
If \[\sin A = \dfrac{3}{4},\,\] find all other Trigonometric-ratios.
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: In this we have one Trigonometric-ratio equal to value that does not belong to the standard angle table.
∴ We apply triangle concept in it.
Formula used: \[\cos A = \dfrac{{base}}{{hyp}},\,\tan A = \dfrac{{perp}}{{base}},\operatorname {cotA} = \dfrac{{base}}{{perp}}, \sec A = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{base}}, cosecA = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{perp}}\]
By Pythagoras theorem: \[{(hyp)^2} = {(perp)^2} + {(base)^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
(1) Given: Trigonometric-ratio, \[sinA = \dfrac{3}{4}\,\]
Also, we know that \[sinA = \dfrac{{perp}}{{hyp}}\]
∴ On comparing, we have
Perpendicular $ = 3$ and hypotenuse $ = 4$
(2) Draw a right angle ΔABC, right angle at B \[(A \ne 90^\circ )\]
(3) Mention two sides \[AC = 4,{\text{ }}BC = 3\]
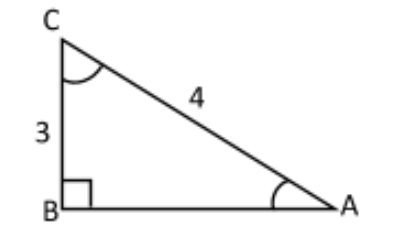
(4) To get the third side in the right angle triangle, we apply Pythagoras theorem.
(5) Using Pythagoras, we calculate base
\[{\left( {hyp} \right)^2} = {(perp)^2} + {(base)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {(4)^2} = {(3)^2} + {(base)^2}\]
$ \Rightarrow 16 = 9 + {(base)^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow 16 - 9 = {(base)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {(base)^2} = 7\]
\[ \Rightarrow base = \sqrt 7 \]
(6) As from above, we got all three sides of the right angle triangle ABC.
(7) Using formula to find various Trigonometric-ratios,
\[
\cos A = \dfrac{{base}}{{hyp.}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{4}\,\,\, \\
\tan A = \dfrac{{perp}}{{base}} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 7 }} \\
\cot A = \dfrac{{base}}{{perp}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{3} \\
\sec A = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{base}} = \dfrac{4}{{\sqrt 7 }}\,\, \\
\operatorname{cosec} A = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{perp}} = \dfrac{4}{3} \\
\]
Note: In trigonometry, there are six functions of an angle commonly used. Their names and abbreviations are sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (cosec). These six trigonometric functions are in relation to a right triangle displayed in the figure.
Use trigonometric ratios. Here, cosecA is a reciprocal of sinA and in the same way secA is a reciprocal of cosA, cotA is a reciprocal of tanA.
∴ We apply triangle concept in it.
Formula used: \[\cos A = \dfrac{{base}}{{hyp}},\,\tan A = \dfrac{{perp}}{{base}},\operatorname {cotA} = \dfrac{{base}}{{perp}}, \sec A = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{base}}, cosecA = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{perp}}\]
By Pythagoras theorem: \[{(hyp)^2} = {(perp)^2} + {(base)^2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
(1) Given: Trigonometric-ratio, \[sinA = \dfrac{3}{4}\,\]
Also, we know that \[sinA = \dfrac{{perp}}{{hyp}}\]
∴ On comparing, we have
Perpendicular $ = 3$ and hypotenuse $ = 4$
(2) Draw a right angle ΔABC, right angle at B \[(A \ne 90^\circ )\]

(3) Mention two sides \[AC = 4,{\text{ }}BC = 3\]

(4) To get the third side in the right angle triangle, we apply Pythagoras theorem.
(5) Using Pythagoras, we calculate base
\[{\left( {hyp} \right)^2} = {(perp)^2} + {(base)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {(4)^2} = {(3)^2} + {(base)^2}\]
$ \Rightarrow 16 = 9 + {(base)^2}$
\[ \Rightarrow 16 - 9 = {(base)^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {(base)^2} = 7\]
\[ \Rightarrow base = \sqrt 7 \]
(6) As from above, we got all three sides of the right angle triangle ABC.
(7) Using formula to find various Trigonometric-ratios,
\[
\cos A = \dfrac{{base}}{{hyp.}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{4}\,\,\, \\
\tan A = \dfrac{{perp}}{{base}} = \dfrac{3}{{\sqrt 7 }} \\
\cot A = \dfrac{{base}}{{perp}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 7 }}{3} \\
\sec A = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{base}} = \dfrac{4}{{\sqrt 7 }}\,\, \\
\operatorname{cosec} A = \dfrac{{hyp}}{{perp}} = \dfrac{4}{3} \\
\]
Note: In trigonometry, there are six functions of an angle commonly used. Their names and abbreviations are sine (sin), cosine (cos), tangent (tan), cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (cosec). These six trigonometric functions are in relation to a right triangle displayed in the figure.
Use trigonometric ratios. Here, cosecA is a reciprocal of sinA and in the same way secA is a reciprocal of cosA, cotA is a reciprocal of tanA.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




