
If \[\sin A=\dfrac{3}{4}\], calculate cos A and tan A
(a) \[\cos A=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{4}\text{ and }\tan A=\dfrac{2}{5}\]
(b) \[\cos A=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\text{ and }\tan A=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{7}}\]
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of these
Answer
613.8k+ views
Hint: Find the right-angled triangle which satisfies the value of the sine given in the question. Using the length of the sides of this triangle, find the values of cos and tan. These values of cos and tan are our required results.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the value of sine of the angle in the question, it is written as
\[\sin A=\dfrac{3}{4}\]
Let us take a right-angled triangle ABC.
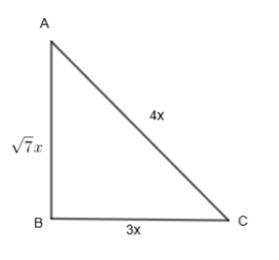
By properties of the triangle, we say the value of sin A to be:
\[\sin A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side to A}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By substituting the values, we get the equation as follows:
\[\dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{3}{4}\]
From the equation, we can say the values of the sides to be:
BC = 3x….(i)
AC = 4x……(ii)
By applying Pythagoras theorem to ABC, we get the equation as:
\[{{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Height} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the sides of the triangle ABC, we get it as:
\[{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the known values, we get the equation as:
\[{{\left( 4x \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3x \right)}^{2}}\]
By simplifying the above equation, we get its value as:
\[16{{x}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+9{{x}^{2}}\]
By subtracting \[9{{x}^{2}}\] on both the sides of the equation, we get it as:
\[A{{B}^{2}}=7{{x}^{2}}\]
By applying the square root on both the sides, we get it as
\[AB=\sqrt{7{{x}^{2}}}\]
By simplifying the expression, we get,
\[AB=\sqrt{7}x\]
By properties of the triangle, we have the relation as:
\[\cos A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side to }\angle \text{A}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\tan A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}}\]
By substituting in the above equation, we get cos value as
\[\cos A=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}x}{4x}\]
By canceling x, we get the value of cos A as
\[\cos A=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\]
By substituting the value of tan, we get,
\[\tan A=\dfrac{3x}{\sqrt{7}x}\]
By canceling x, we get the value of tan to be
\[\tan A=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{7}}\]
Therefore, these are the values of tan and cos.
Hence, option (b) is the right answer.
Note: Be careful while calculating the sides as if it is the main point of the whole solution. After getting the sides, don’t confuse between tan and cos as if you write them wrong, the whole result will be wrong. When you divide the sides, make it more simplified and you would get the final fraction as the result. Because the cos value is written as \[\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ not }\dfrac{2}{6}\] though both are the same.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given the value of sine of the angle in the question, it is written as
\[\sin A=\dfrac{3}{4}\]
Let us take a right-angled triangle ABC.

By properties of the triangle, we say the value of sin A to be:
\[\sin A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side to A}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By substituting the values, we get the equation as follows:
\[\dfrac{BC}{AC}=\dfrac{3}{4}\]
From the equation, we can say the values of the sides to be:
BC = 3x….(i)
AC = 4x……(ii)
By applying Pythagoras theorem to ABC, we get the equation as:
\[{{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{Height} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{Base} \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the sides of the triangle ABC, we get it as:
\[{{\left( AC \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( BC \right)}^{2}}\]
By substituting the known values, we get the equation as:
\[{{\left( 4x \right)}^{2}}={{\left( AB \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3x \right)}^{2}}\]
By simplifying the above equation, we get its value as:
\[16{{x}^{2}}=A{{B}^{2}}+9{{x}^{2}}\]
By subtracting \[9{{x}^{2}}\] on both the sides of the equation, we get it as:
\[A{{B}^{2}}=7{{x}^{2}}\]
By applying the square root on both the sides, we get it as
\[AB=\sqrt{7{{x}^{2}}}\]
By simplifying the expression, we get,
\[AB=\sqrt{7}x\]
By properties of the triangle, we have the relation as:
\[\cos A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side to }\angle \text{A}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
\[\tan A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Adjacent side}}\]
By substituting in the above equation, we get cos value as
\[\cos A=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}x}{4x}\]
By canceling x, we get the value of cos A as
\[\cos A=\dfrac{\sqrt{7}}{4}\]
By substituting the value of tan, we get,
\[\tan A=\dfrac{3x}{\sqrt{7}x}\]
By canceling x, we get the value of tan to be
\[\tan A=\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{7}}\]
Therefore, these are the values of tan and cos.
Hence, option (b) is the right answer.
Note: Be careful while calculating the sides as if it is the main point of the whole solution. After getting the sides, don’t confuse between tan and cos as if you write them wrong, the whole result will be wrong. When you divide the sides, make it more simplified and you would get the final fraction as the result. Because the cos value is written as \[\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ not }\dfrac{2}{6}\] though both are the same.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




