , then \[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\phi + {\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }}} \right)\] will be
\[\left( 1 \right)\] \[\dfrac{{ - 56}}{{61}}\]
\[\;\left( 2 \right)\] \[\dfrac{{ - 56}}{{65}}\]
\[\;\left( 3 \right)\] \[\dfrac{1}{{65}}\]
\[\left( 4 \right)\] \[ - 56\]
Answer
502.5k+ views
Hint: We have to find the value of \[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }}} \right)\] . We solve this using the concept of the quadrant system . We should know the concept of sign and value of the trigonometric functions in four quadrants . The values of the trigonometric function have different values for different trigonometric functions with different signs .
We also apply the formula of \[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right)\] and putting the values in the required formula we get the value .
Complete step-by-step answer:
\[sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}{\text{ }},{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}0{\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{2}{\text{ }}} \right)\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5},{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\pi {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\phi < {\text{ }}\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)\]
The value of $ \theta $ lies in the first quadrant
We also know that ,
\[sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\;\dfrac{{{\text{ }}perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse\;}}\]
Comparing the two
Perpendicular \[\left( {{\text{ }}P{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}12\] and hypotenuse \[\left( {{\text{ }}H{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}13\]
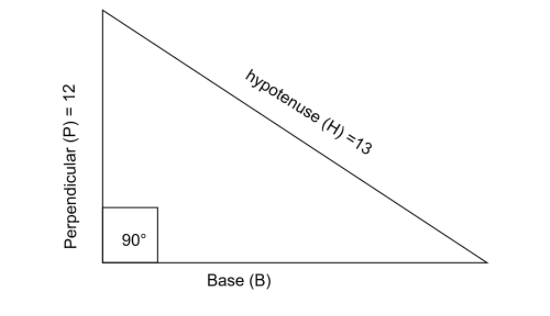
Using the formula ,
$ {(base)^2} + {(P)^2} = {(H)^2} $
So ,
Value of base \[\left( {{\text{ }}B{\text{ }}} \right)\] $ = \sqrt {[{H^2} - {P^2}] } $
$ B = \sqrt {[{{13}^2} - {{12}^2}] } $
$ B = \sqrt {[169 - 144] } $
$ B = \sqrt {[25] } $
\[B{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}5\]
As the value of cos is positive in first quadrant , then
\[cos{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{B}{H}\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}\]
Similarly , calculating the value of \[sin{\text{ }}\phi \]
As ,
\[cos{\text{ }}\phi = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5}\]
As $ \phi $ lies in third quadrant
We also know that ,
\[cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = \dfrac{B}{H}\]
Comparing the two
Base \[ = {\text{ }}3\] and hypotenuse \[ = {\text{ }}5\]
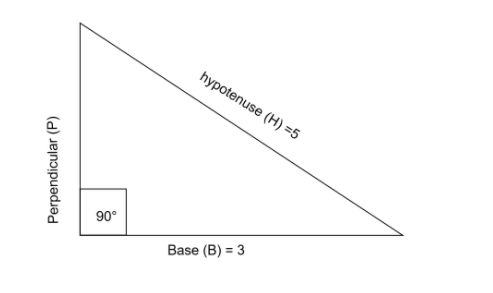
Using the formula of hypotenuse
$ {B^2} + {P^2} = {H^2} $
So ,
Value of $ P = \sqrt {[{5^2} - {3^2}] } $
$ P = \sqrt {[25 - 9] } $
$ P = \sqrt {[16] } $
\[P{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4\]
As the value of sin is negative in third quadrant , then
\[sin{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{P}{H}\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 4}}{5}\]
Using the formula
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a\]
Now putting the values in the formula , we get
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi } \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} \times cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} \times cos{\text{ }}\theta \]
Substituting the values in the formula , we get
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5}} \right){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 4}}{5}{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 36}}{{65}}{\text{ }} - \dfrac{{20}}{{65}}\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 56}}{{65}}\]
Hence , the value of \[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 56}}{{65}}\]
Thus , the correct option is \[\left( 2 \right)\]
So, the correct answer is “Option 2”.
Note: We have various trigonometric formulas used to solve the problem
The various trigonometric formulas used :
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a\]
All the trigonometric functions are positive in first quadrant , the sin function are positive in second quadrant and rest are negative , the tan function are positive in third quadrant and rest are negative , the cos function are positive in fourth quadrant and rest are negative .
We also apply the formula of \[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right)\] and putting the values in the required formula we get the value .
Complete step-by-step answer:
\[sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = \dfrac{{12}}{{13}}{\text{ }},{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}0{\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\dfrac{\pi }{2}{\text{ }}} \right)\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5},{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\pi {\text{ }} < {\text{ }}\phi < {\text{ }}\dfrac{{3\pi }}{2}} \right)\]
The value of $ \theta $ lies in the first quadrant
We also know that ,
\[sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\;\dfrac{{{\text{ }}perpendicular}}{{hypotenuse\;}}\]
Comparing the two
Perpendicular \[\left( {{\text{ }}P{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}12\] and hypotenuse \[\left( {{\text{ }}H{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}13\]

Using the formula ,
$ {(base)^2} + {(P)^2} = {(H)^2} $
So ,
Value of base \[\left( {{\text{ }}B{\text{ }}} \right)\] $ = \sqrt {[{H^2} - {P^2}] } $
$ B = \sqrt {[{{13}^2} - {{12}^2}] } $
$ B = \sqrt {[169 - 144] } $
$ B = \sqrt {[25] } $
\[B{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}5\]
As the value of cos is positive in first quadrant , then
\[cos{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{B}{H}\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}\]
Similarly , calculating the value of \[sin{\text{ }}\phi \]
As ,
\[cos{\text{ }}\phi = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5}\]
As $ \phi $ lies in third quadrant
We also know that ,
\[cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = \dfrac{B}{H}\]
Comparing the two
Base \[ = {\text{ }}3\] and hypotenuse \[ = {\text{ }}5\]

Using the formula of hypotenuse
$ {B^2} + {P^2} = {H^2} $
So ,
Value of $ P = \sqrt {[{5^2} - {3^2}] } $
$ P = \sqrt {[25 - 9] } $
$ P = \sqrt {[16] } $
\[P{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}4\]
As the value of sin is negative in third quadrant , then
\[sin{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{P}{H}\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 4}}{5}\]
Using the formula
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a\]
Now putting the values in the formula , we get
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi } \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} \times cos{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }} \times cos{\text{ }}\theta \]
Substituting the values in the formula , we get
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{12}}{{13}}{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 3}}{5}} \right){\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 4}}{5}{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}\dfrac{5}{{13}}\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 36}}{{65}}{\text{ }} - \dfrac{{20}}{{65}}\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 56}}{{65}}\]
Hence , the value of \[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}\theta {\text{ }} + {\text{ }}\phi {\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}\dfrac{{ - 56}}{{65}}\]
Thus , the correct option is \[\left( 2 \right)\]
So, the correct answer is “Option 2”.
Note: We have various trigonometric formulas used to solve the problem
The various trigonometric formulas used :
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a\]
\[sin{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a\]
\[cos{\text{ }}\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }} = {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}cos{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}b{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}sin{\text{ }}a\]
All the trigonometric functions are positive in first quadrant , the sin function are positive in second quadrant and rest are negative , the tan function are positive in third quadrant and rest are negative , the cos function are positive in fourth quadrant and rest are negative .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




