
If one end of the minor axis forms an equilateral triangle with the foci of the ellipse, then find the eccentricity of the ellipse.
A.$\dfrac{1}{2}$
B.$\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
C.$\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}$
D.$\dfrac{1}{4}$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: The major axis bisects the equilateral triangle in the middle and forms two right angled triangles. Take one right angled triangle and use Pythagoras theorem which states that , “In a right angled triangle, the square of the longest side (hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the two other sides”
$ \Rightarrow $ ${H^2} = {P^2} + {B^2}$ Where H is hypotenuse, P is the perpendicular and B is the base, to find the side joining foci to one point of triangle formed on the minor axes. Then find the value of a and b and use the formula of eccentricity of ellipse which is given by-
Eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $ where a and b are half lengths of major and minor axes respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let BB’ be the end of the minor axis forming an equilateral triangle$\Delta ABB'$ with foci A of the ellipse. Now we know that the length of major axes of ellipse is $2a$ and length of minor axes is $2b$. Then, let O be the centre where the major axis and minor axes meet. So we get,
OA=a, OB=OB’=b as BB’=$2b$
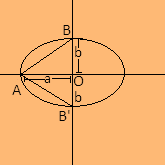
Now since it is clear from the diagram $\Delta AOB'$ is a right angled triangle where OA=’a’ and OB’=b.
We have to find AB’.
By Pythagoras theorem,
In a right angled triangle, the square of the longest side (hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the two other sides. It is written as-
${H^2} = {P^2} + {B^2}$
Where H is hypotenuse, P is the perpendicular and B is the base.
Here AB’ is the hypotenuse, OB’ is the base and OA is the perpendicular. Then on putting the values in the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow $ $AB{'^2} = OB{'^2} + O{A^2}$
On putting OA=’a’ and OB’=b, we get-
$ \Rightarrow AB{'^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AB' = \sqrt {{b^2} + {a^2}} $
Now we know that $\Delta ABB'$ is an equilateral triangle then, all the sides of given triangle are equal.
$ \Rightarrow $ AB’=BB’
On putting the values we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{b^2} + {a^2}} = 2b$
On squaring both side we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} + {a^2} = 4{b^2}$
On simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = 4{b^2} - {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = 3{b^2}$
On taking the ratio of$\dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$ , we get-
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
Now we know that eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $
On putting the values we get,
Eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{1}{3}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3 - 1}}{3}} $
On solving we get,
Eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} $
Note: Here, we have to find the values of ‘a’ and b to calculate the eccentricity of ellipse which is not easy to find. Hence we find the ratio of b/a by using the value of the sides of the equilateral triangle. Equilateral triangle is a triangle which has equal sides and equal angles which means AB= AB’=BB’. So the students can also take triangle AOB to use Pythagoras theorem and find the value of side AB.
On putting the values in the theorem-
$ \Rightarrow $ $A{B^2} = O{B^2} + O{A^2}$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{b^2} + {a^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow $ ${H^2} = {P^2} + {B^2}$ Where H is hypotenuse, P is the perpendicular and B is the base, to find the side joining foci to one point of triangle formed on the minor axes. Then find the value of a and b and use the formula of eccentricity of ellipse which is given by-
Eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $ where a and b are half lengths of major and minor axes respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let BB’ be the end of the minor axis forming an equilateral triangle$\Delta ABB'$ with foci A of the ellipse. Now we know that the length of major axes of ellipse is $2a$ and length of minor axes is $2b$. Then, let O be the centre where the major axis and minor axes meet. So we get,
OA=a, OB=OB’=b as BB’=$2b$

Now since it is clear from the diagram $\Delta AOB'$ is a right angled triangle where OA=’a’ and OB’=b.
We have to find AB’.
By Pythagoras theorem,
In a right angled triangle, the square of the longest side (hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the two other sides. It is written as-
${H^2} = {P^2} + {B^2}$
Where H is hypotenuse, P is the perpendicular and B is the base.
Here AB’ is the hypotenuse, OB’ is the base and OA is the perpendicular. Then on putting the values in the formula we get,
$ \Rightarrow $ $AB{'^2} = OB{'^2} + O{A^2}$
On putting OA=’a’ and OB’=b, we get-
$ \Rightarrow AB{'^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AB' = \sqrt {{b^2} + {a^2}} $
Now we know that $\Delta ABB'$ is an equilateral triangle then, all the sides of given triangle are equal.
$ \Rightarrow $ AB’=BB’
On putting the values we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt {{b^2} + {a^2}} = 2b$
On squaring both side we get,
$ \Rightarrow {b^2} + {a^2} = 4{b^2}$
On simplifying we get,
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = 4{b^2} - {b^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {a^2} = 3{b^2}$
On taking the ratio of$\dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$ , we get-
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}} = \dfrac{1}{3}$
Now we know that eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{{{b^2}}}{{{a^2}}}} $
On putting the values we get,
Eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {1 - \dfrac{1}{3}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3 - 1}}{3}} $
On solving we get,
Eccentricity of ellipse=$\sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}} $
Note: Here, we have to find the values of ‘a’ and b to calculate the eccentricity of ellipse which is not easy to find. Hence we find the ratio of b/a by using the value of the sides of the equilateral triangle. Equilateral triangle is a triangle which has equal sides and equal angles which means AB= AB’=BB’. So the students can also take triangle AOB to use Pythagoras theorem and find the value of side AB.
On putting the values in the theorem-
$ \Rightarrow $ $A{B^2} = O{B^2} + O{A^2}$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} = {b^2} + {a^2}$
$ \Rightarrow AB = \sqrt {{b^2} + {a^2}} $
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




