
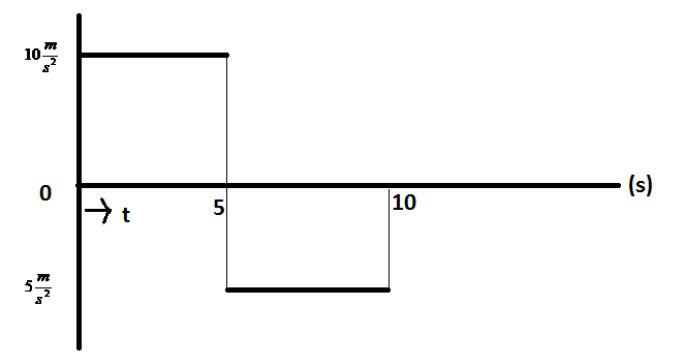
If particle starts from $10m/s$ then velocity of particle at $t=10s$ according to given curve is

Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint:To find the velocity at 10 seconds, we will use the first equation of linear motion for kinematics for constant acceleration. We will first find the velocity at 5 seconds for its particular acceleration and then using this velocity as initial velocity, we will find the final velocity of the object for a 5 to 10 seconds time period.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are given that the velocity of a particle when the time is zero is 10m/s and hence the particle’s initial velocity is 10m/s. We need to find the velocity of the particle at time t=10s. As in the curve it is given that the particle is moving at a constant acceleration for the first five seconds and the value of that acceleration is\[10\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}\]. For the next five seconds, the car is moving at a constant acceleration and the value of that acceleration is\[ - 5\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}\]. Now, to find the velocity at 10s, we will use the first equation of kinematics for constant acceleration twice; one for 5 seconds and the other for 5 to 10 seconds. Thus,
\[v = u + at\]
Where, v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the constant acceleration and t is the time taken. Now, for the first five seconds,
\[v = 10 + (10)(5) = 60\dfrac{m}{s}\]
For the next five seconds;
\[v = 60 + ( - 5)(5) \\
\therefore v = 35\dfrac{m}{s}\]
Thus the final velocity at 10 seconds is \[35\dfrac{m}{s}\].
Note: Here, as the acceleration for the next 5 seconds is below the X axis and hence we take its negative value. Also we cannot directly use this formula for 10 seconds, as the equations of kinematics for linear motion is based upon the fact the object is moving at constant acceleration which is not in this case as the acceleration breaks at 5 seconds.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, we are given that the velocity of a particle when the time is zero is 10m/s and hence the particle’s initial velocity is 10m/s. We need to find the velocity of the particle at time t=10s. As in the curve it is given that the particle is moving at a constant acceleration for the first five seconds and the value of that acceleration is\[10\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}\]. For the next five seconds, the car is moving at a constant acceleration and the value of that acceleration is\[ - 5\dfrac{m}{{{s^2}}}\]. Now, to find the velocity at 10s, we will use the first equation of kinematics for constant acceleration twice; one for 5 seconds and the other for 5 to 10 seconds. Thus,
\[v = u + at\]
Where, v is the final velocity, u is the initial velocity, a is the constant acceleration and t is the time taken. Now, for the first five seconds,
\[v = 10 + (10)(5) = 60\dfrac{m}{s}\]
For the next five seconds;
\[v = 60 + ( - 5)(5) \\
\therefore v = 35\dfrac{m}{s}\]
Thus the final velocity at 10 seconds is \[35\dfrac{m}{s}\].
Note: Here, as the acceleration for the next 5 seconds is below the X axis and hence we take its negative value. Also we cannot directly use this formula for 10 seconds, as the equations of kinematics for linear motion is based upon the fact the object is moving at constant acceleration which is not in this case as the acceleration breaks at 5 seconds.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




