
If one of the diameters of the circle given by the equation \[{x^2} + {y^2} - 4x + 6y - 12 = 0\], is a chord of a circle ‘S’, whose center is a \[\left( { - 3,\,2} \right)\], then the radius of ‘S’ is
A. $5\sqrt 3 $
B. 5
C. 10
D. $5\sqrt 2 $
Answer
587.4k+ views
Hint: Circle: - The set of all points on a plane that are a fixed distance from a centre.
Chord: - A line that links two points on a circle is called a chord.
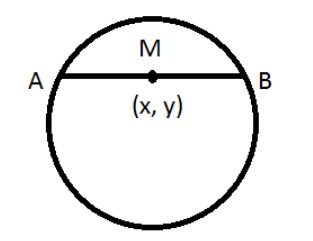
The equation of the chord of the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0\].
We will use this equation to solve the question.
With M\[\left( {{x_1},\,{y_1}} \right)\]as the midpoint of the chord.
Centre \[ - \]g\[ = \,\dfrac{{ - x}}{2}\] or \[ - f = \dfrac{{ - y}}{2}\]
\[\left( { - g,\, - f} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{ - x}}{2},\,\dfrac{{ - y}}{2}} \right)\]
Radius \['r' = \sqrt {{g^2} + {g^2} - c} \]
\[dis\tan ce = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
When two points \[\left( {{x_1},\,{y_1}} \right)\]&\[\left( {{x_2},\,{y_2}} \right)\] are given.
Complete step by step solution:
The equation of given circle
${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x + 6y - 12 = 0$.
Now we compare this equation with general equation i.e.
${x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$.
Center, $ - g = \dfrac{{ - x}}{2} = - \left( {\dfrac{4}{2}} \right) = 2$
\[ - f = \dfrac{{ - y}}{2} = - \left( {\dfrac{6}{2}} \right) = - 3\].
Centre \[\left( { - g,\, - f} \right) = \left( {2,\, - 3} \right)\]
\[r = \sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 3} \right)}^2} - \left( { - 12} \right)} \]
\[ = \sqrt {4 + 9 + 12} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25} = 5\]
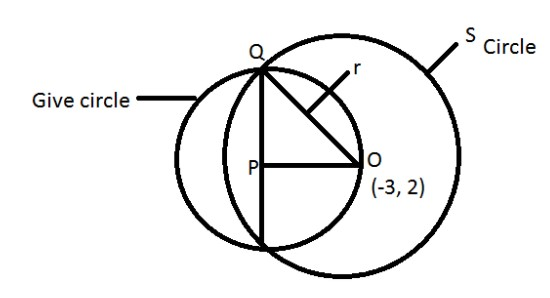
P is middle point of AB
P \[ = (2,\, - 3)\]
PQ \[ = 5\].
The coordinate of ‘o’ is \[( - 3,\,2)\]
In \[\vartriangle POQ\]:-
\[{(PO)^2} + {(PQ)^2} = {r^2}\] [By Pythagoras theorem].
\[{\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( {PQ} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
\[{\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( {2 + 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 2 - 3} \right)}^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( {PQ} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
\[{\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( 5 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 5} \right)}^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( 5 \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
\[{\left( {\sqrt {50} } \right)^2} + 25 = {r^2}\]
\[50 + 25 = {r^2}\]
\[75 = {r^2}\]
\[r = \sqrt[5]{3}\]
Hence, the radius of ‘S’ is \[\sqrt[5]{3}\].
Note: In case, you are given the radius and the distance of the centre of circle to the chord you can apply this formula:
Chord length \[ = 2\sqrt {{r^2} - {d^2}} \]
Where, ‘r’ is the radius or the circle and ‘d’ is the perpendicular distance of the centre of the circle to the chord.
Chord: - A line that links two points on a circle is called a chord.

The equation of the chord of the circle \[{x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0\].
We will use this equation to solve the question.
With M\[\left( {{x_1},\,{y_1}} \right)\]as the midpoint of the chord.
Centre \[ - \]g\[ = \,\dfrac{{ - x}}{2}\] or \[ - f = \dfrac{{ - y}}{2}\]
\[\left( { - g,\, - f} \right) = \left( {\dfrac{{ - x}}{2},\,\dfrac{{ - y}}{2}} \right)\]
Radius \['r' = \sqrt {{g^2} + {g^2} - c} \]
\[dis\tan ce = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_2} - {y_1}} \right)}^2}} \]
When two points \[\left( {{x_1},\,{y_1}} \right)\]&\[\left( {{x_2},\,{y_2}} \right)\] are given.
Complete step by step solution:

The equation of given circle
${x^2} + {y^2} - 4x + 6y - 12 = 0$.
Now we compare this equation with general equation i.e.
${x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$.
Center, $ - g = \dfrac{{ - x}}{2} = - \left( {\dfrac{4}{2}} \right) = 2$
\[ - f = \dfrac{{ - y}}{2} = - \left( {\dfrac{6}{2}} \right) = - 3\].
Centre \[\left( { - g,\, - f} \right) = \left( {2,\, - 3} \right)\]
\[r = \sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} \]
\[ = \sqrt {{{\left( 2 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 3} \right)}^2} - \left( { - 12} \right)} \]
\[ = \sqrt {4 + 9 + 12} \]
\[ = \sqrt {25} = 5\]
P is middle point of AB
P \[ = (2,\, - 3)\]
PQ \[ = 5\].
The coordinate of ‘o’ is \[( - 3,\,2)\]
In \[\vartriangle POQ\]:-
\[{(PO)^2} + {(PQ)^2} = {r^2}\] [By Pythagoras theorem].
\[{\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( {PQ} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
\[{\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( {2 + 3} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 2 - 3} \right)}^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( {PQ} \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
\[{\left( {\sqrt {{{\left( 5 \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 5} \right)}^2}} } \right)^2} + {\left( 5 \right)^2} = {r^2}\]
\[{\left( {\sqrt {50} } \right)^2} + 25 = {r^2}\]
\[50 + 25 = {r^2}\]
\[75 = {r^2}\]
\[r = \sqrt[5]{3}\]
Hence, the radius of ‘S’ is \[\sqrt[5]{3}\].
Note: In case, you are given the radius and the distance of the centre of circle to the chord you can apply this formula:
Chord length \[ = 2\sqrt {{r^2} - {d^2}} \]
Where, ‘r’ is the radius or the circle and ‘d’ is the perpendicular distance of the centre of the circle to the chord.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




