
If P is any point on the ellipse \[(\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{36}}) + (\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{16}}) = 1\]and\[\;S\] and \[S'\] are the foci, then \[PS{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}PS'{\text{ }} = \]
\[1)\]$4$
\[2)\]$8$
\[3)\]$10$
\[4)\]$12$
Answer
507.6k+ views
Hint: We have to find the value of sum of \[PS\] and \[PS'\] . We solve this question using the concept of an ellipse . We should have the knowledge about the terms such as foci , vertex point and the centre point of the ellipse . We use the formula of focal distance of any point P on the ellipse . We should also have the concept of length of major axis and minor axis .
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given :
\[(\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{36}}) + (\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{16}}) = 1\]
We know that the general equation of ellipse is given by :-
$\dfrac{{{{(x - h)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y - k)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
Where a and b are the length of major axis and minor axis respectively \[\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }}.{\text{ }}\left( {h{\text{ }},{\text{ }}k} \right)\] are the centre point of the ellipse .
Comparing the two equations , we compute that ${a^2} = 36,{b^2} = 16,h = 0$ and \[k{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0\] .
The centre point of the ellipse is \[\left( {0{\text{ }},{\text{ }}0} \right)\] .
The length of major axis \[ = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}units\]
The length of minor axis \[ = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}units\]
Point of foci of an ellipse is \[\left( {{\text{ }} \pm {\text{ }}c{\text{ }},{\text{ }}0{\text{ }}} \right)\]
The formula for calculating the foci is $c = \sqrt {[{a^2} - {b^2}]} $
The point of foci of the ellipse $ = ( \pm \sqrt {[36 - 16]} ,0)$
The point of foci of the ellipse $ = ( \pm 2\sqrt 5 ,0)$
The sum of distance of a point P on the ellipse from the foci is equal to twice the length of the major axis .
So ,
\[PS{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}PS'{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}6\]
\[PS{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}PS'{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}12{\text{ }}units\]
Thus , the sum of distance of point $P$ from the foci $S$ and $S'$ is \[12{\text{ }}units\] .
Hence , the correct option is \[\left( 4 \right)\]
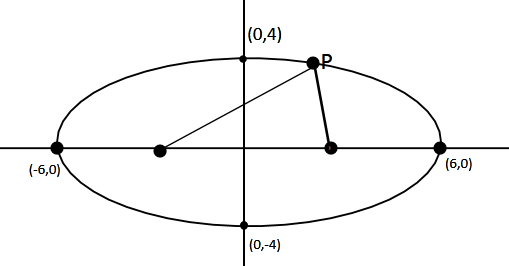
Note: An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane , the sum of whose distance from two fixed points in the plane is a constant . The Latus Rectum of an ellipse is a line segment perpendicular to the major axis through any of the foci and whose endpoints lie on the ellipse . Length of the Latus Rectum of the ellipse $(\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}}) + (\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}}) = 1$ is $2 \times (\dfrac{{{b^2}}}{a})$ .
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given :
\[(\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{36}}) + (\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{16}}) = 1\]
We know that the general equation of ellipse is given by :-
$\dfrac{{{{(x - h)}^2}}}{{{a^2}}} + \dfrac{{{{(y - k)}^2}}}{{{b^2}}} = 1$
Where a and b are the length of major axis and minor axis respectively \[\left( {{\text{ }}a{\text{ }} > {\text{ }}b{\text{ }}} \right){\text{ }}.{\text{ }}\left( {h{\text{ }},{\text{ }}k} \right)\] are the centre point of the ellipse .
Comparing the two equations , we compute that ${a^2} = 36,{b^2} = 16,h = 0$ and \[k{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}0\] .
The centre point of the ellipse is \[\left( {0{\text{ }},{\text{ }}0} \right)\] .
The length of major axis \[ = {\text{ }}6{\text{ }}units\]
The length of minor axis \[ = {\text{ }}4{\text{ }}units\]
Point of foci of an ellipse is \[\left( {{\text{ }} \pm {\text{ }}c{\text{ }},{\text{ }}0{\text{ }}} \right)\]
The formula for calculating the foci is $c = \sqrt {[{a^2} - {b^2}]} $
The point of foci of the ellipse $ = ( \pm \sqrt {[36 - 16]} ,0)$
The point of foci of the ellipse $ = ( \pm 2\sqrt 5 ,0)$
The sum of distance of a point P on the ellipse from the foci is equal to twice the length of the major axis .
So ,
\[PS{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}PS'{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}2{\text{ }} \times {\text{ }}6\]
\[PS{\text{ }} + {\text{ }}PS'{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}12{\text{ }}units\]
Thus , the sum of distance of point $P$ from the foci $S$ and $S'$ is \[12{\text{ }}units\] .
Hence , the correct option is \[\left( 4 \right)\]

Note: An ellipse is the set of all points in a plane , the sum of whose distance from two fixed points in the plane is a constant . The Latus Rectum of an ellipse is a line segment perpendicular to the major axis through any of the foci and whose endpoints lie on the ellipse . Length of the Latus Rectum of the ellipse $(\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{{{a^2}}}) + (\dfrac{{{y^2}}}{{{b^2}}}) = 1$ is $2 \times (\dfrac{{{b^2}}}{a})$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




