
If O is the centre of the circle and $\angle ADC={{140}^{\circ }}$, then what is the value of $x$?
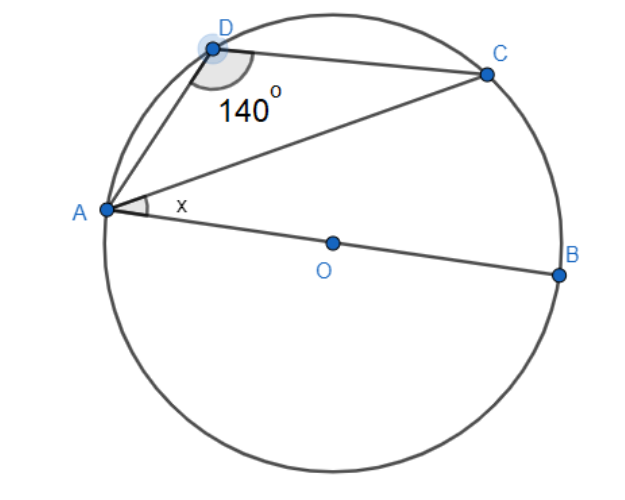
A. ${{35}^{\circ }}$
B. ${{55}^{\circ }}$
C. ${{60}^{\circ }}$
D. ${{50}^{\circ }}$

Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: We first get the formula of centred angle for the same arc as double of the inscribed angle. We find that the centred angle for greater angle $\angle AOC$. We also use the equality of the radii to find the variable angle of $x$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We first join the points O and C.
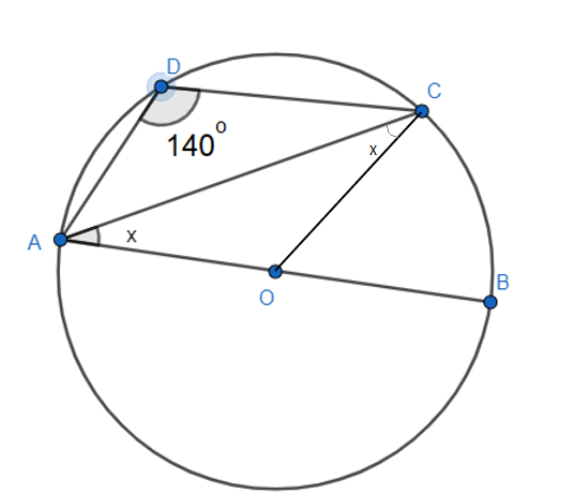
We know that the centred angle for the same arc is double of the inscribed angle.
We take the greater arc form of $\overset\frown{AC}$. The inscribed angle is $\angle ADC={{140}^{\circ }}$ and the central angle is greater angle $\angle AOC$.
Therefore, $\angle AOC=2\times \angle ADC=2\times {{140}^{\circ }}={{280}^{\circ }}$.
The total angle around point O is ${{360}^{\circ }}$.
Therefore, smaller $\angle AOC={{360}^{\circ }}-{{280}^{\circ }}={{80}^{\circ }}$.
In $\Delta AOC$, we have $\angle AOC+\angle OAC+\angle OCA={{180}^{\circ }}$.
We get $\angle AOC={{360}^{\circ }}-{{280}^{\circ }}={{80}^{\circ }}$.
Therefore, $\angle OAC+\angle OCA={{180}^{\circ }}-{{80}^{\circ }}={{100}^{\circ }}$.
We have two radii $AO=OC$. Therefore, in $\Delta AOC$, we get $\angle OAC=\angle OCA$.
As both are equal, we get $\angle OAC=\angle OCA=x=\dfrac{{{100}^{\circ }}}{2}={{50}^{\circ }}$.
The correct option is D.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We have to be careful about the arc difference for greater and smaller ones. The change of arc for the circle creates different angle relations. We have to also consider the direct proportional relation for the arc and the respective angle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We first join the points O and C.

We know that the centred angle for the same arc is double of the inscribed angle.
We take the greater arc form of $\overset\frown{AC}$. The inscribed angle is $\angle ADC={{140}^{\circ }}$ and the central angle is greater angle $\angle AOC$.
Therefore, $\angle AOC=2\times \angle ADC=2\times {{140}^{\circ }}={{280}^{\circ }}$.
The total angle around point O is ${{360}^{\circ }}$.
Therefore, smaller $\angle AOC={{360}^{\circ }}-{{280}^{\circ }}={{80}^{\circ }}$.
In $\Delta AOC$, we have $\angle AOC+\angle OAC+\angle OCA={{180}^{\circ }}$.
We get $\angle AOC={{360}^{\circ }}-{{280}^{\circ }}={{80}^{\circ }}$.
Therefore, $\angle OAC+\angle OCA={{180}^{\circ }}-{{80}^{\circ }}={{100}^{\circ }}$.
We have two radii $AO=OC$. Therefore, in $\Delta AOC$, we get $\angle OAC=\angle OCA$.
As both are equal, we get $\angle OAC=\angle OCA=x=\dfrac{{{100}^{\circ }}}{2}={{50}^{\circ }}$.
The correct option is D.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: We have to be careful about the arc difference for greater and smaller ones. The change of arc for the circle creates different angle relations. We have to also consider the direct proportional relation for the arc and the respective angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




