
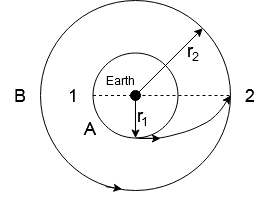
If ${r_2} = 3{r_1}$ and time period of revolution for $B$ be $T$ than time taken by $A$ in moving from position 1 to position 2 is:
(A). $T\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
(B). $T\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
(C). $\dfrac{{T\sqrt 2 }}{{3\sqrt 3 }}$
(D). $\dfrac{{T\sqrt 2 }}{3}$

Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: You can start by calculating the average radius of satellite A when it moves from position 1 to position 2 by using the equation $a = \dfrac{{{r_1} + {r_2}}}{2}$. Then use the $\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{{{a^3}}}{{r_2^3}}$ to find the value of ${T_1}$. Then divide the time period of satellite A by half to reach the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given problem we are given two satellites A and B. B is revolving around the earth with a radius ${r_2}$ and A is revolving around the earth with a radius ${r_1}$.
Given ${r_2} = 3{r_1}$
Let the average radius of satellite A (when it goes from position 1 to position 2) be$a$.
We know that a will be the average radius of satellite A, so
$a = \dfrac{{{r_1} + {r_2}}}{2}$
$a = \dfrac{{{r_1} + 3{r_1}}}{2}$
$a = 2{r_1}$
Kepler’s law are very important laws in physics, these laws are used to describe the motion of planets and some other celestial bodies.
Let’s take the time taken of the period of revolution of satellite A in the elliptical path as ${T_1}$
We know by Kepler’s law
$\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{{{a^3}}}{{r_2^3}}$
$\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{{{{(2{r_1})}^3}}}{{{{(3{r_1})}^3}}} = \dfrac{{8r_1^3}}{{27r_1^3}}$
$\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{8}{{27}}$
${T_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{8}{{27}}} T$
If we see the movement of satellite A from position 1 to position 2 is half of the whole revolution so the time taken by the satellite in moving from position 1 to position 2 is $\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{{3\sqrt 3 }}T$.
Hence, option C is the correct choice.
Note: In the problem there is no specific mention that the objects A and B are satellites. But in these types of questions, it is very important to figure out what the objects are. We figured it out in this case as in this case, the image provided in the problem has earth in the center and satellites revolve around the earth.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In the given problem we are given two satellites A and B. B is revolving around the earth with a radius ${r_2}$ and A is revolving around the earth with a radius ${r_1}$.
Given ${r_2} = 3{r_1}$
Let the average radius of satellite A (when it goes from position 1 to position 2) be$a$.
We know that a will be the average radius of satellite A, so
$a = \dfrac{{{r_1} + {r_2}}}{2}$
$a = \dfrac{{{r_1} + 3{r_1}}}{2}$
$a = 2{r_1}$
Kepler’s law are very important laws in physics, these laws are used to describe the motion of planets and some other celestial bodies.
Let’s take the time taken of the period of revolution of satellite A in the elliptical path as ${T_1}$
We know by Kepler’s law
$\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{{{a^3}}}{{r_2^3}}$
$\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{{{{(2{r_1})}^3}}}{{{{(3{r_1})}^3}}} = \dfrac{{8r_1^3}}{{27r_1^3}}$
$\dfrac{{T_1^2}}{{{T^2}}} = \dfrac{8}{{27}}$
${T_1} = \sqrt {\dfrac{8}{{27}}} T$
If we see the movement of satellite A from position 1 to position 2 is half of the whole revolution so the time taken by the satellite in moving from position 1 to position 2 is $\dfrac{{{T_1}}}{2} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 2 }}{{3\sqrt 3 }}T$.
Hence, option C is the correct choice.
Note: In the problem there is no specific mention that the objects A and B are satellites. But in these types of questions, it is very important to figure out what the objects are. We figured it out in this case as in this case, the image provided in the problem has earth in the center and satellites revolve around the earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




