
If \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\] then show that \[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\]
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: In this type of question we have to use the concept of a straight line. We know that if the point lies on the same line then they are said to be collinear points. Also if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is a point lying on a straight line which joins the points \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] then the equation of line is given by,
\[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{x-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\].
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now, we have to prove \[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\], if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\]
We know that, if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is a point lying on a straight line which joins the points \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] then the equation of line is given by, \[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{x-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\].
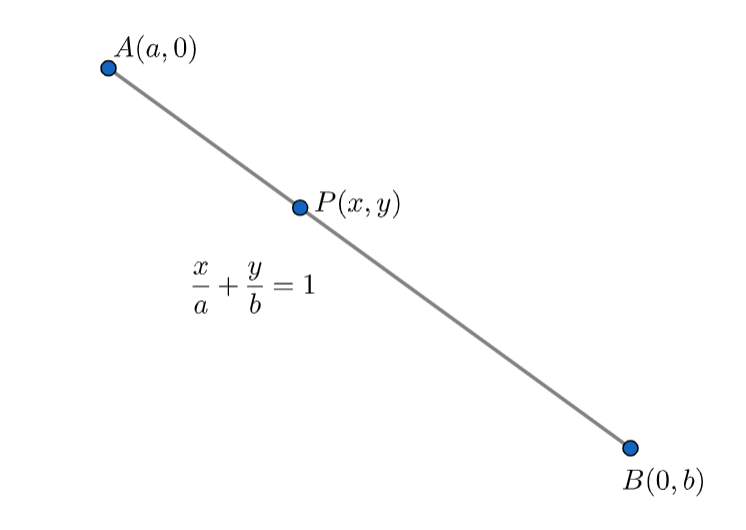
We have given that \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\].
Hence, by substituting the points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( 0,b \right)\] we can write the equation of the line as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y-0}{x-a}=\dfrac{b-0}{0-a} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x-a}=-\dfrac{b}{a} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by performing cross multiplication and simplifying the equation we can write
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ay=-b\left( x-a \right) \\
& \Rightarrow ay=-bx+ab \\
& \Rightarrow bx+ay=ab \\
\end{align}\]
Dividing both sides by \[ab\] we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{bx}{ab}+\dfrac{ay}{ab}=\dfrac{ab}{ab} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence proved
Thus, if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\] then the equation of line is given by \[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\].
Note: In this type of question students have to remember the formula of the equation of the line passing through a point. Students have to take care when they find the equation of the line; they have to substitute the values of \[{{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}},{{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}}\] carefully to obtain the correct result. Also students have to take care when they obtain the final result; they have to remember to divide the equation \[bx+ay=ab\] by \[ab\].
\[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{x-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\].
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now, we have to prove \[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\], if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\]
We know that, if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is a point lying on a straight line which joins the points \[A\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)\] and \[B\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] then the equation of line is given by, \[\dfrac{y-{{y}_{1}}}{x-{{x}_{1}}}=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\].

We have given that \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\].
Hence, by substituting the points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right)=\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)=\left( 0,b \right)\] we can write the equation of the line as,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y-0}{x-a}=\dfrac{b-0}{0-a} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{y}{x-a}=-\dfrac{b}{a} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, by performing cross multiplication and simplifying the equation we can write
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow ay=-b\left( x-a \right) \\
& \Rightarrow ay=-bx+ab \\
& \Rightarrow bx+ay=ab \\
\end{align}\]
Dividing both sides by \[ab\] we get,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{bx}{ab}+\dfrac{ay}{ab}=\dfrac{ab}{ab} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1 \\
\end{align}\]
Hence proved
Thus, if \[P\left( x,y \right)\] is any point on the line joining the points \[A\left( a,0 \right)\] and \[B\left( 0,b \right)\] then the equation of line is given by \[\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}=1\].
Note: In this type of question students have to remember the formula of the equation of the line passing through a point. Students have to take care when they find the equation of the line; they have to substitute the values of \[{{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}},{{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}}\] carefully to obtain the correct result. Also students have to take care when they obtain the final result; they have to remember to divide the equation \[bx+ay=ab\] by \[ab\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




