
If \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{5}{4}\], show that \[\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right) = \dfrac{{12}}{7}\]?
Answer
476.1k+ views
Hint:In order to solve this question we have given a trigonometry relation and from that function, we are going to use the relation of sides of a right-angle triangle and then find perpendicular by using Pythagoras theorem. Then find all the required relations and put them on the left-hand side of the proof equation and solve that to get the final answer.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given the value of a trigonometric function \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{5}{4}\]. We have to prove \[\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right) = \dfrac{{12}}{7}\].
On the left hand side of the equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right)\]
To solve this side we must know all the values of the trigonometric function. So, now we are going to find all the values.
\[\sec \theta = \dfrac{5}{4}\]..........(given)
On writing the sec trigonometric function in terms of sides of a right-angle triangle.
Right angle triangle is as shown in the figure.
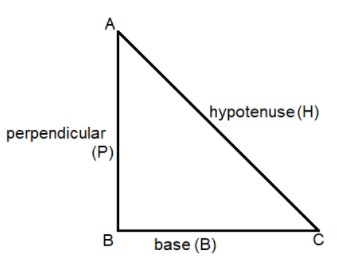
\[\dfrac{H}{B} = \dfrac{{12}}{7}\]
From this relation we use Pythagoras theorem and find the value of perpendicular.
\[{P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2}\]
On rearranging this theorem.
\[P = \sqrt {{H^2} - {B^2}} \]
On putting the value of base and hypotenuse.
\[P = \sqrt {25 - 16} \]
On further calculating
\[P = 3\]
Now we are going to find all the required values that are used in the left side of the proof part.
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right)\]
On putting all these values in the left side of the proof part.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{5} - 2\dfrac{4}{5}}}{{\dfrac{3}{4} - \dfrac{4}{5}}}} \right)\]
On calculating some of this equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{{3 - 8}}{5}}}{{\dfrac{{15 - 16}}{{20}}}}} \right)\]
On further simplifying this equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{{3 - 8}}{5}}}{{\dfrac{{15 - 16}}{{20}}}}} \right)\]
On further solving
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{5} \times \dfrac{{20}}{{ - 1}}} \right)\]
Negative is canceled by negative and 5 is canceled because this is a common factor.
\[ \Rightarrow 20\]
Hence, the left-hand side is not equal to the right-hand side.
So the proved relation is wrong.
Note:In order to solve this question, students must have a knowledge of all the trigonometric relations in terms of sides of the right-angle triangle and theorems related to the triangle. There is another way to solve this question that is changing all the trigonometric functions in only one but there is a higher probability of committing mistakes.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given the value of a trigonometric function \[\sec \theta = \dfrac{5}{4}\]. We have to prove \[\left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right) = \dfrac{{12}}{7}\].
On the left hand side of the equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right)\]
To solve this side we must know all the values of the trigonometric function. So, now we are going to find all the values.
\[\sec \theta = \dfrac{5}{4}\]..........(given)
On writing the sec trigonometric function in terms of sides of a right-angle triangle.
Right angle triangle is as shown in the figure.

\[\dfrac{H}{B} = \dfrac{{12}}{7}\]
From this relation we use Pythagoras theorem and find the value of perpendicular.
\[{P^2} + {B^2} = {H^2}\]
On rearranging this theorem.
\[P = \sqrt {{H^2} - {B^2}} \]
On putting the value of base and hypotenuse.
\[P = \sqrt {25 - 16} \]
On further calculating
\[P = 3\]
Now we are going to find all the required values that are used in the left side of the proof part.
\[\sin \theta = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{4}{5}\]
\[\Rightarrow \tan \theta = \dfrac{3}{4}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\sin \theta - 2\cos \theta }}{{\tan \theta - \cos \theta }}} \right)\]
On putting all these values in the left side of the proof part.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{3}{5} - 2\dfrac{4}{5}}}{{\dfrac{3}{4} - \dfrac{4}{5}}}} \right)\]
On calculating some of this equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{{3 - 8}}{5}}}{{\dfrac{{15 - 16}}{{20}}}}} \right)\]
On further simplifying this equation.
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{\dfrac{{3 - 8}}{5}}}{{\dfrac{{15 - 16}}{{20}}}}} \right)\]
On further solving
\[ \Rightarrow \left( {\dfrac{{ - 5}}{5} \times \dfrac{{20}}{{ - 1}}} \right)\]
Negative is canceled by negative and 5 is canceled because this is a common factor.
\[ \Rightarrow 20\]
Hence, the left-hand side is not equal to the right-hand side.
So the proved relation is wrong.
Note:In order to solve this question, students must have a knowledge of all the trigonometric relations in terms of sides of the right-angle triangle and theorems related to the triangle. There is another way to solve this question that is changing all the trigonometric functions in only one but there is a higher probability of committing mistakes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




