
If $\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}+\mathbf{c}=0,\left| \mathbf{a} \right|=3,\left| \mathbf{b} \right|=5$ and $\left| \mathbf{c} \right|=7$, then find the angle between the vectors a and b.
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that if a+b+c=0, then the vectors a, b and c can be represented by the sides of a triangle. Let the triangle by ABC as shown below, with BC = a, CA=b and AB = c. Apply cosine rule on angle C, i.e. $\cos C=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}$. Hence find the measure of $\angle C$ and hence the angle between the vectors a and b.
Complete step-by-step answer:
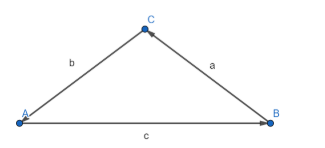
Since a+b+c=0, the vectors can be represented by a triangle, as shown above.
Now, we have AC = |b|, AB=|c| and BC=|a|.
Hence, we have AC = 5, AB = 7 and BC = 3.
Now, we have from cosine rule $\cos C=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}$
Hence, we have
$\cos C=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}-{{7}^{2}}}{2\times 3\times 5}=\dfrac{9+25-49}{30}=\dfrac{-15}{30}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$
Hence, we have
$C={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)$
We know that ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}x$
Hence, we have $C=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{2}$
We know that $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence, we have
${{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Hence, we have $C=\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3}=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$
Now, we know that the angle between a and b is given by $\theta =\pi -C$
Hence, we have
$\theta =\pi -\dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Hence the angle between a and b is equal to $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$.
Note: Alternative Solution:
We have $\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}+\mathbf{c}=0$
Subtracting c from both sides of the equation, we get
$\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}=-\mathbf{c}$
Squaring both sides, we get
${{\left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( -\mathbf{c} \right)}^{2}}$
We know that ${{\mathbf{a}}^{2}}=\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{a}$
Hence, we have
$\left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} \right)\cdot \left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} \right)={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
We know that dot product is distributive and commutative.
Hence, we have
$\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\cdot \mathbf{b}+\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{b}+\mathbf{b}\cdot \mathbf{b}={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
${{\left| \mathbf{a} \right|}^{2}}+{{\left| \mathbf{b} \right|}^{2}}+2\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{b}={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
Now, we know that $\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{b}=\left| \mathbf{a} \right|\left| \mathbf{b} \right|\cos \theta $, where $\theta $ is the angle between a and b.
Hence, we have
${{\left| \mathbf{a} \right|}^{2}}+{{\left| \mathbf{b} \right|}^{2}}+2\left| \mathbf{a} \right|\left| \mathbf{b} \right|\cos \theta ={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
${{3}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}+2\times 3\times 5\cos \theta ={{7}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
$30\cos \theta =15$
Dividing both sides by 30, we get
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Hence, the angle between the vectors is $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$, which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Since a+b+c=0, the vectors can be represented by a triangle, as shown above.
Now, we have AC = |b|, AB=|c| and BC=|a|.
Hence, we have AC = 5, AB = 7 and BC = 3.
Now, we have from cosine rule $\cos C=\dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}-{{c}^{2}}}{2ab}$
Hence, we have
$\cos C=\dfrac{{{3}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}-{{7}^{2}}}{2\times 3\times 5}=\dfrac{9+25-49}{30}=\dfrac{-15}{30}=\dfrac{-1}{2}$
Hence, we have
$C={{\cos }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{-1}{2} \right)$
We know that ${{\cos }^{-1}}\left( -x \right)=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}x$
Hence, we have $C=\pi -{{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{2}$
We know that $\cos \dfrac{\pi }{3}=\dfrac{1}{2}$
Hence, we have
${{\cos }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Hence, we have $C=\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{3}=\dfrac{2\pi }{3}$
Now, we know that the angle between a and b is given by $\theta =\pi -C$
Hence, we have
$\theta =\pi -\dfrac{2\pi }{3}=\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Hence the angle between a and b is equal to $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$.
Note: Alternative Solution:
We have $\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}+\mathbf{c}=0$
Subtracting c from both sides of the equation, we get
$\mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}=-\mathbf{c}$
Squaring both sides, we get
${{\left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( -\mathbf{c} \right)}^{2}}$
We know that ${{\mathbf{a}}^{2}}=\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{a}$
Hence, we have
$\left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} \right)\cdot \left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b} \right)={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
We know that dot product is distributive and commutative.
Hence, we have
$\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{b}\cdot \mathbf{b}+\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{b}+\mathbf{b}\cdot \mathbf{b}={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
${{\left| \mathbf{a} \right|}^{2}}+{{\left| \mathbf{b} \right|}^{2}}+2\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{b}={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
Now, we know that $\mathbf{a}\cdot \mathbf{b}=\left| \mathbf{a} \right|\left| \mathbf{b} \right|\cos \theta $, where $\theta $ is the angle between a and b.
Hence, we have
${{\left| \mathbf{a} \right|}^{2}}+{{\left| \mathbf{b} \right|}^{2}}+2\left| \mathbf{a} \right|\left| \mathbf{b} \right|\cos \theta ={{\left| \mathbf{c} \right|}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
${{3}^{2}}+{{5}^{2}}+2\times 3\times 5\cos \theta ={{7}^{2}}$
Hence, we have
$30\cos \theta =15$
Dividing both sides by 30, we get
$\cos \theta =\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{3}$
Hence, the angle between the vectors is $\dfrac{\pi }{3}$, which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE

Explain sex determination in humans with line diag class 12 biology CBSE

Organisms of a higher trophic level which feed on several class 12 biology CBSE




